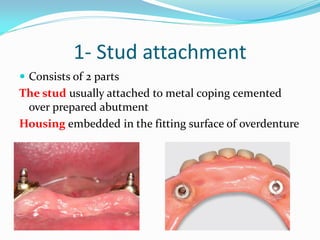
This document discusses overdentures, which are complete or partial dentures constructed over existing teeth, roots, or implants to provide additional support, stability, and retention. It describes different types of overdentures including tooth-supported and implant-supported overdentures. Various techniques for constructing tooth-supported overdentures are presented, including different ways of preparing and covering abutment teeth. Indications and contraindications for overdentures are also outlined.