The document outlines steps that good schools take when students are failing:
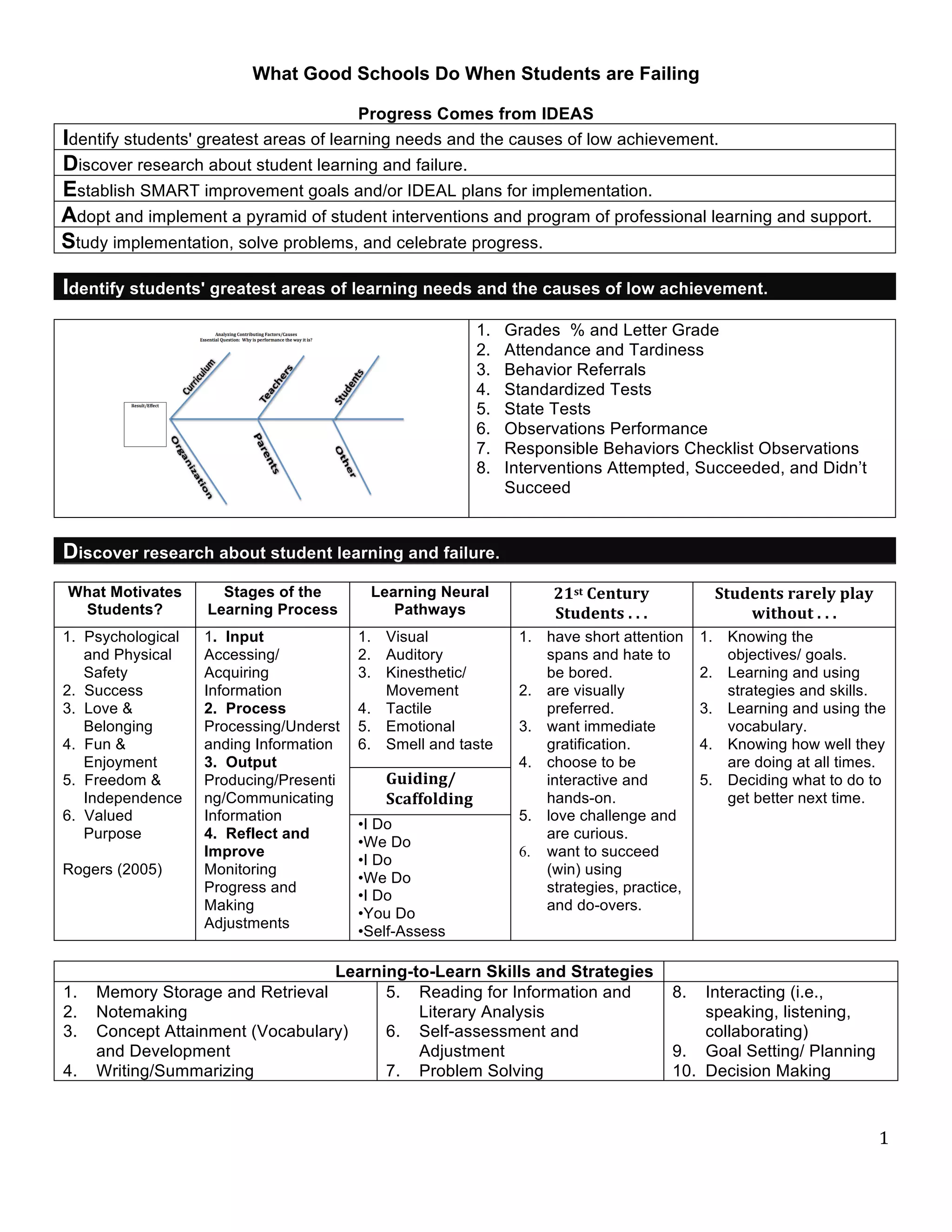
1. Schools identify students' greatest learning needs and causes of low achievement. They also discover research on student learning and failure.
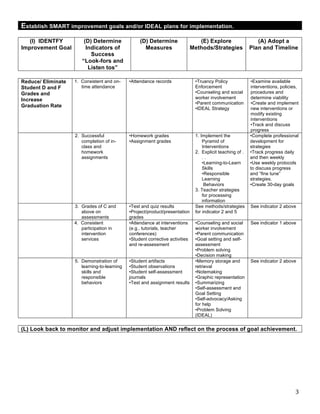
2. Schools establish measurable improvement goals and plans to address the problems. They implement a pyramid of interventions for students and professional development for teachers.
3. Schools study the implementation process, solve arising problems, and celebrate progress toward the goals. The overall approach focuses on applying research-based strategies to identify and address the specific reasons for students' failures in order to help them improve.