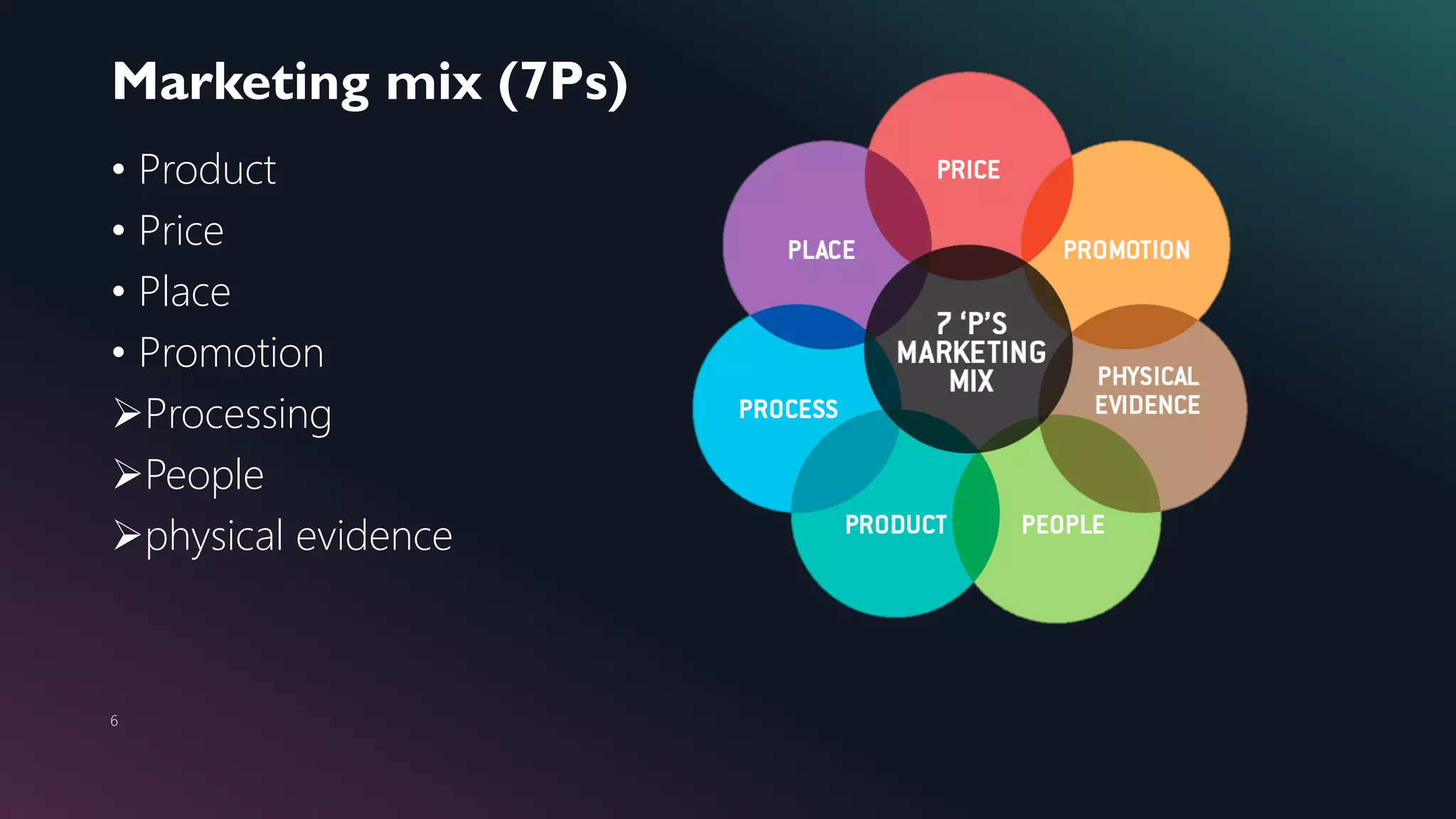
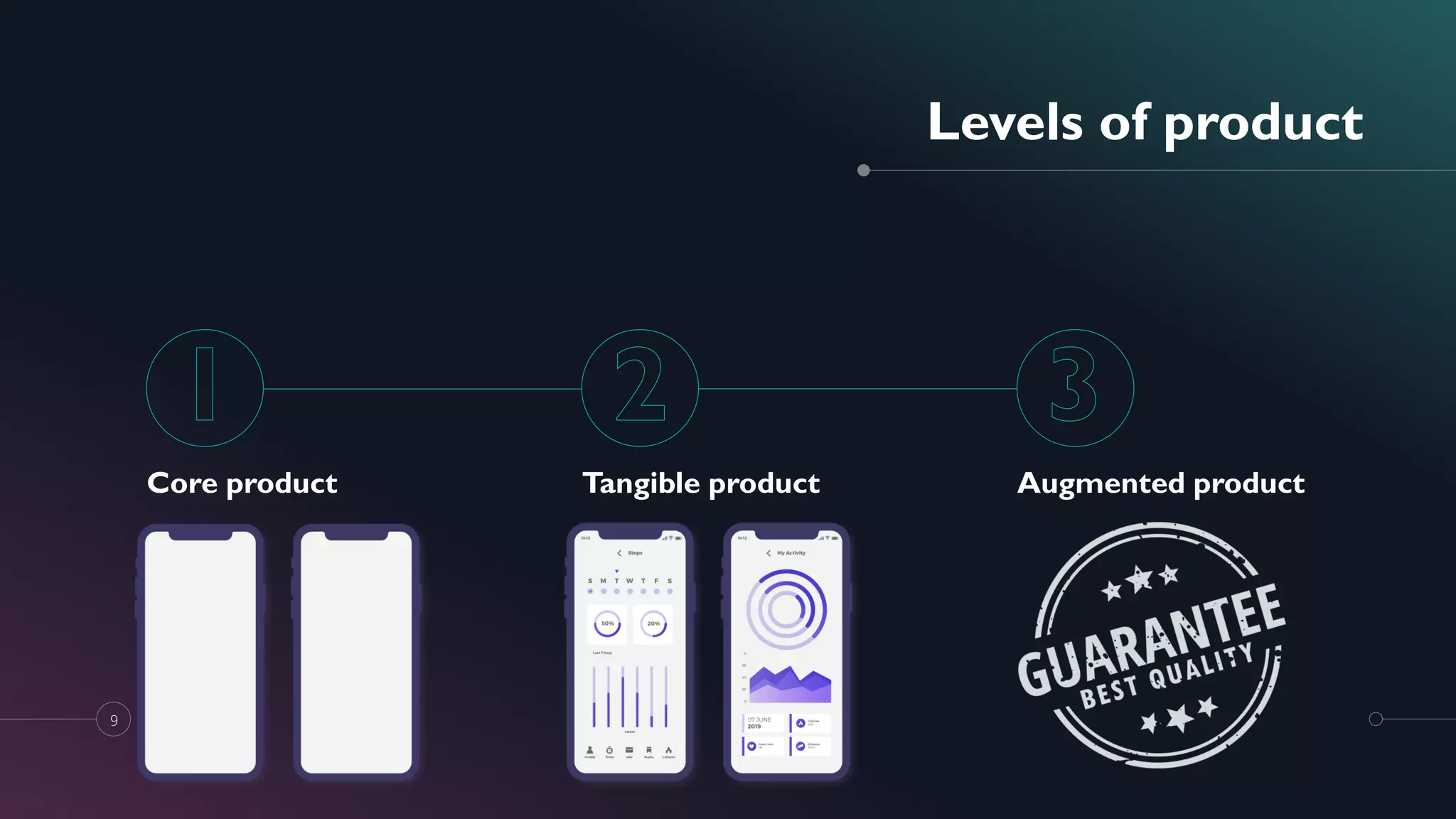
This document provides an introduction to marketing and branding, defining key concepts such as the marketing mix, target markets, and the elements of branding. It emphasizes the importance of differentiation, focus, simplicity, innovation, visual appeal, and continuity in building a strong brand. Additionally, it outlines various marketing strategies and pricing methods while addressing factors affecting pricing and the significance of corporate social responsibility.