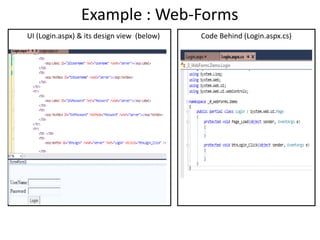
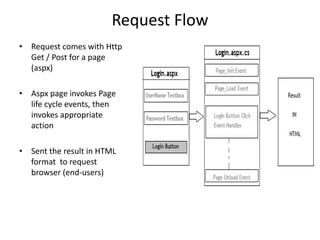
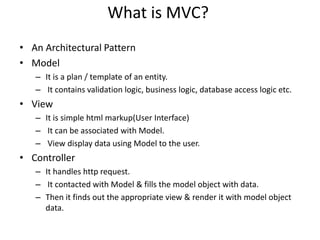
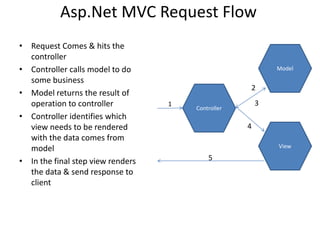
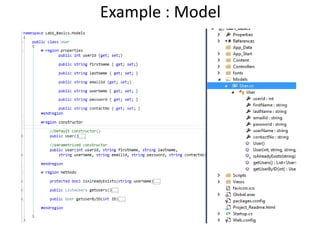
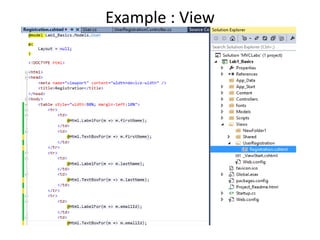
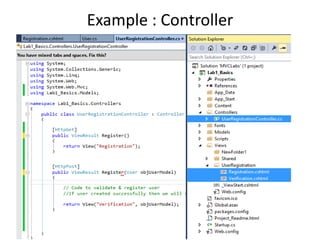
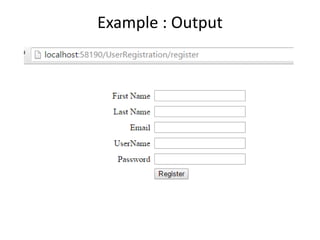
This document provides an introduction to ASP.NET MVC, including a comparison to ASP.NET Web Forms. It outlines some problems with the Web Forms approach like tight coupling and difficulty with unit testing. MVC is introduced as an architectural pattern that enforces separation of concerns into models, views, and controllers. The request flow for ASP.NET MVC is described as starting with a request hitting a controller, which calls a model and identifies a view to render the model data and send a response. Examples of an MVC model, view, and controller are also provided.