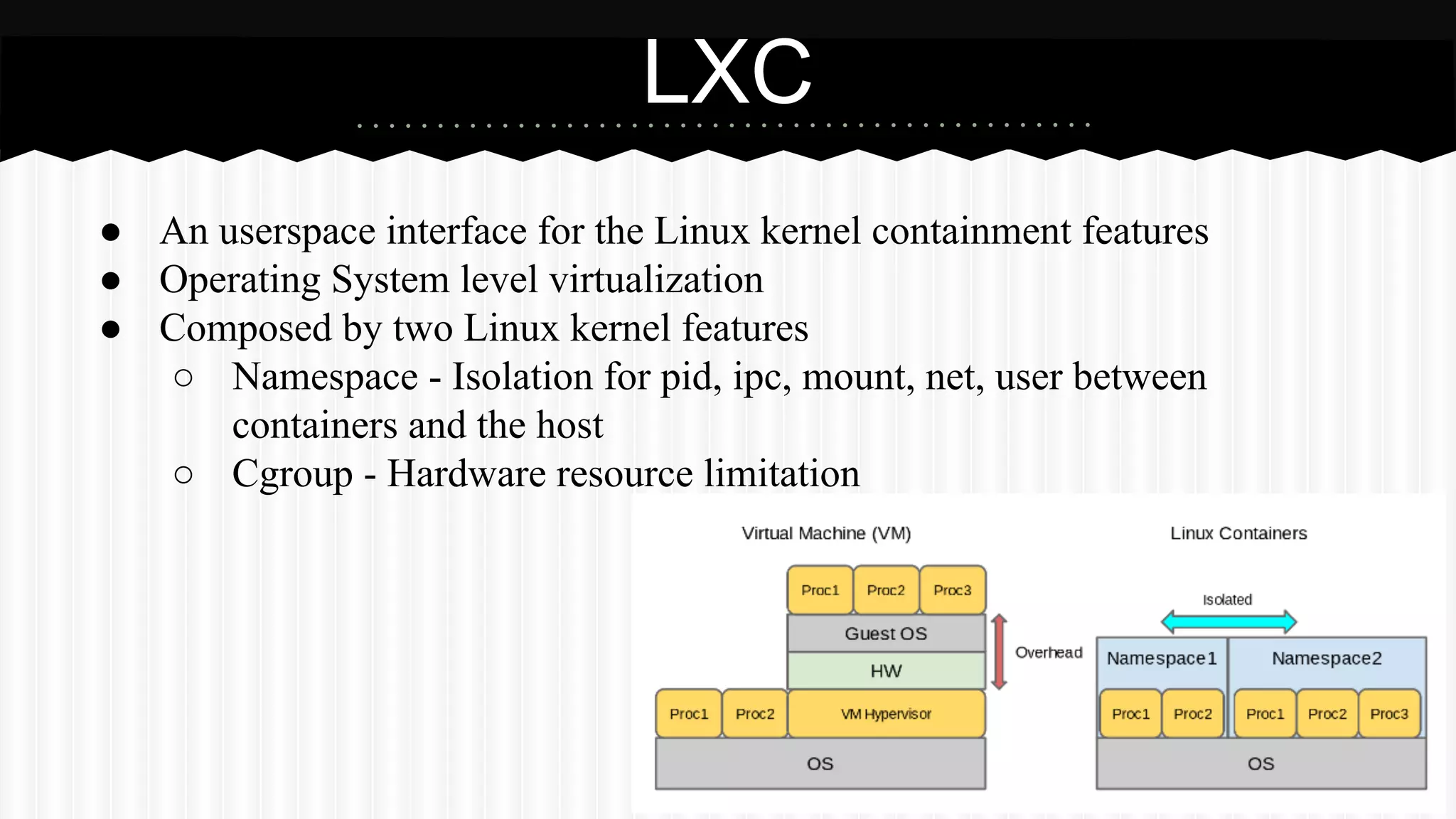
