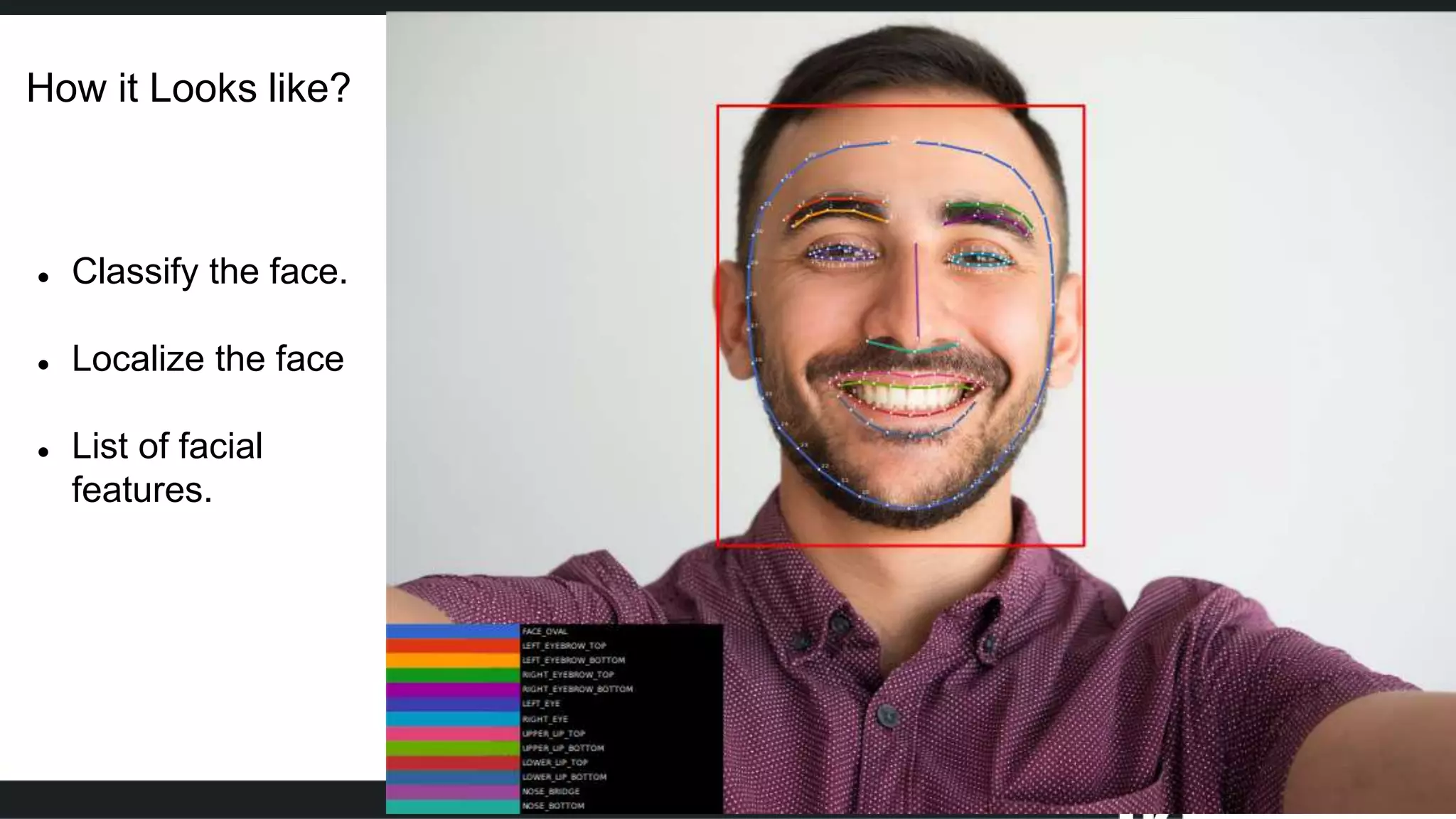
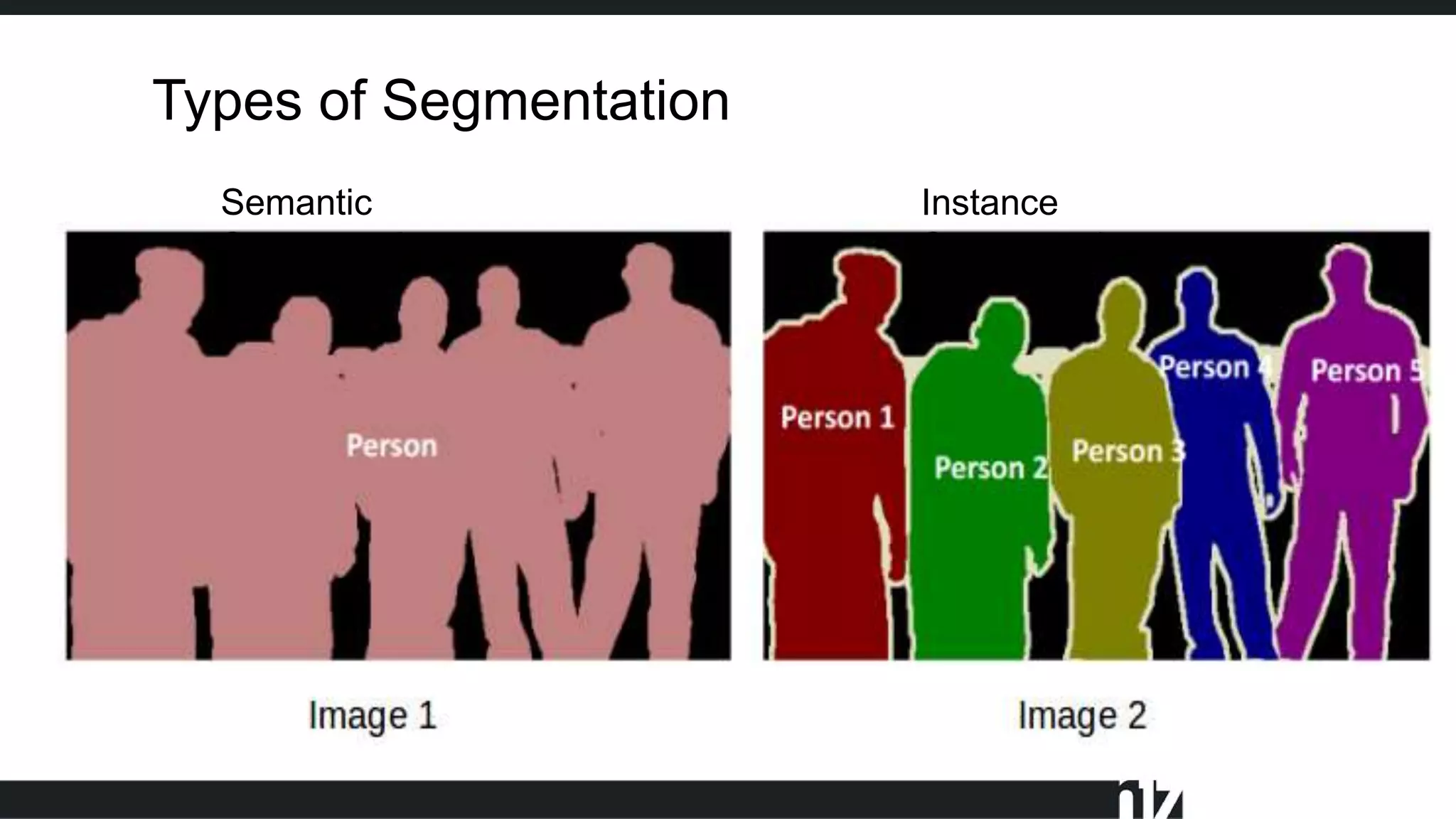
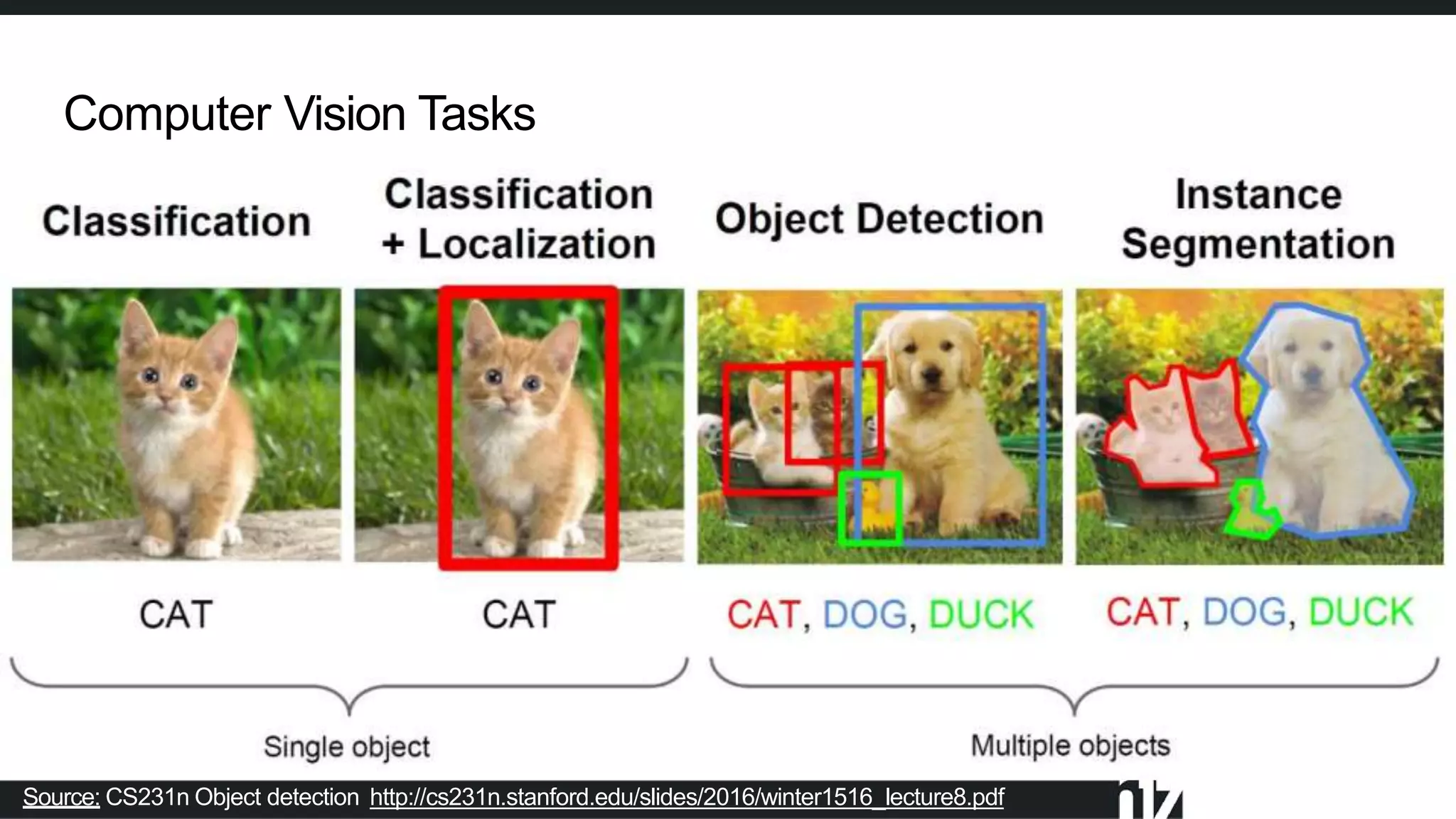
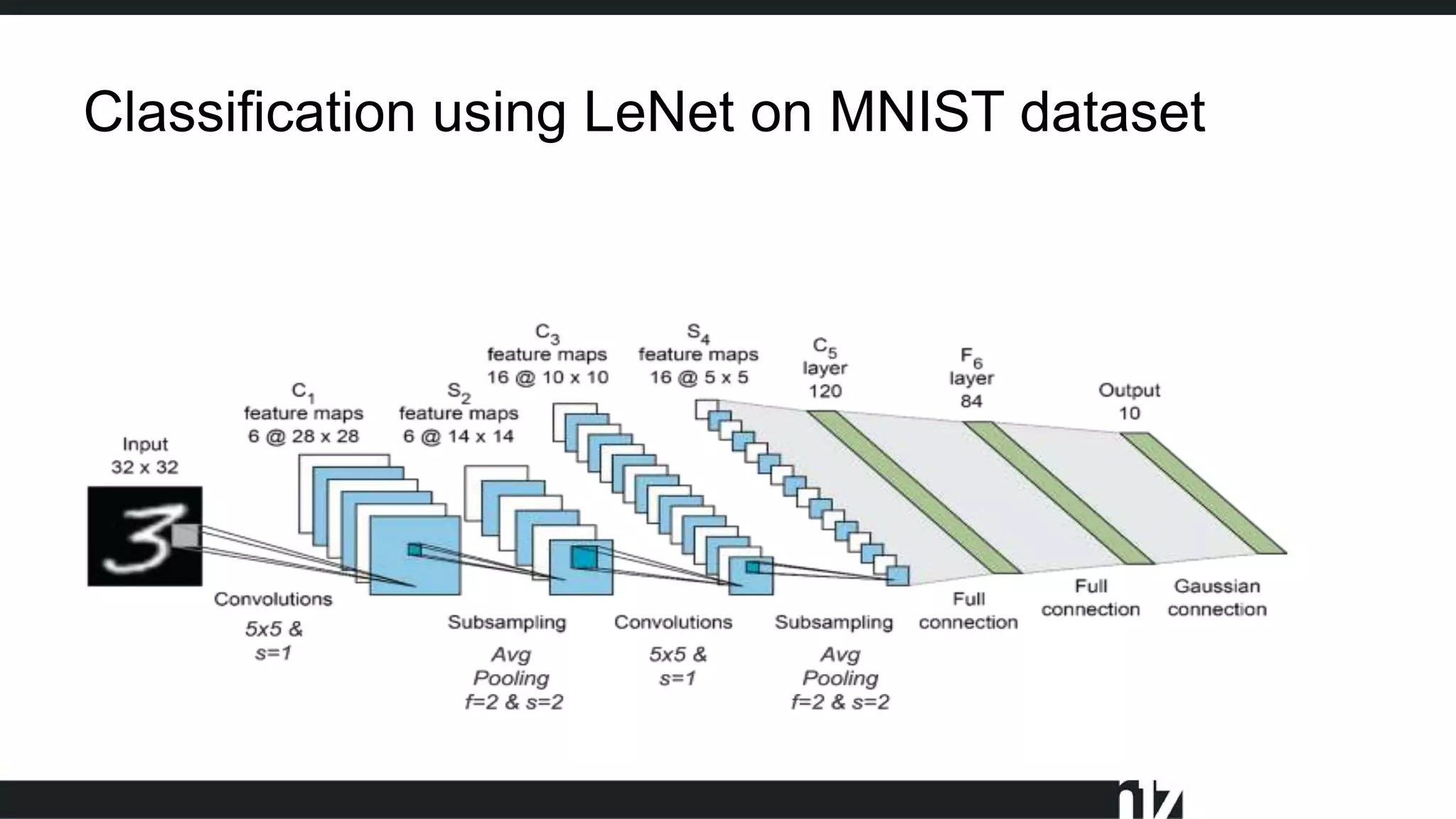
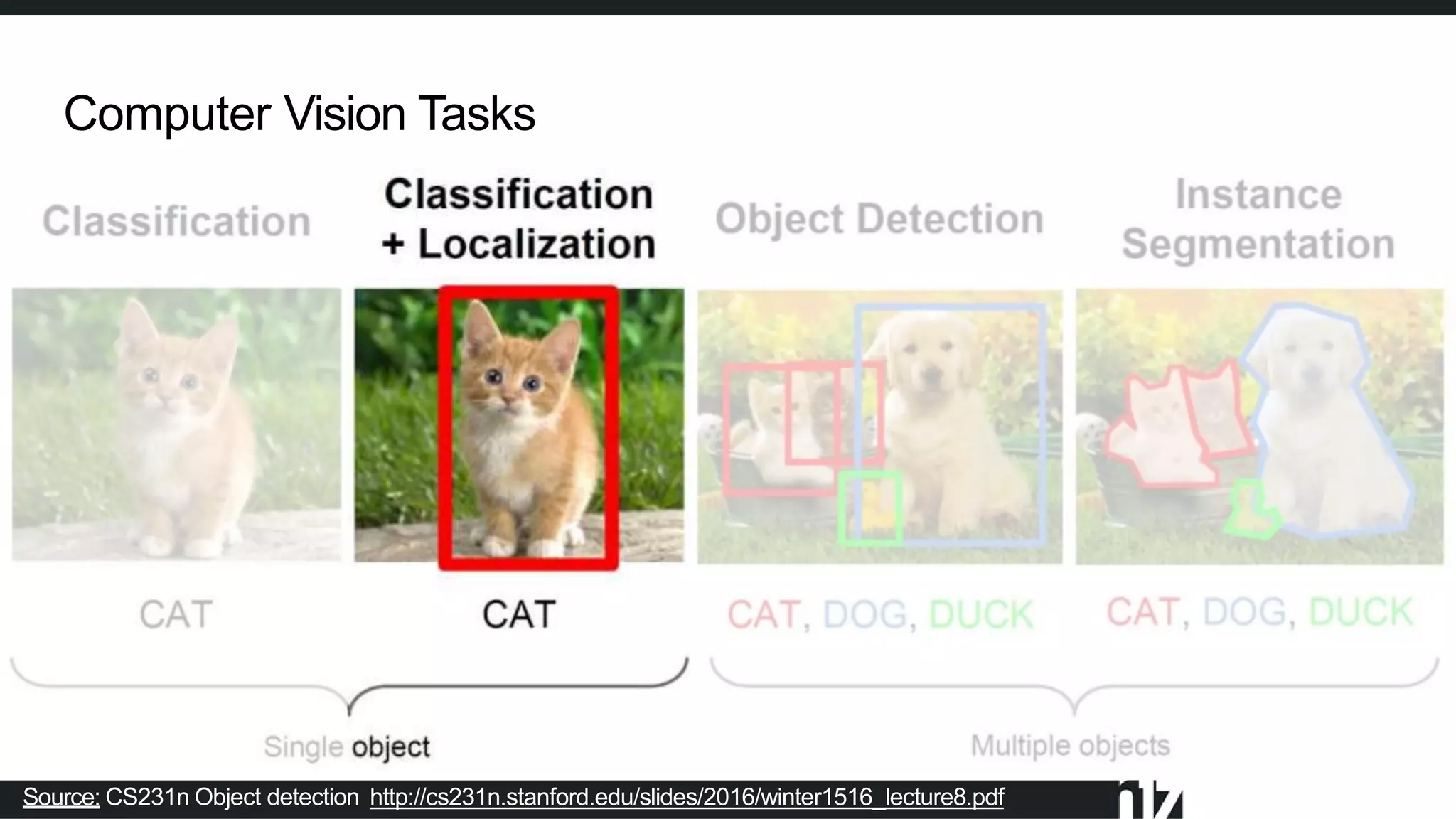
