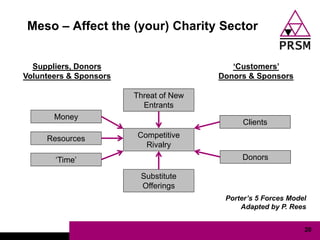
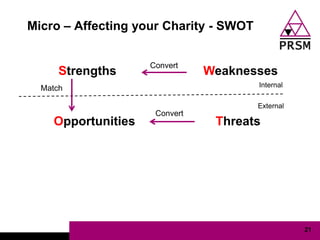
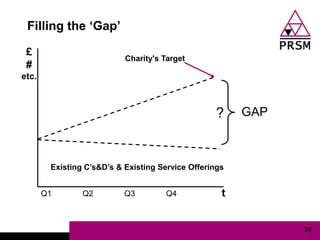
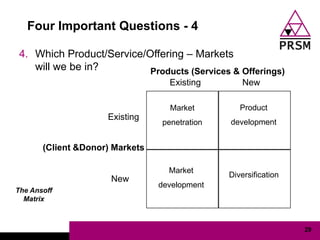
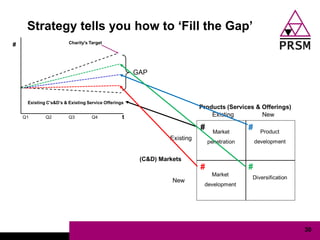
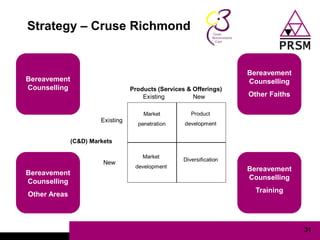
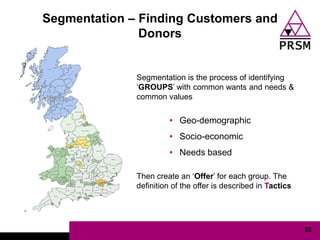
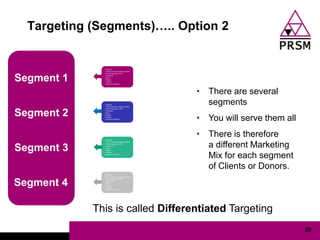
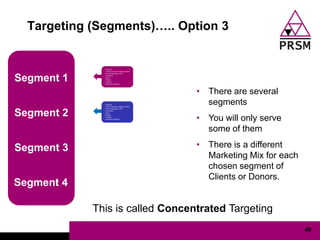
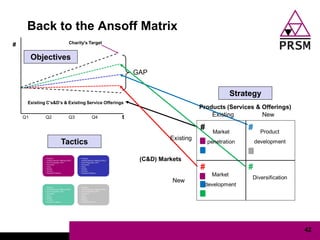
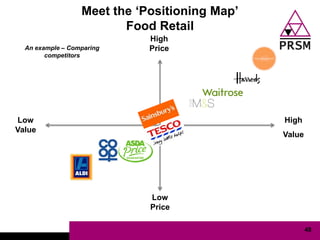
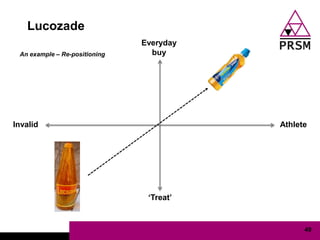
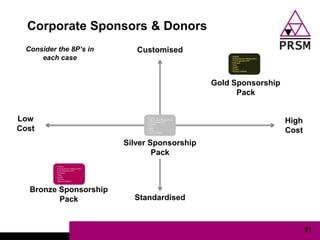
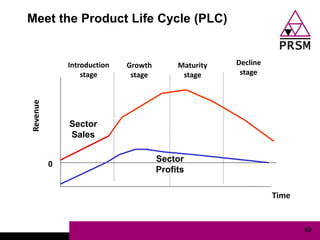
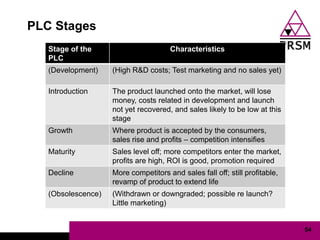
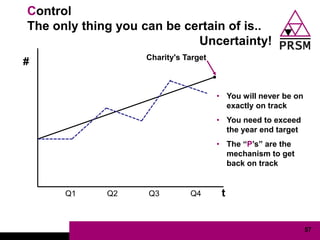
The document discusses marketing planning for charities. It begins with defining marketing and explaining its evolution and role in not-for-profit organizations. It then covers marketing planning processes like conducting a situation analysis, setting objectives, developing a strategy and tactics, and implementing an action plan. The rest of the document provides details on various marketing planning frameworks and concepts that can be applied for charities, including segmentation, targeting, the marketing mix, product lifecycles, and performance tracking.