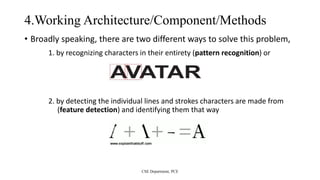
The document summarizes a seminar presentation on improvements to optical character recognition (OCR) algorithms. It discusses how OCR works to convert images of text into machine-encoded text, along with its applications. The presentation compares OCR to similar technologies like intelligent character recognition and describes the typical components of OCR systems. It notes that while OCR accuracy has improved, full accuracy is still not achieved for handwritten text and other scripts. The presentation concludes that accuracy can be increased through human review and using data dictionaries during automatic correction.