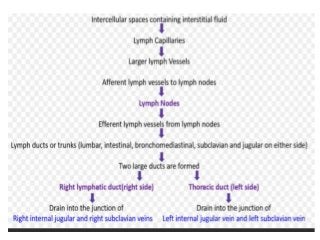
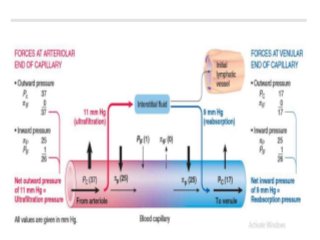
The lymphatic system functions as an accessory route for fluid transport from interstitial spaces to the blood, with lymph being a modified tissue fluid containing various substances. Lymph is formed from interstitial fluid and plays essential roles in nutrient absorption, maintaining interstitial fluid pressure, transporting proteins, and serving as a defense mechanism against foreign particles. Various medical conditions related to the lymphatic system include edema, lymphangitis, and lymphocytosis, among others.