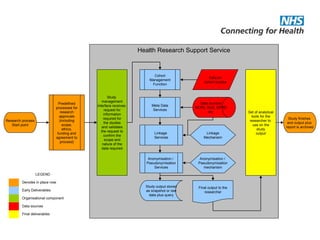
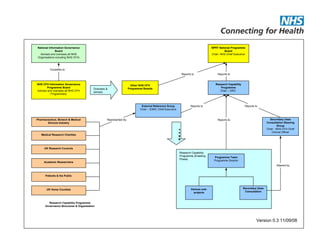
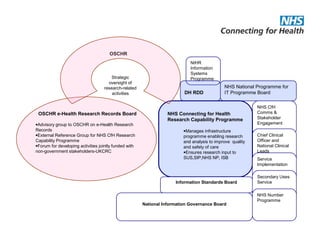
The document provides an overview of the Research Capability Programme (RCP) which aims to enable use of NHS data for research purposes. It discusses the RCP's enabling phase where governance structures and stakeholder engagement were established. The implementation phase will develop infrastructure to provide research support services including access to data sources, cohort management, and anonymization/coding of data. Key challenges include ensuring opportunities are maximized, improving data linkage and quality, and navigating complex information governance issues.

![Research Capability Programme
Recent news:
• HM Revenue and Customs loses CD with millions of
records…….
• Home Office loses personal details of prison officers…..
• Ministry of Defence hard disc with 100,000 servicemen’s
detailed records disappears……..
• 722,000 DNA samples added to National Database which
now covers 4million people…….
[44,000 DNA samples identified at crime scenes…]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/markham2009-140725093914-phpapp01/85/Markham2009-2-320.jpg)