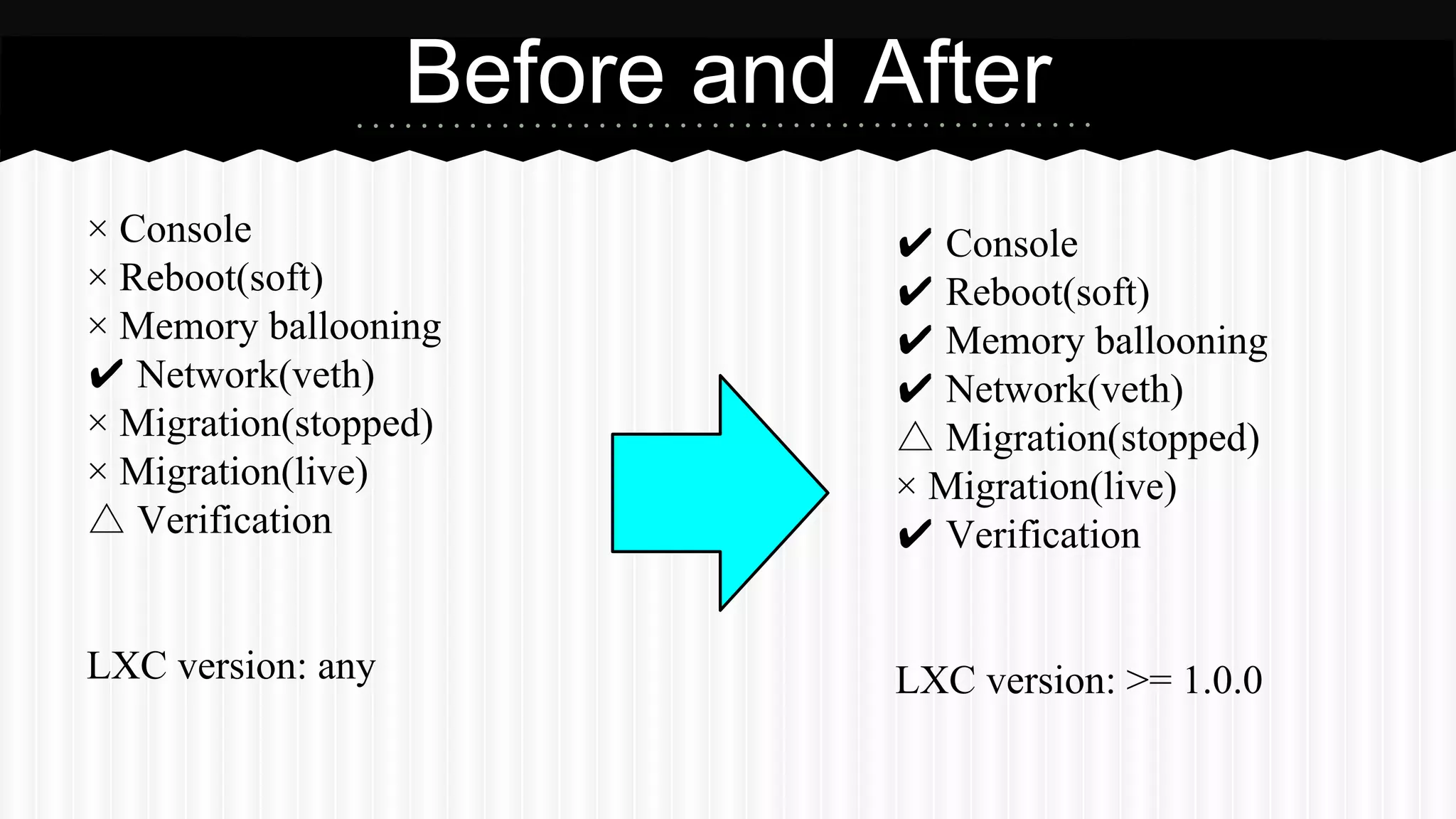
