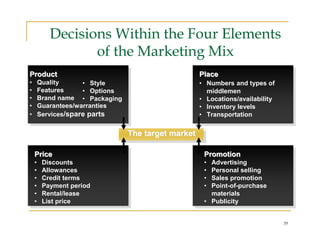
The document provides an overview of marketing concepts and strategies. It begins with several definitions of marketing from different universities. It then discusses that knowing customer wants is not enough on its own for success, and that strategies and tactics are also important. The true nature of marketing today involves conflict between corporations, not just satisfying needs. The document goes on to discuss key marketing concepts like the marketing mix, relationship marketing, common marketing errors, and differences between production-oriented versus market-oriented businesses. It also covers strategic planning components and various corporate growth strategies.




![Marketing Overview
“the process of creating, distributing,
promoting, and pricing goods, services and
ideas to facilitate satisfying exchange
relationships with customers in a dynamic
environment”
(Pride [Texas A&M] - Ferrell, [Colorado State])
5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chaps123-100125013811-phpapp01/85/marketing-5-320.jpg)