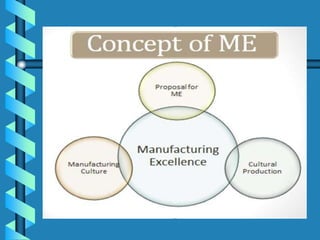
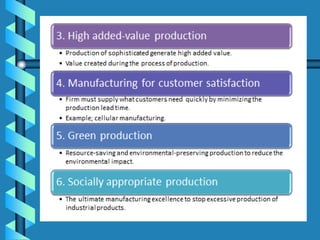
1) Green manufacturing aims to minimize waste and pollution through product and process design in order to support future generations and attain sustainability.
2) It works by rethinking technology, exploring market potential, supplying goods/services, extending producer responsibility, reducing energy use, and integrating environmental costs.
3) A real world example is using corn to produce biodegradable plastics like PHA instead of petroleum-based plastic, with the process involving growing, extracting, fermenting, washing, and drying corn into a bioplastic powder.