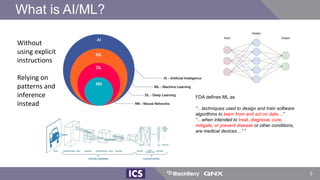
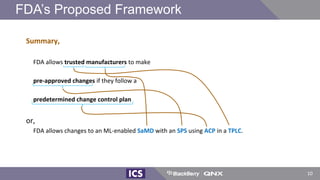
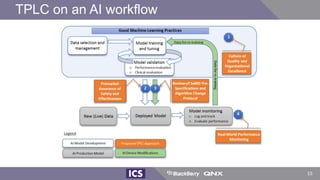
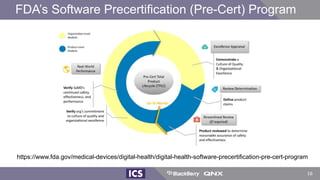
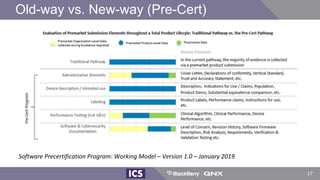
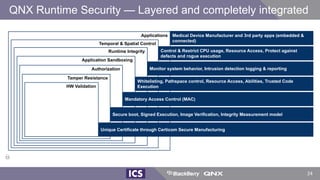
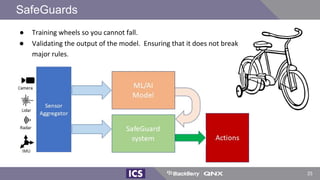
The document discusses machine learning in medical devices. It describes how the FDA regulates machine learning as a medical device and proposes a framework for modifications to AI/ML models. The framework allows manufacturers to make pre-approved changes if they follow a predetermined change control plan or submit changes through an algorithm change protocol, software pre-specifications, and total product lifecycle approach. The document also discusses developing medical devices with machine learning and important safety considerations.