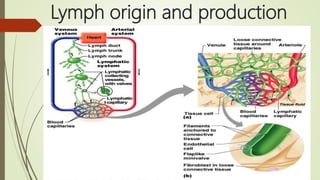
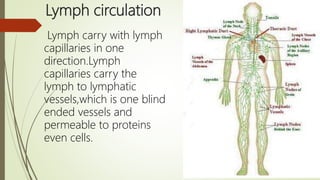
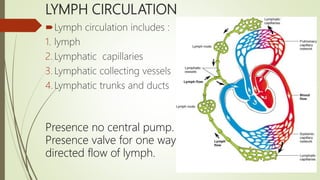
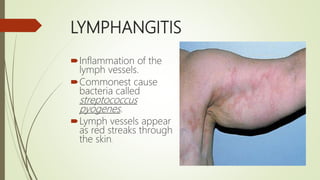
Lymph is a pale fluid derived from interstitial fluid that contains white blood cells. It is collected through lymph capillaries and transported unidirectionally through afferent lymphatic vessels. Lymph originates from interstitial fluid and is produced as fluid efflux across capillary walls exceeds influx. It circulates through lymph capillaries, vessels, trunks and ducts via valve-guided one-way flow without a central pump. Lymph functions include supporting tissue fluid levels, transporting nutrients and filtering bacteria which are destroyed in lymph nodes. Diseases associated with lymph include lymphangitis, filariasis, lymphedema, lymphadenopathy, lymphomas and lymphadenitis.