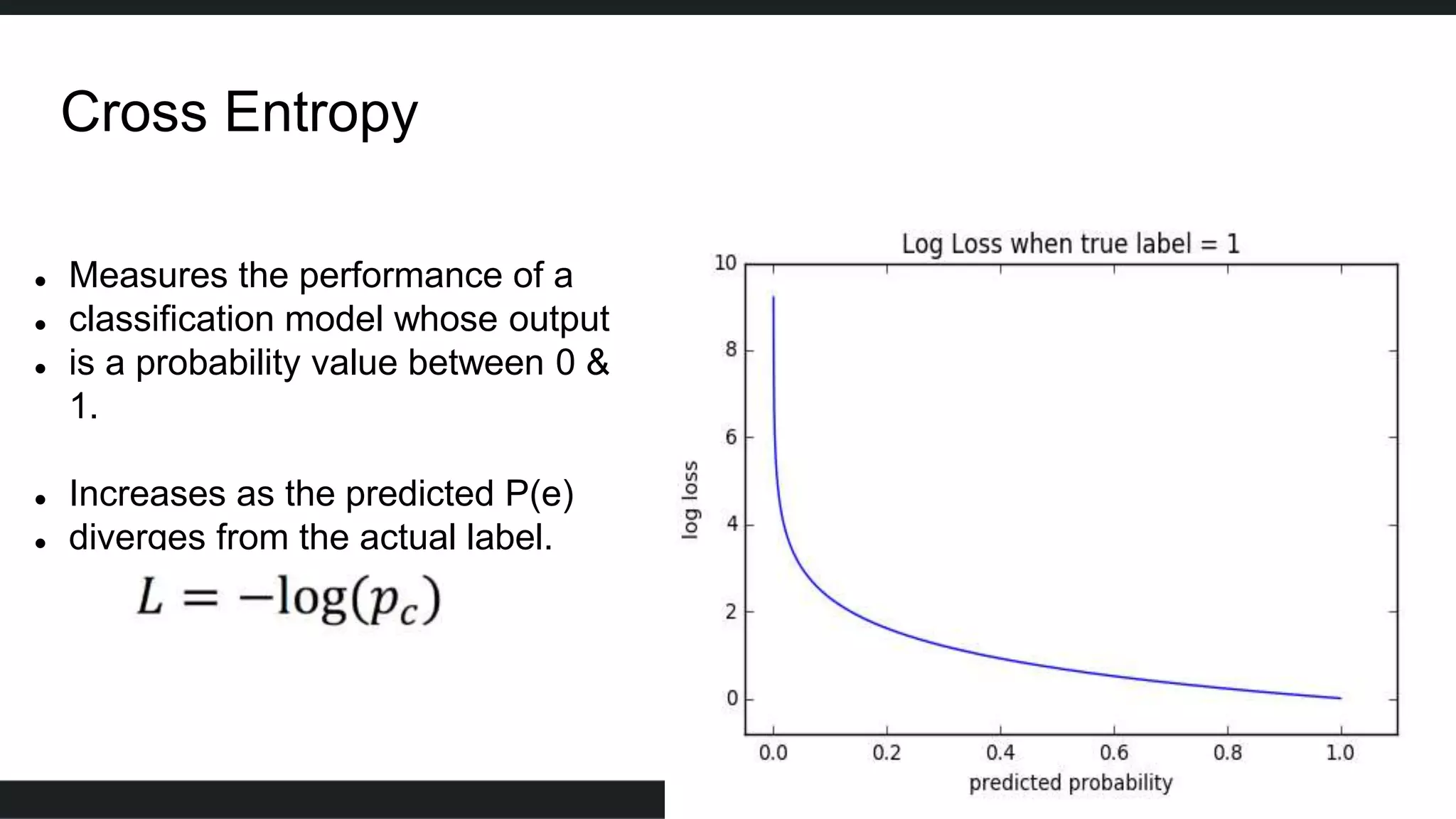
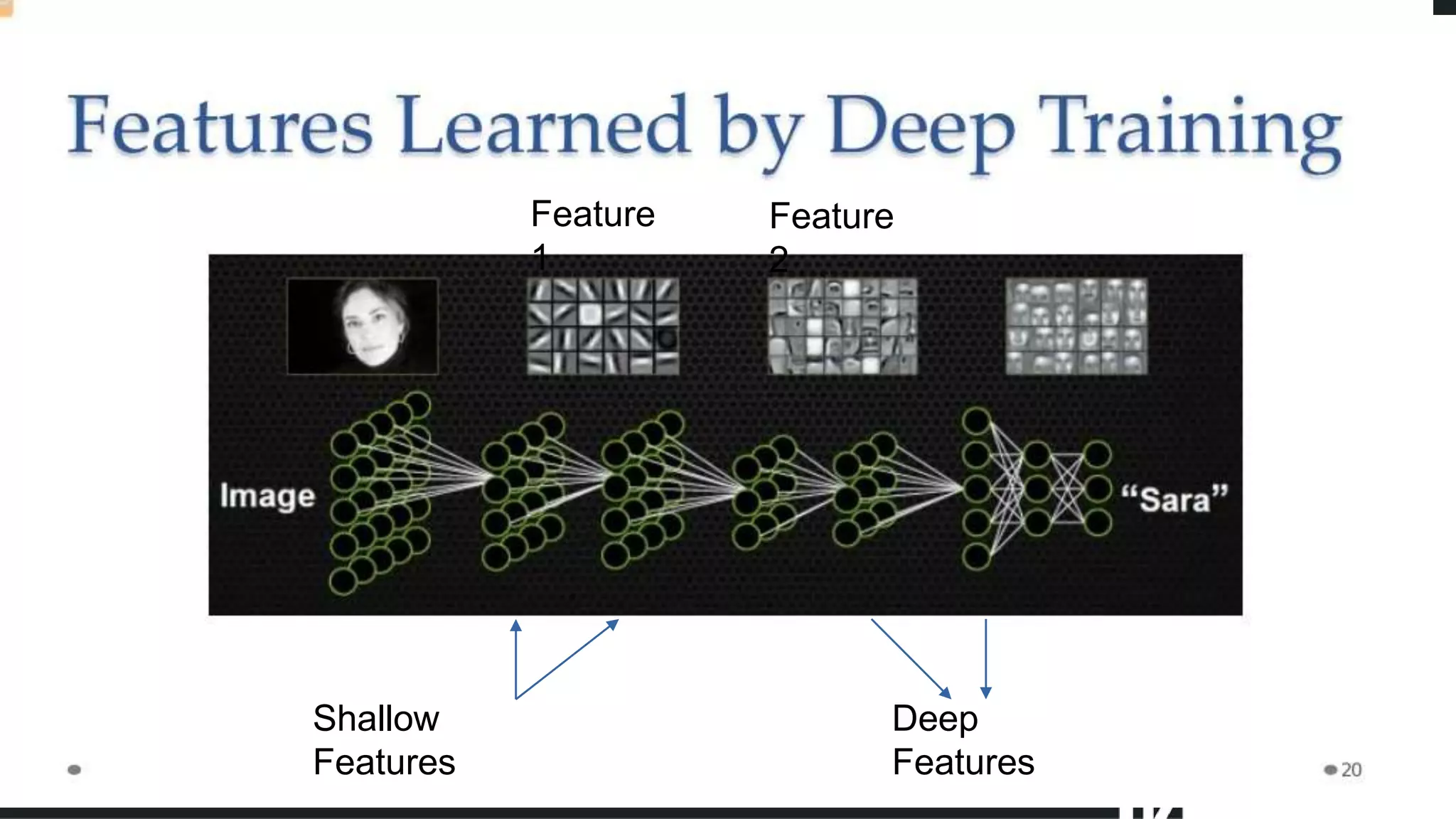
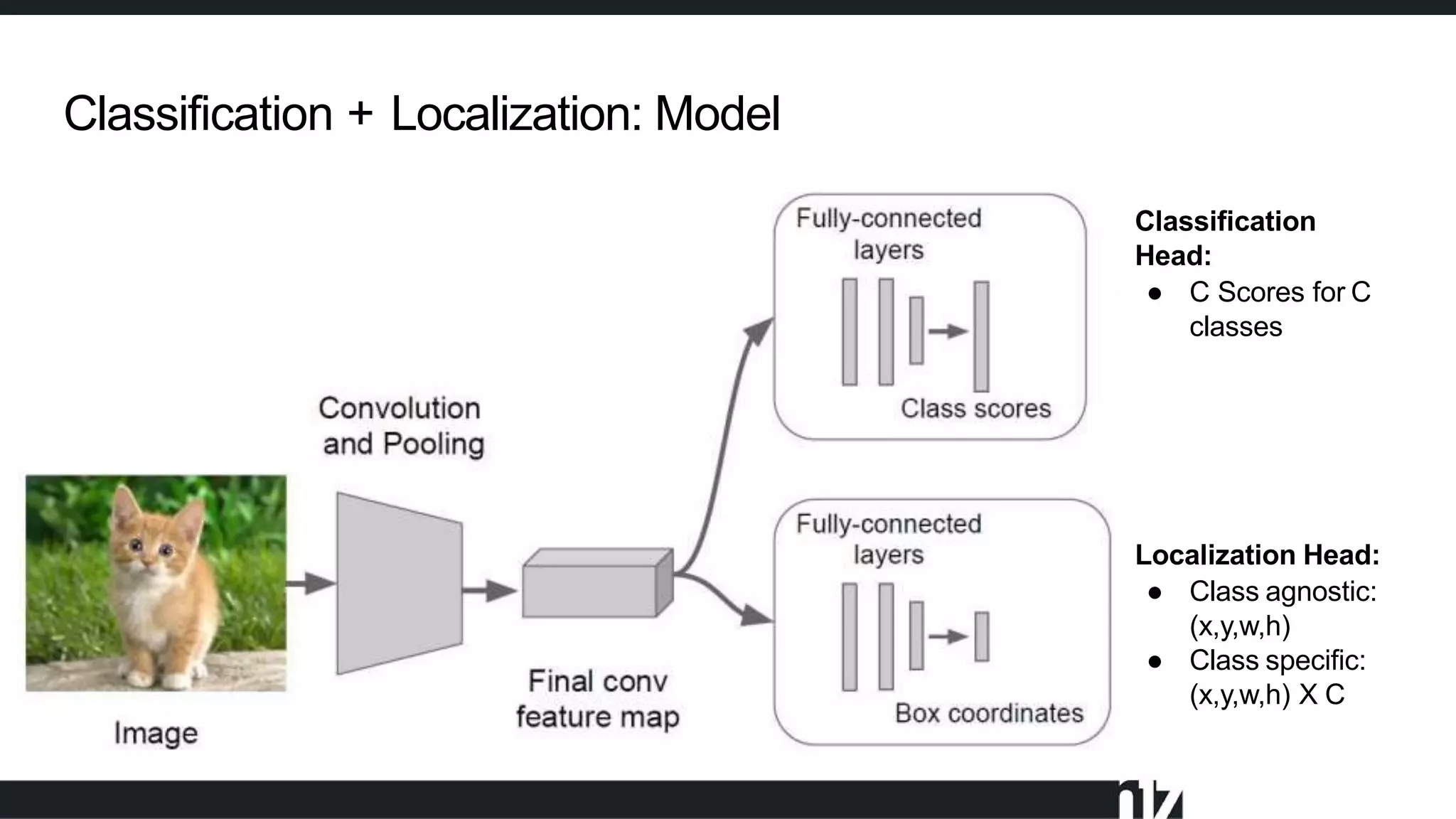
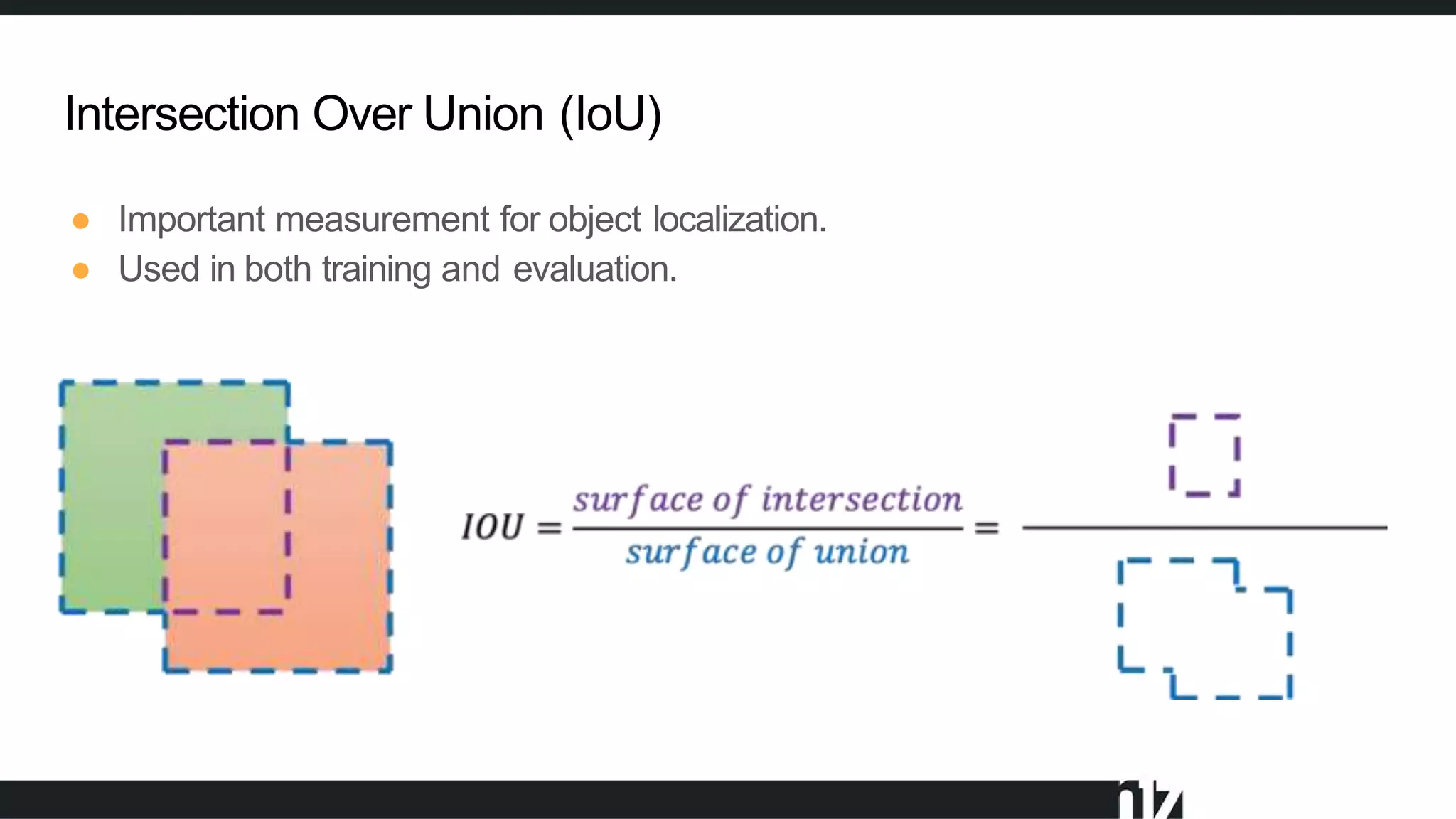
Face detection uses computer vision and image processing techniques to classify and localize faces within images. It involves detecting faces, identifying key facial features, and determining their locations. Common methods include semantic and instance segmentation using convolutional neural networks, as well as YOLO-based approaches that divide images into grids and predict detection bounding boxes and confidence scores for each grid cell. Face detection performance is typically evaluated using metrics like average precision (AP) and mean average precision (mAP) which measure accuracy of localization across different probability thresholds or object sizes. It has various applications including face unlock, person identification, and video surveillance.



