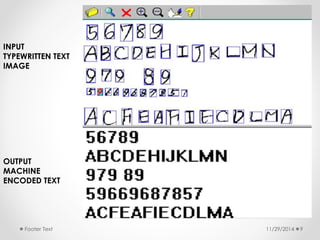
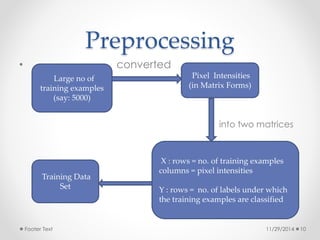
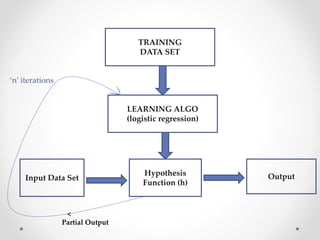
The document discusses machine learning and optical character recognition (OCR). It defines machine learning as the study of algorithms that can learn from data without being explicitly programmed. It discusses the types of machine learning algorithms and applications such as spam detection and medical research. The aim of the presentation is to implement OCR using supervised machine learning to convert images of text into machine-encoded text. It describes the OCR process and prospects for using OCR in applications like processing business documents.