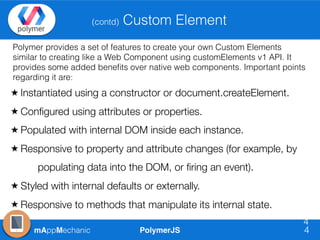
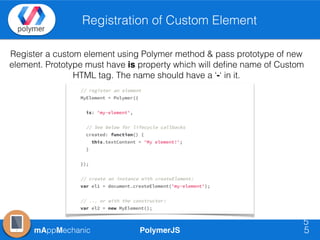
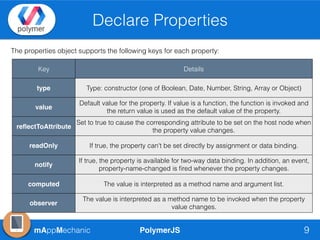
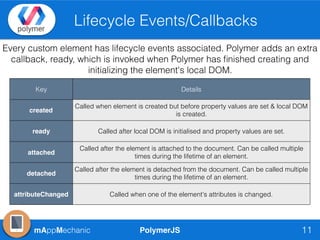
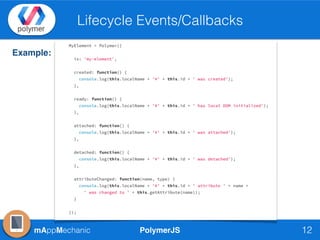
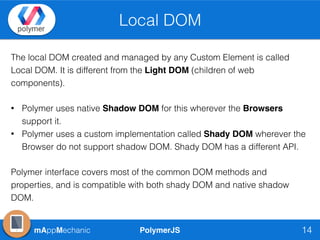
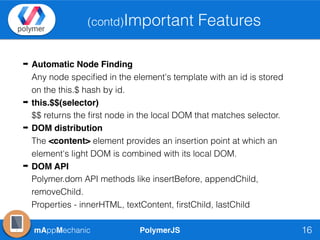
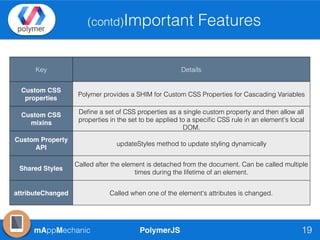
The document outlines essential features of creating custom elements using PolymerJS, including registration, property declaration, lifecycle events, and styling methods. It explains how to instantiate custom elements, define properties and their attributes, and manage local and light DOM. Additionally, it discusses the use of shadow DOM for styling and the Polymer API for managing dynamic content and events.