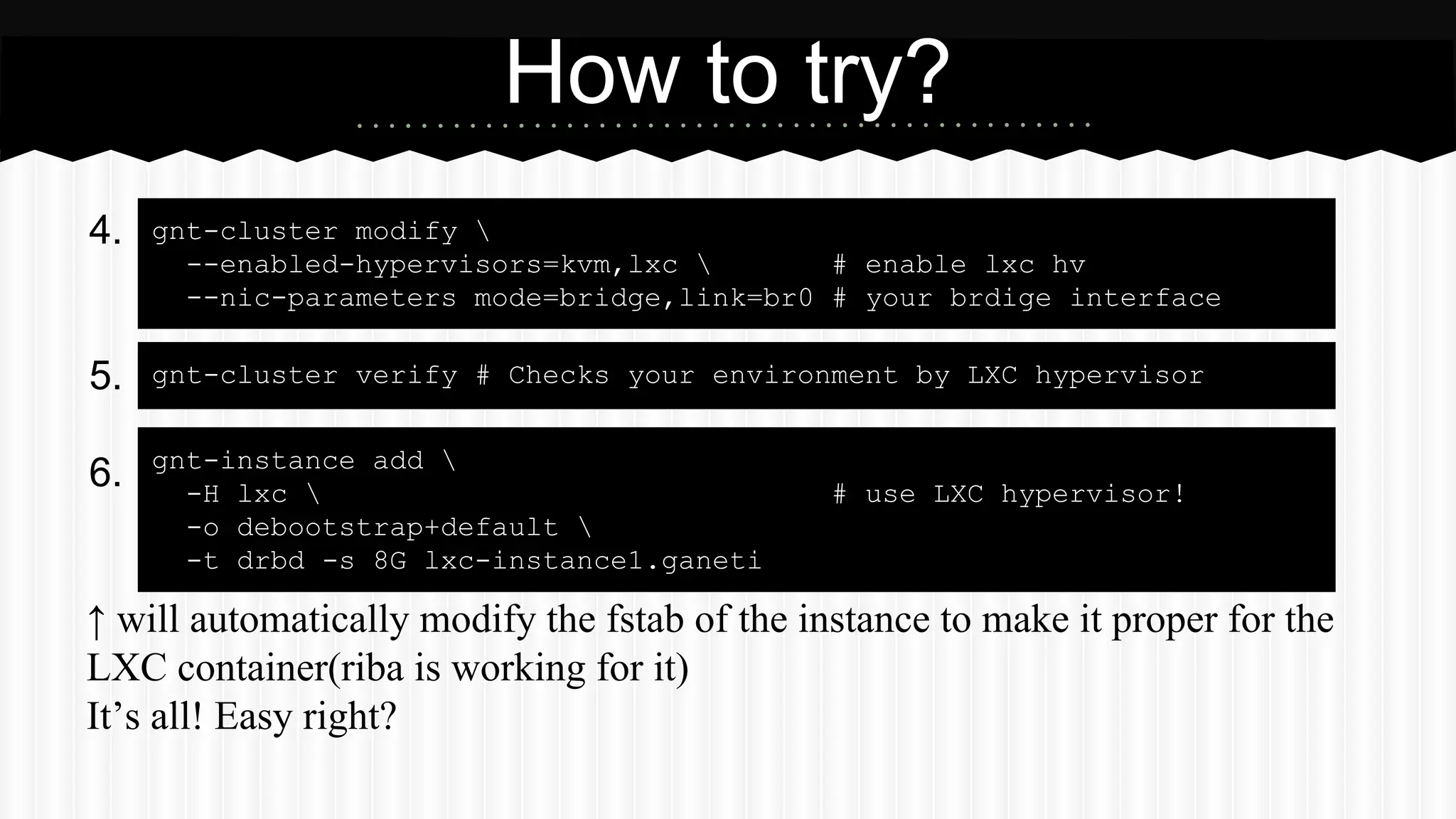
