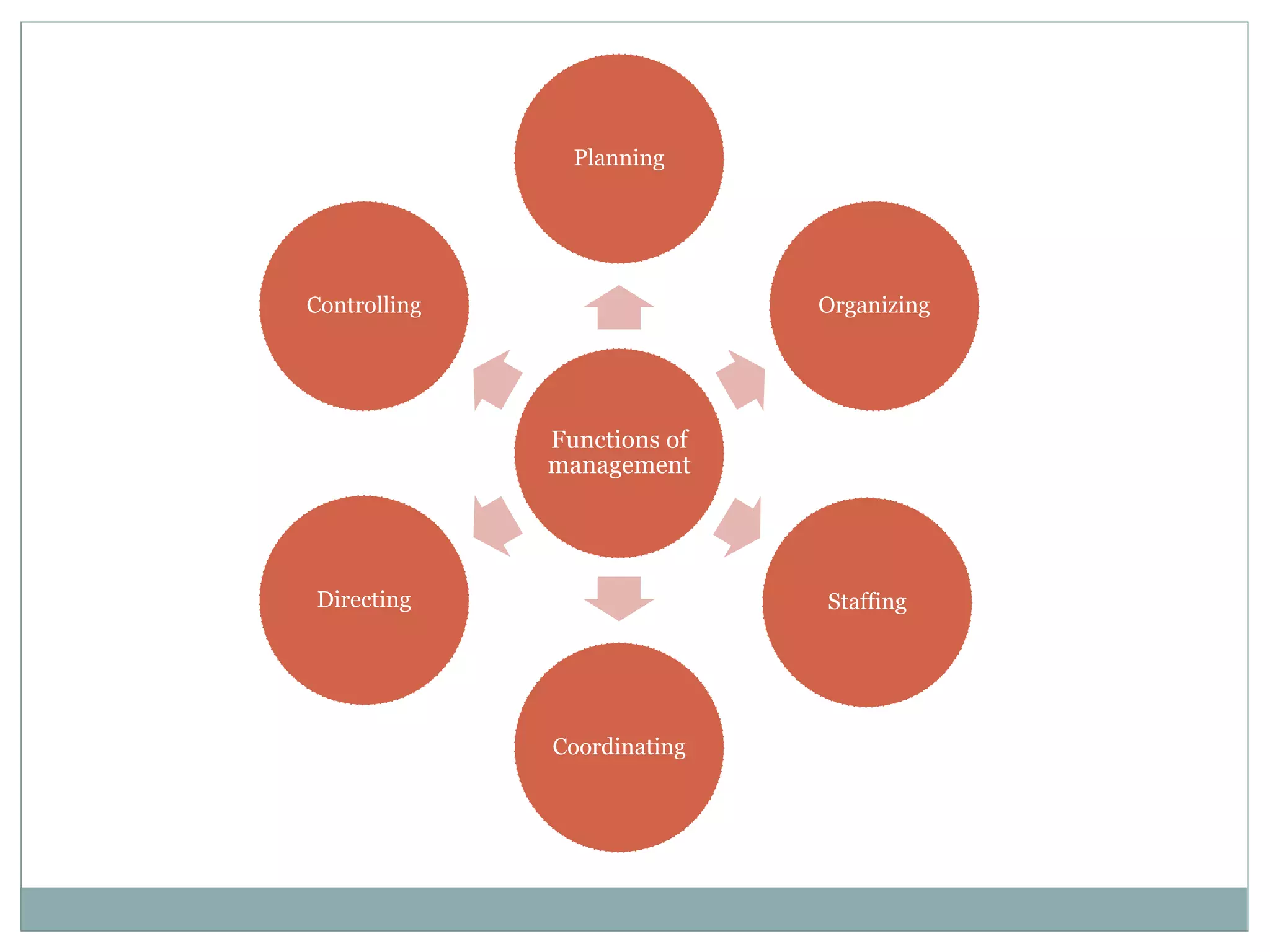
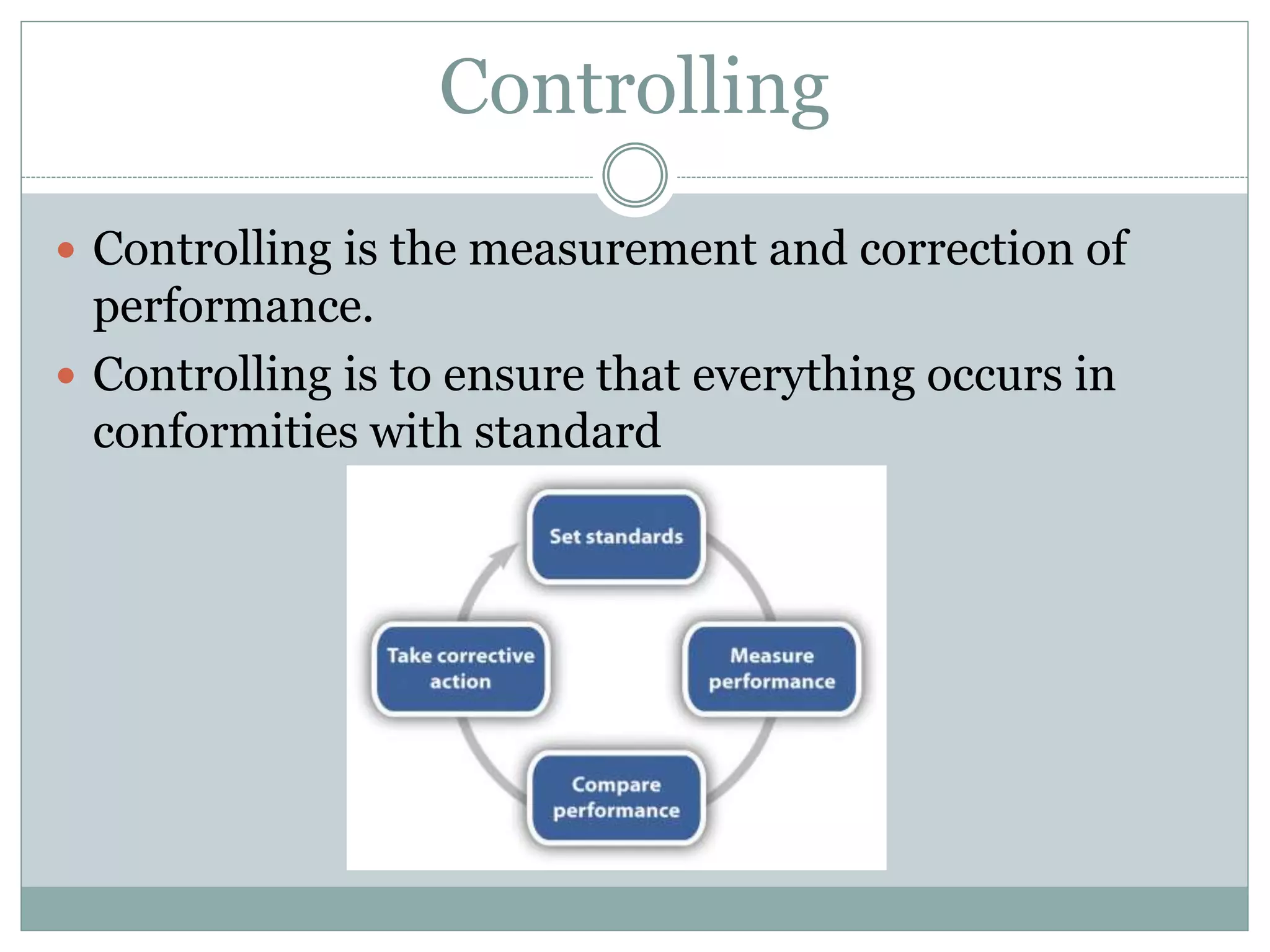
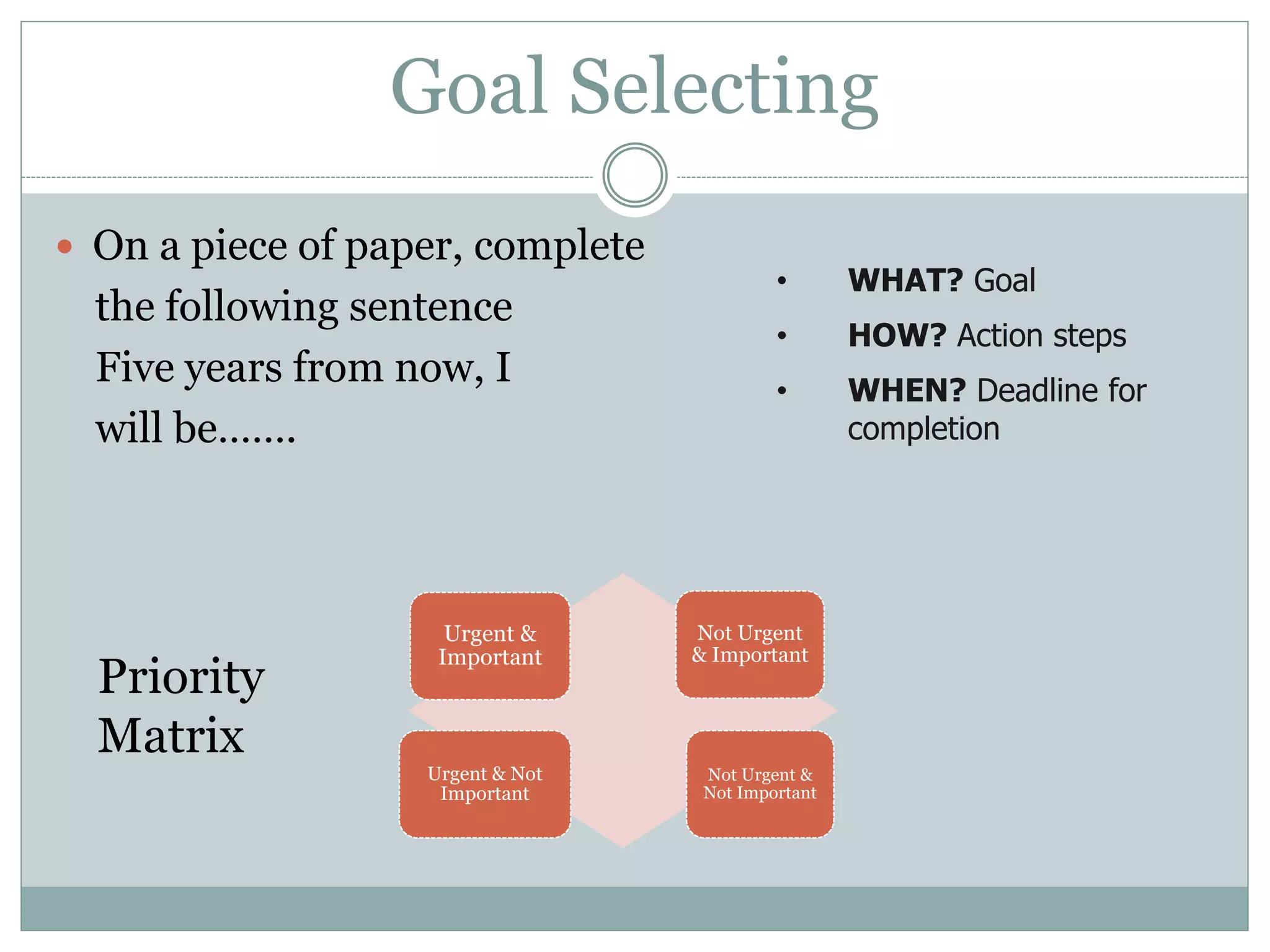
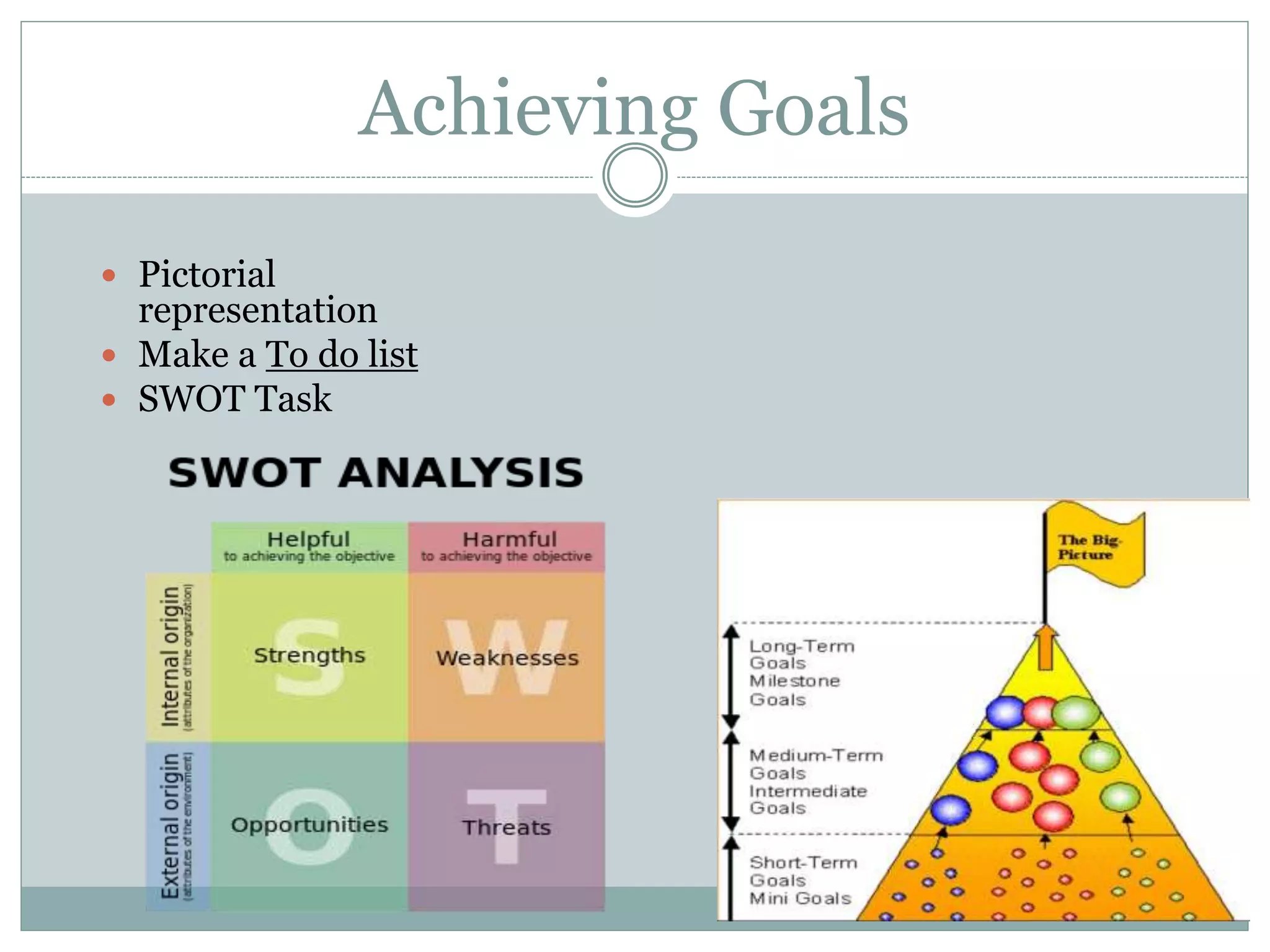
