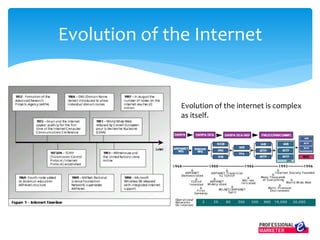
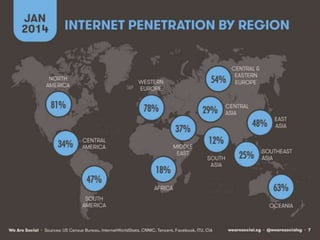
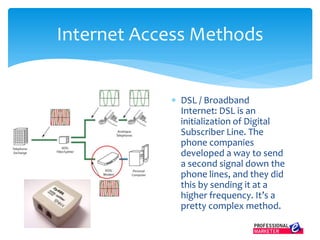
The document outlines the evolution of the Internet from ARPANET in 1969 to its current state, highlighting key developments such as the invention of email, the World Wide Web, and the rise of e-commerce. It explains how Internet Service Providers (ISPs) are essential for access by investing in infrastructure and ensuring connectivity, while also detailing various Internet access methods. The document illustrates the transformative impact of the Internet on business, marketing, and communication, emphasizing the integration of online marketing into the corporate landscape.