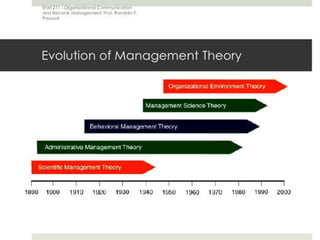
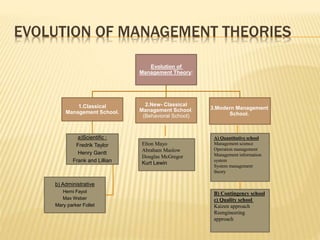
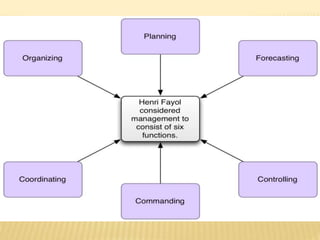
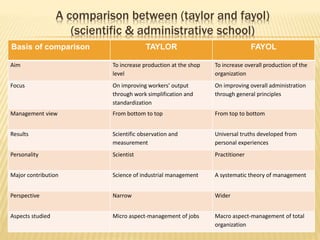
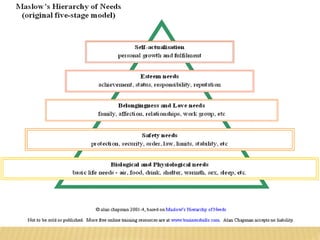
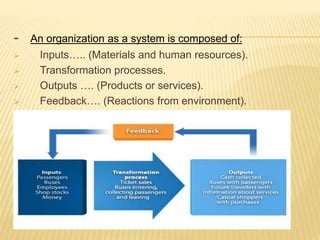
This document outlines the evolution of management theories from classical to modern approaches. It begins by defining management and management theories. The classical approaches are then described, including scientific management pioneered by Taylor which focused on efficiency. Administrative theories by Fayol and Weber emphasized formal structure. The behavioral school emerged next, exemplified by Mayo who stressed the importance of human relationships. Maslow's hierarchy of needs also influenced this period. Later, quantitative and contingency approaches analyzed organizational problems using mathematical and statistical methods to improve decision making. Modern theories strive for a balanced focus on both technical and human aspects of management.