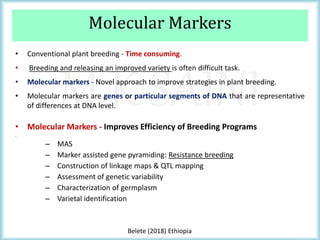
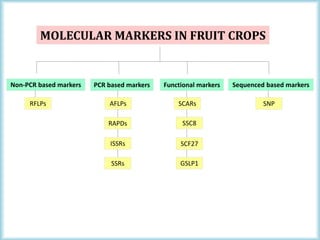
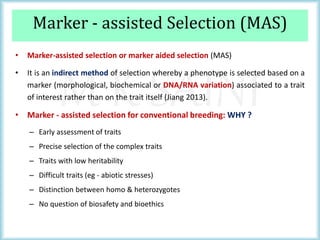
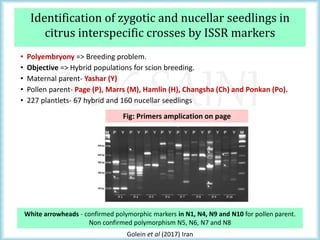
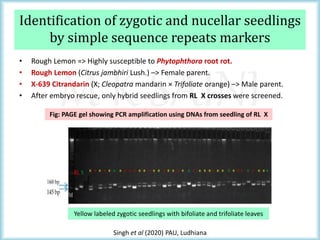
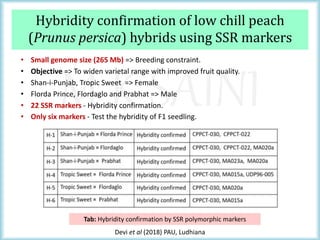
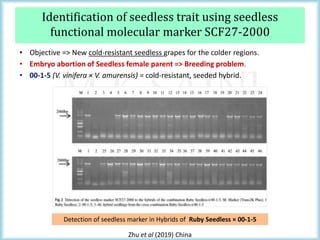
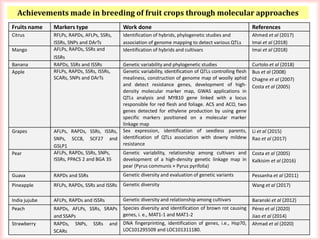
This document discusses the use of molecular markers in fruit crop breeding. It begins by explaining how molecular markers like RFLPs, AFLPs, RAPDs, ISSRs, SSRs, and SNPs can be used in marker-assisted selection to improve the efficiency of breeding programs through early trait assessment, selection of complex traits, and distinguishing hybrids from parental lines. It then provides examples of studies using ISSR and SSR markers in citrus and peach breeding. The document concludes by summarizing achievements in various fruit crops using different molecular marker techniques and outlining ongoing research projects at PAU utilizing biotechnology approaches like marker-assisted breeding.