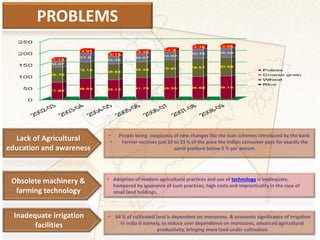
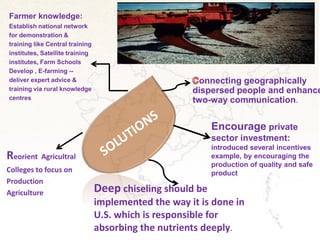
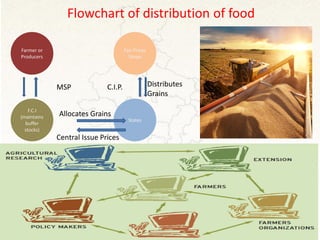
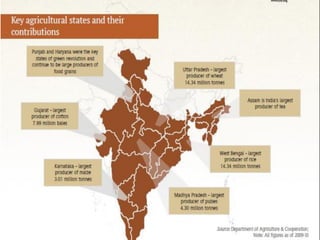
This document proposes solutions to problems facing Indian agriculture and outlines their potential impacts. It identifies issues such as lack of education, obsolete technology, inadequate irrigation, unstable policies, and negative perceptions of farming. Solutions proposed include increasing private investment, improving farmer knowledge through training programs, reorienting agriculture colleges, doubling productivity through better soil/water management, and strengthening research/implementation links. Challenges to the solutions include the expense of new equipment, replacing chemical fertilizers, addressing farmer suicides, improving agricultural education, and seeking international support. The solutions aim to meet future food demands in a sustainable way and improve farmer profitability and lives.