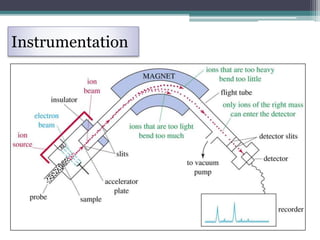
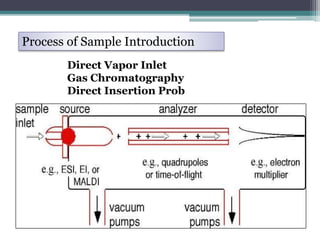
Mass spectrometry is a technique used widely in science to determine the relative atomic mass of elements, molecular mass of compounds, and structure of compounds. It works by ionizing sample vapors with an electron beam, which causes fragmentation of molecular ions. A mass analyzer then separates the ions by their mass-to-charge ratio to produce a mass spectrum. Common ionization techniques include electron ionization, chemical ionization, field desorption, and fast atom bombardment. Mass spectrometry has applications like molecular mass determination, isotope detection, and distinguishing between cis and trans isomers.