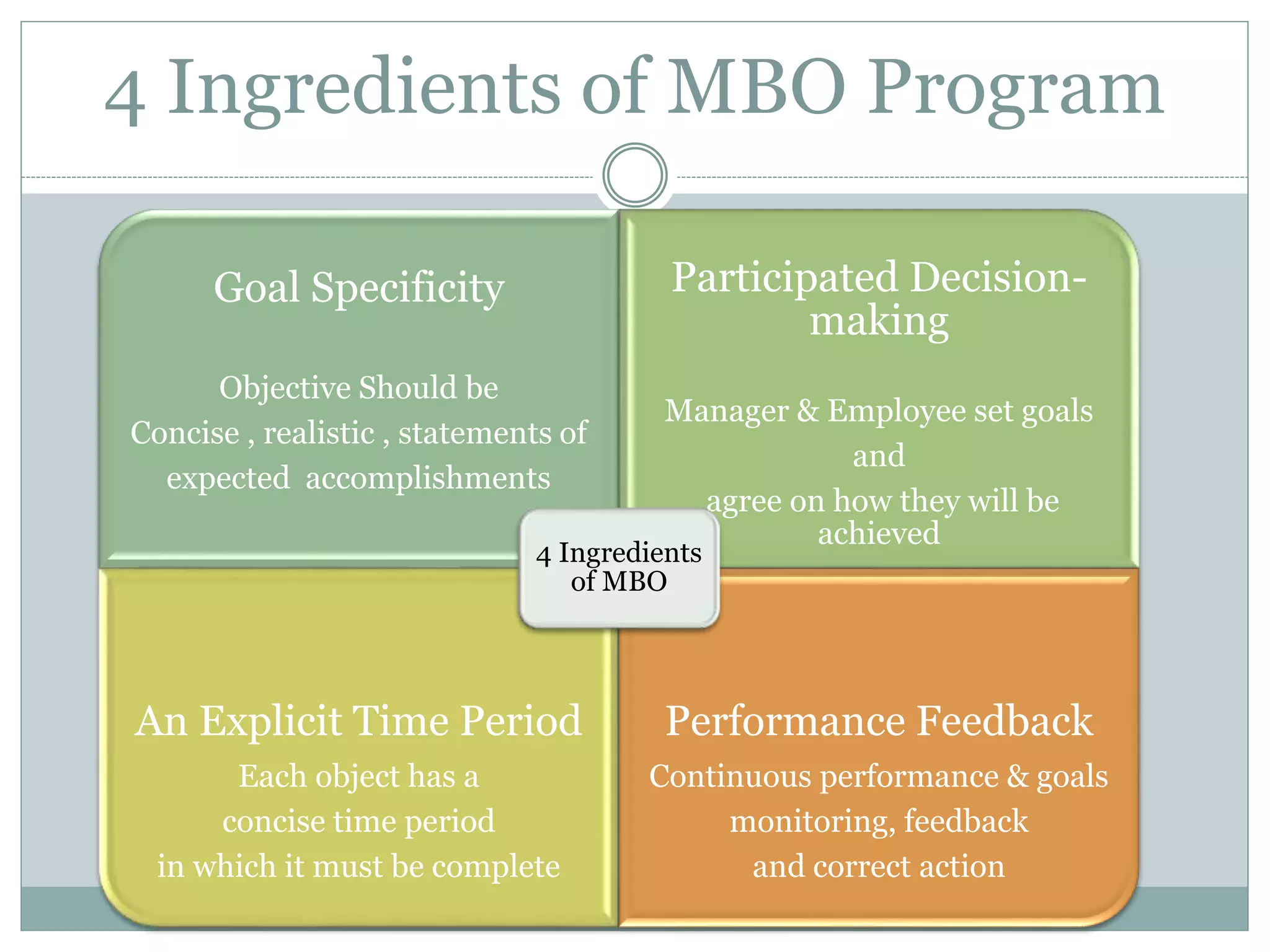
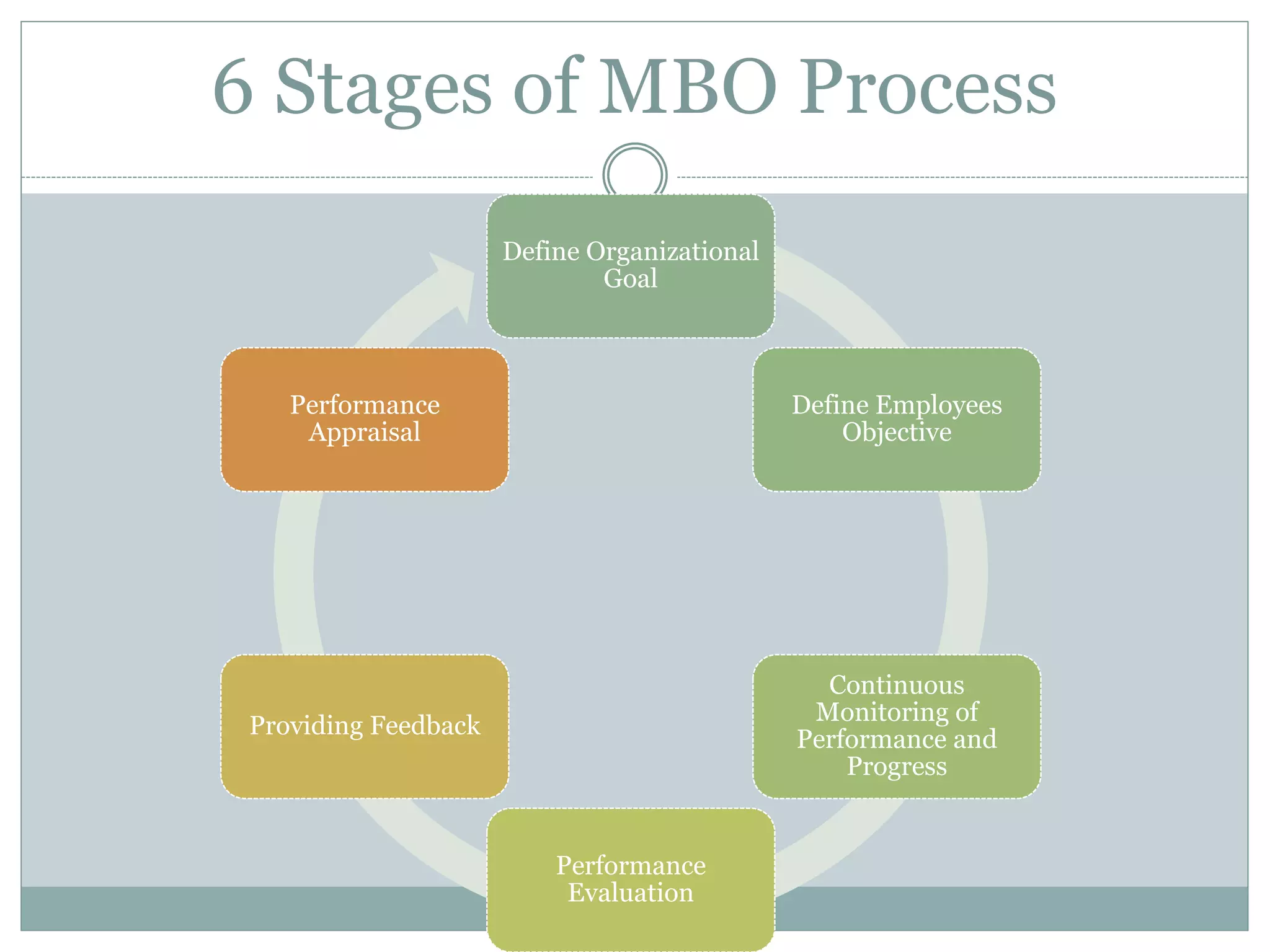
This document discusses key management functions including planning, organizing, staffing, coordinating, directing, and controlling. It provides details on each function, such as the importance of planning to reduce risks and waste. It also covers organizing techniques like subdivision of work and allocation of authority. Additional topics include characteristics of coordination, techniques of directing employees, and the importance of controlling to ensure goals are met. The document concludes with information on goal setting, including characteristics of effective goals and the process of management by objectives.