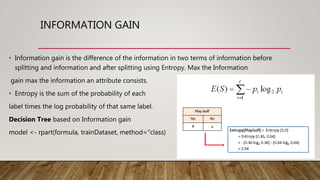
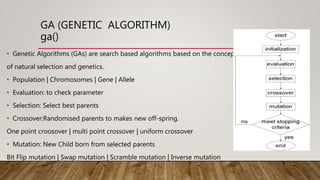
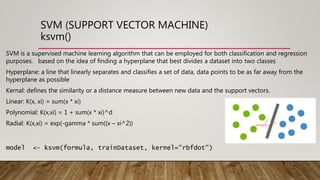
This document provides an overview of machine learning techniques using R. It discusses regression, classification, linear models, decision trees, neural networks, genetic algorithms, support vector machines, and ensembling methods. Evaluation metrics and algorithms like lm(), rpart(), nnet(), ksvm(), and ga() are presented for different machine learning tasks. The document also compares inductive learning, analytical learning, and explanation-based learning approaches.