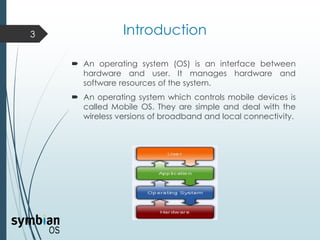
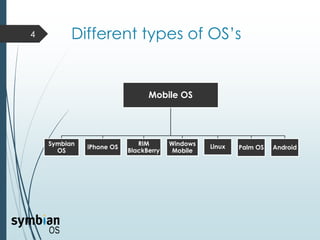
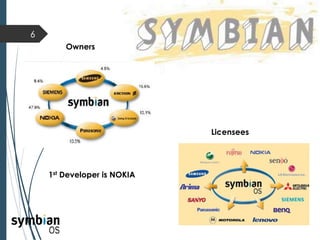
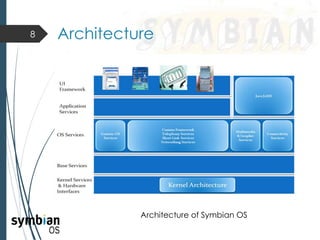
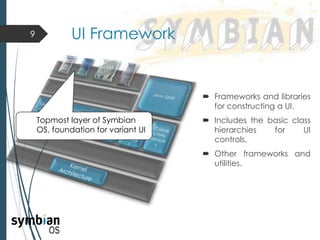
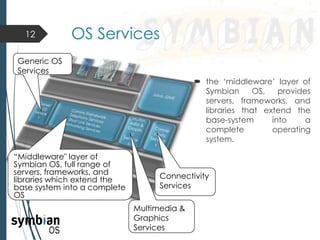
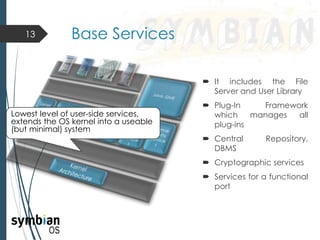
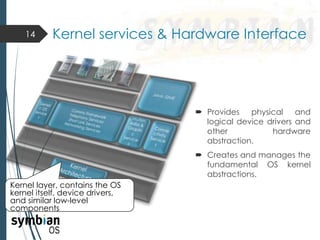
This document provides an overview of the Symbian mobile operating system. It discusses the architecture and components of Symbian OS, including the user interface framework, Java support, application services layer, OS services layer, base services layer, and kernel services. It also covers the different versions of Symbian OS released over time as well as key features like multitasking, memory management, and support for common file systems and networking. Applications developed for Symbian and technologies used in its development like the Symbian SDK and Carbide.c++ are also mentioned.