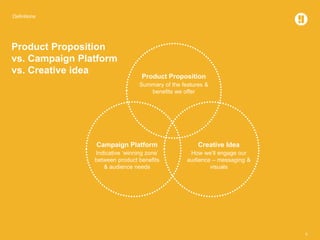
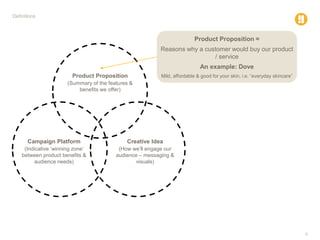
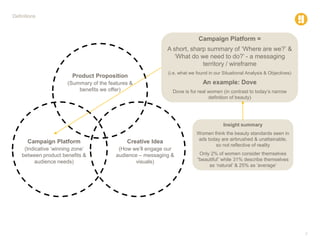
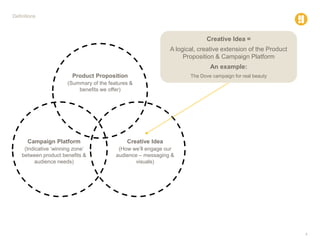
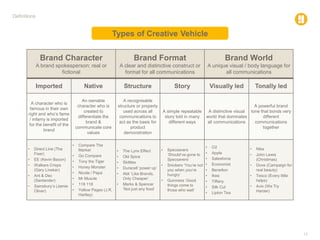
The document defines various marketing and advertising terms, concepts, and frameworks. It distinguishes between strategy and tactics, insight and observation, and differentiates among product propositions, campaign platforms, and creative ideas. It also defines brands and branding, brand identity versus look and feel, and types of creative vehicles. Finally, it outlines the differences between segmentation and targeting, provides examples of types of each, and includes a glossary of common media terminology.