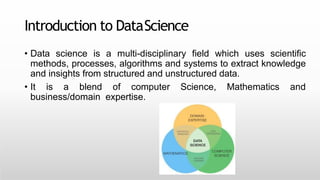
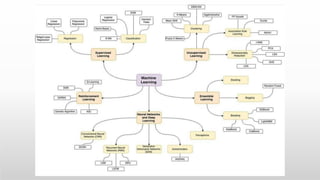
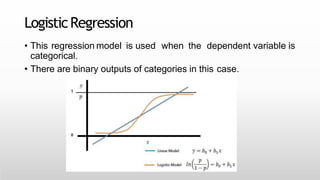
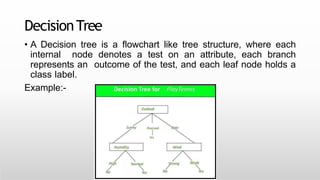
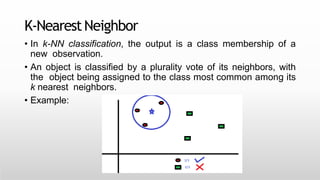
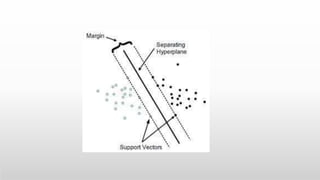
This document provides an introduction to machine learning for data science. It discusses the applications and foundations of data science, including statistics, linear algebra, computer science, and programming. It then describes machine learning, including the three main categories of supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and reinforcement learning. Supervised learning algorithms covered include logistic regression, decision trees, random forests, k-nearest neighbors, and support vector machines. Unsupervised learning methods discussed are principal component analysis and cluster analysis.