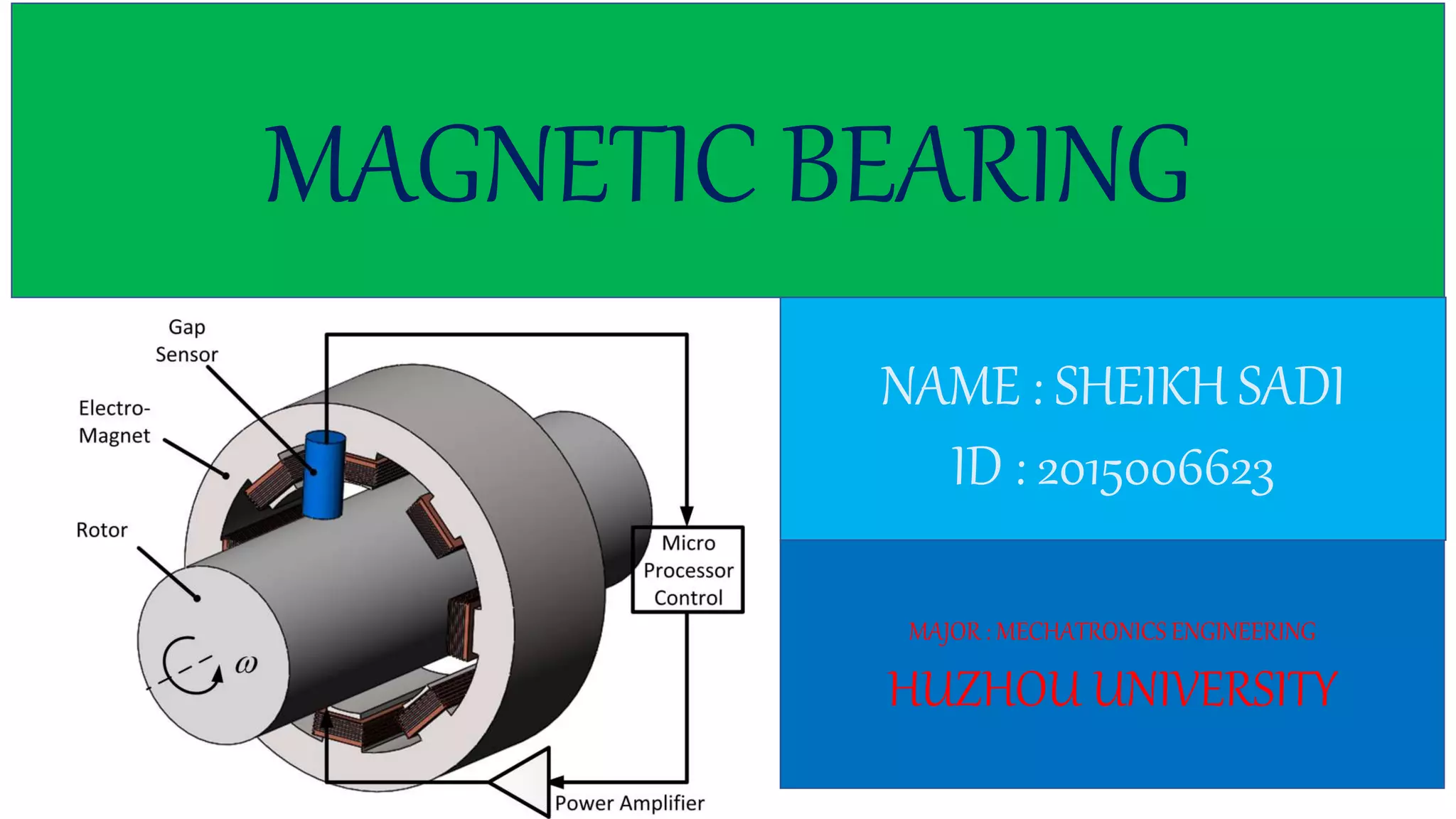
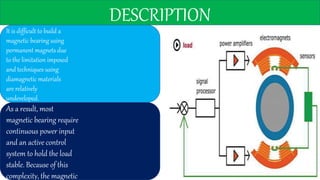
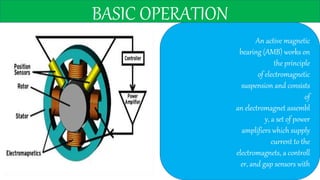
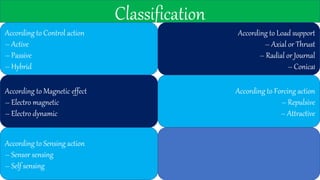
This document discusses magnetic bearings. Magnetic bearings support loads using magnetic levitation without physical contact. They use electromagnets to attract ferromagnetic materials and levitate rotors. Magnetic bearings require continuous power and active control systems to maintain stability. They have advantages over traditional bearings like higher speeds, less wear, and longer life. However, they are also more expensive and large in size. Magnetic bearings are increasingly used in industrial machines like compressors, turbines, pumps, motors and generators.