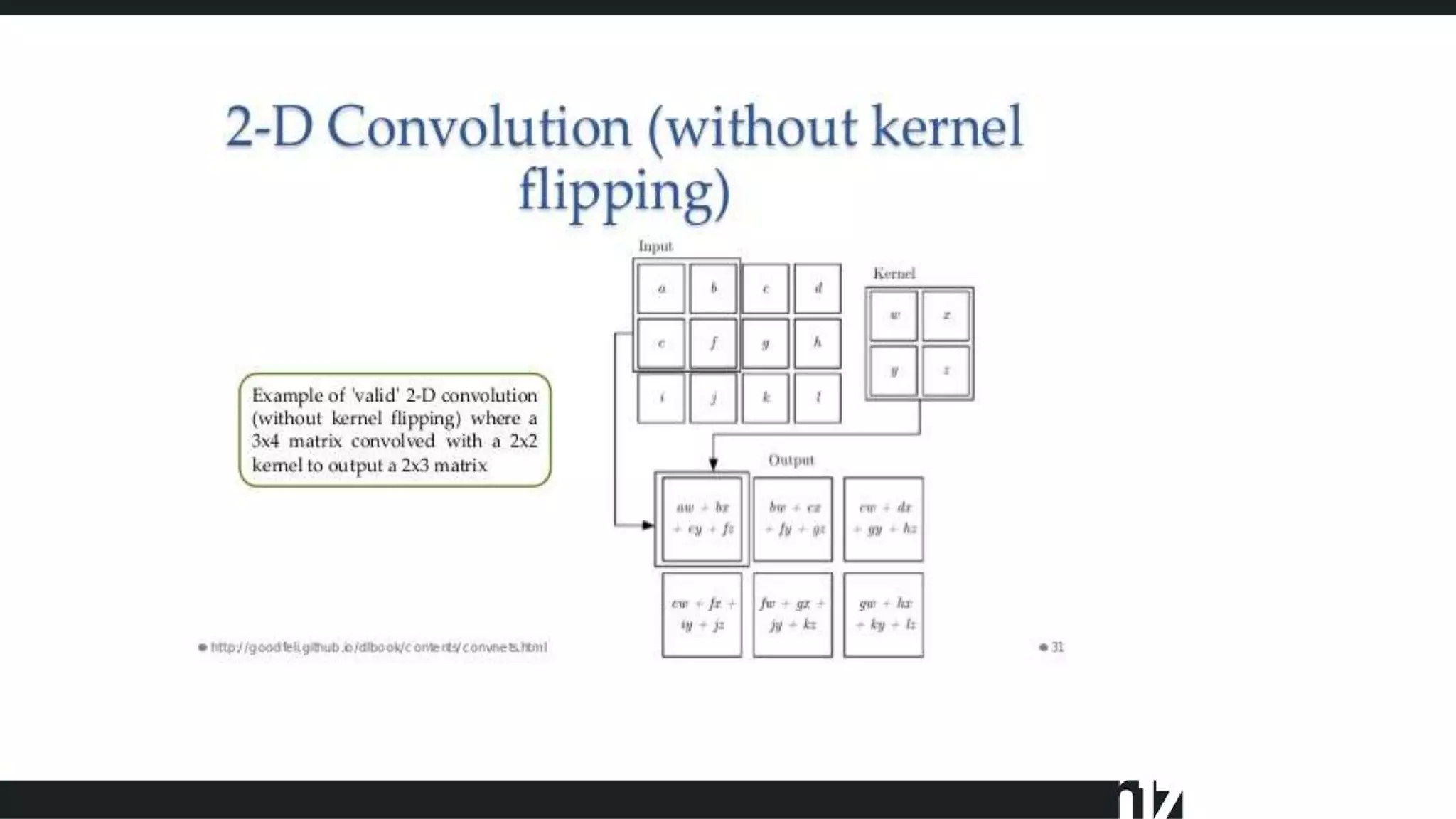
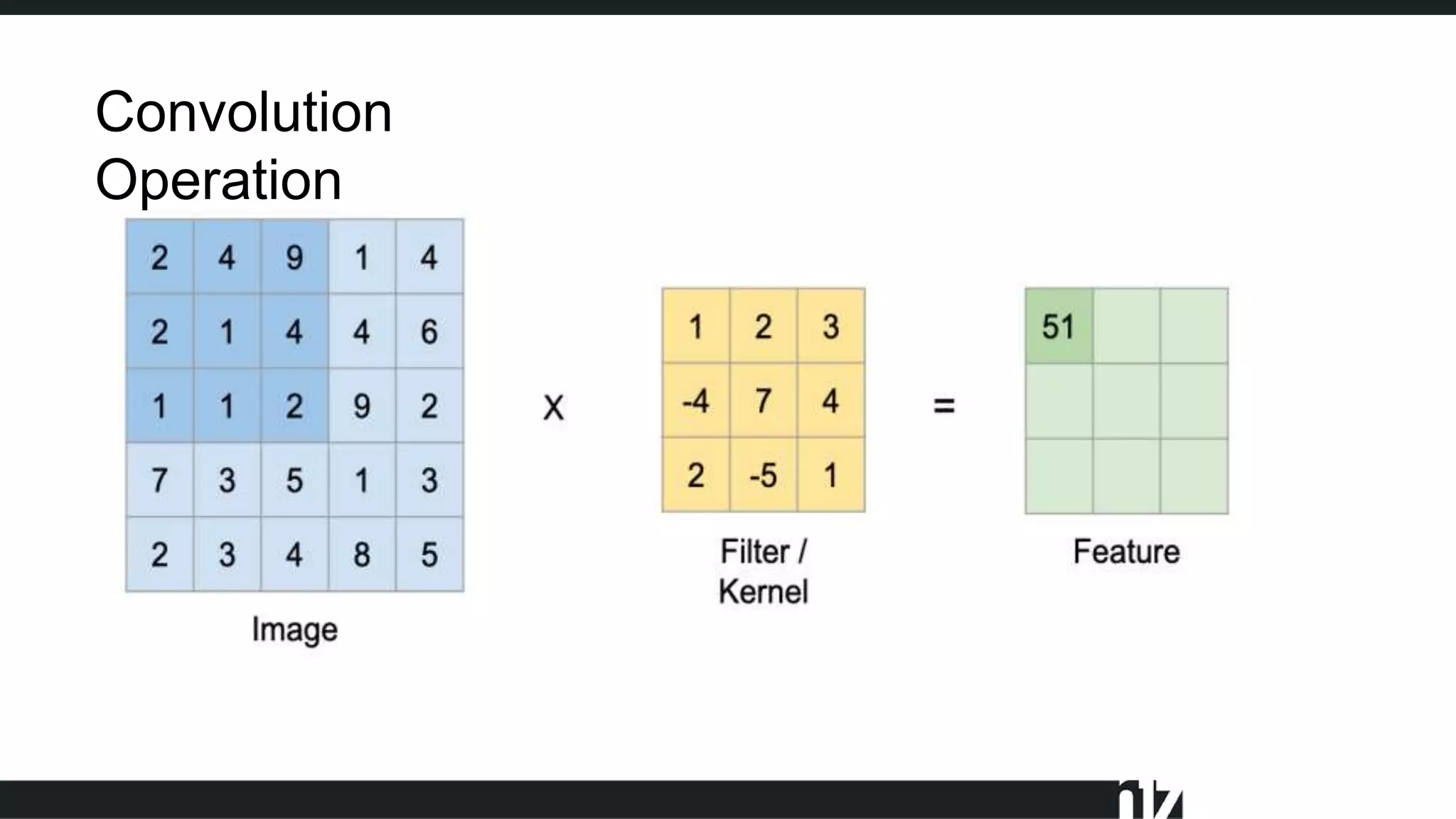





![ 2x [8 filter convolutional layer on 288x288 image]
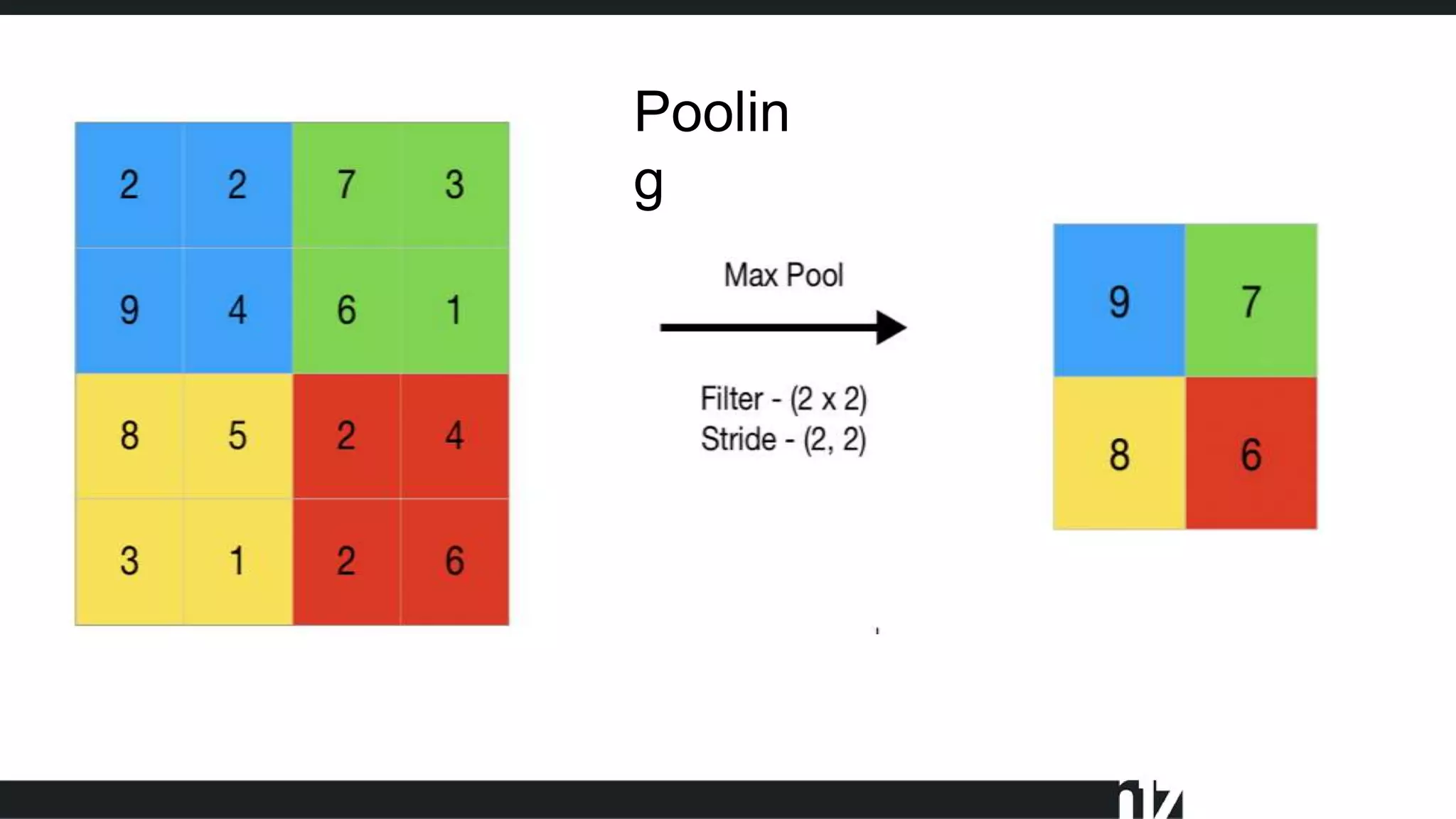
Max pooling (288x288 to 144x144 feature map)
2x [16 filter convolutional layer on 144x144 feature map]
Max pooling (144x144 to 72x72 feature map)
2x [32 filter convolutional layer on 72x72 feature map]
Max pooling (72x72 to 36x36 feature map)
2x [64 filter convolutional layer on 36x36 feature map]
Max pooling (36x36 to 18x18 feature map)
2x [128 filter convolutional layer on 18x18 feature map]
Max pooling (18x18 to 9x9 feature map)
4x [192 filter convolutional layer on 9x9 feature map]
5 filter convolutional layer on 9x9 feature map for the final
grid](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontoobjectdetection-210120070241/75/Introduction-to-object-detection-22-2048.jpg)


![Average Precision (AP)
● [In the vision community] AP is the estimated area under the PR curve](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontoobjectdetection-210120070241/75/Introduction-to-object-detection-26-2048.jpg)



