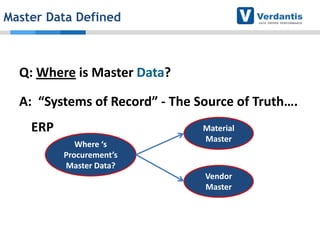
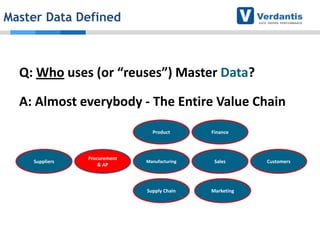
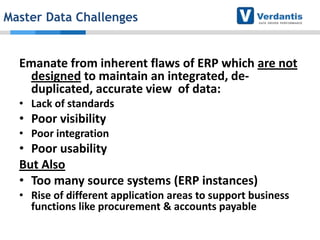
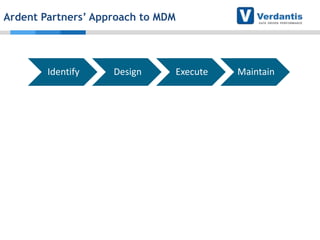
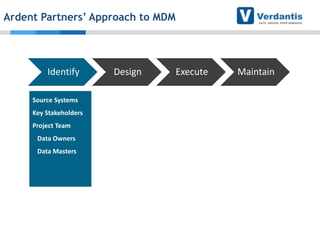
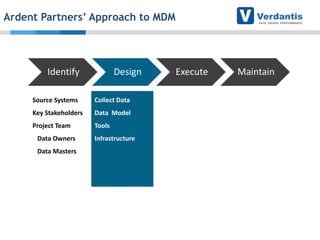
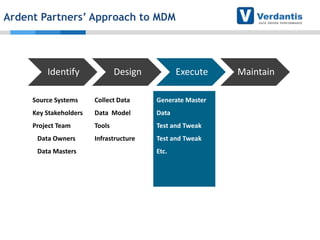
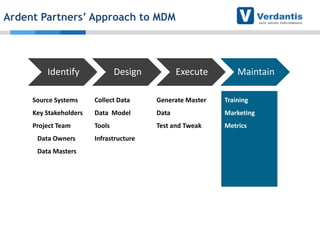
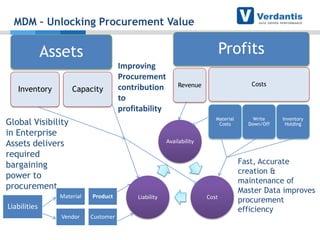
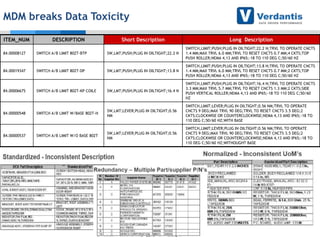
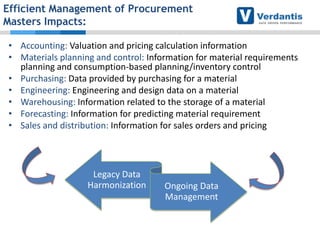
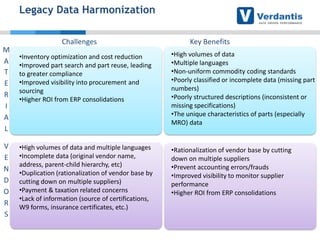
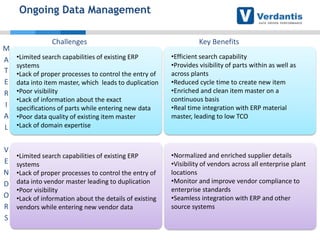
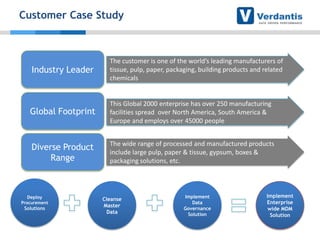
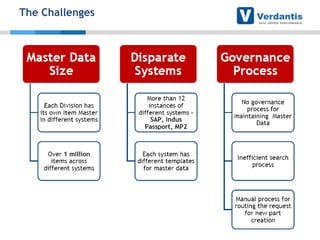
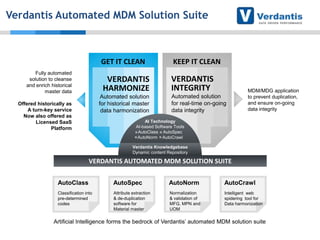
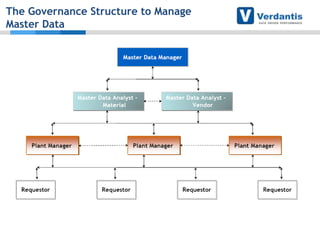
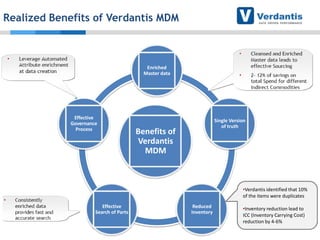
The document discusses master data management (MDM) strategies to enhance procurement performance, emphasizing the importance of accurate and clean master data for effective business operations. It describes the challenges related to data management, outlines best practices for MDM implementation, and provides recommendations for procurement leaders to integrate MDM into their processes. The presentation highlights the significant impact of MDM on working capital, savings, and overall risk management in a data-driven world.