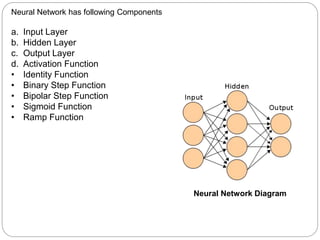
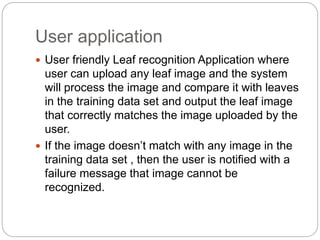
This document discusses leaf recognition through analyzing algorithms like the multi-scale distance matrix and backpropagation neural network. It aims to develop an efficient leaf recognition system with optimal accuracy and a user-friendly application. The multi-scale distance matrix algorithm takes the leaf edge into account to classify leaves by creating distance matrices. A neural network can forecast and classify using input, hidden and output layers along with an activation function. The application will process uploaded leaf images, compare them to a training dataset, and output the matching leaf or a failure message.

![Leaf
A leaf is an organ of a vascular plant, and is the
principal appendage of the vascular plant stem.[1]
The leaves and stem together form the shoot.
Typically a leaf is a thin, dorsiventrally flattened
organ, borne above ground and specialized for
photosynthesis. Most leaves have distinctive
upper (adaxial) and lower (abaxial) surfaces that
differ in colour, hairiness, the number of stomata
and other features.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/majorppt-140529235621-phpapp01/85/final-year-project_leaf-recognition-2-320.jpg)