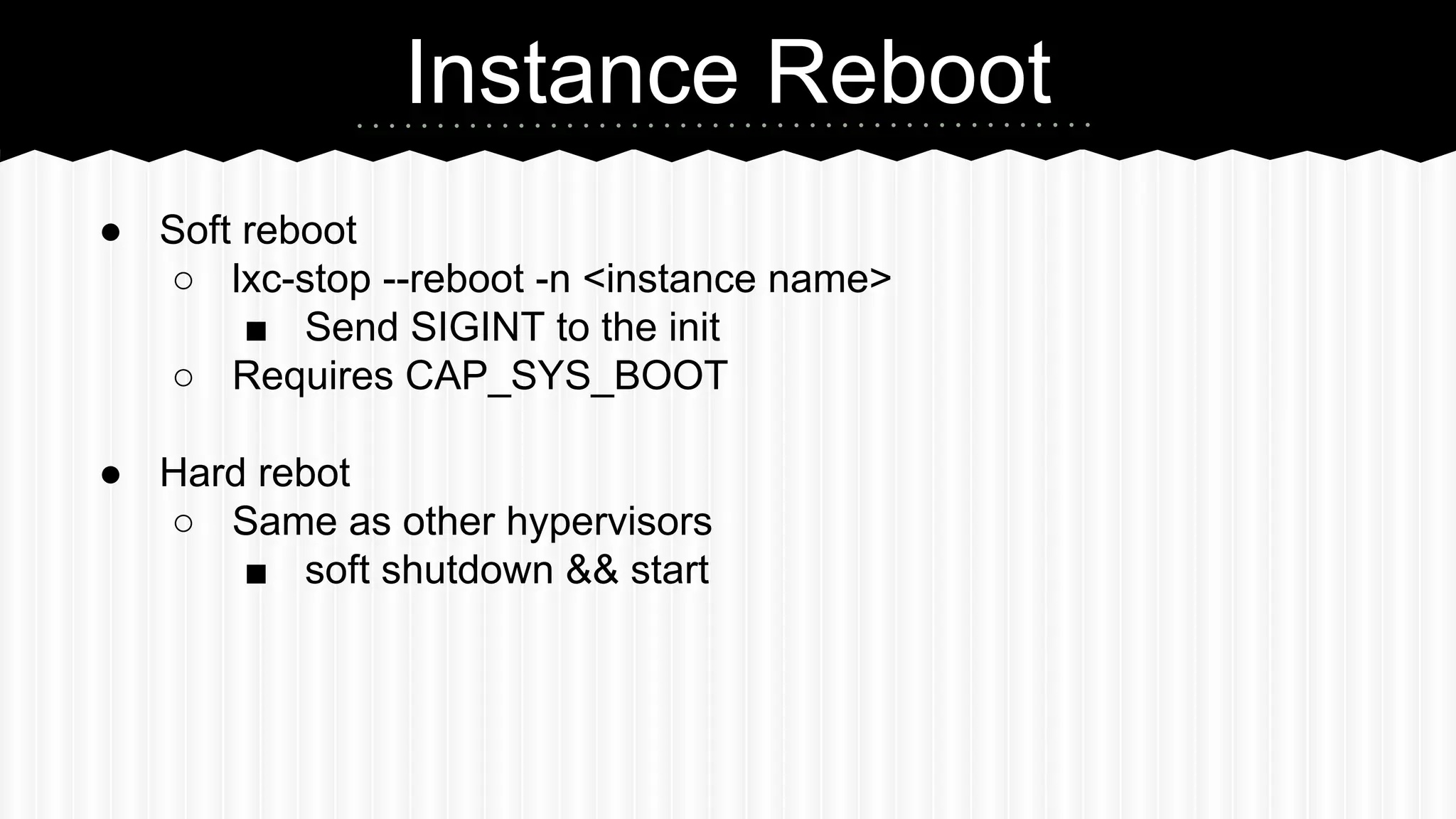
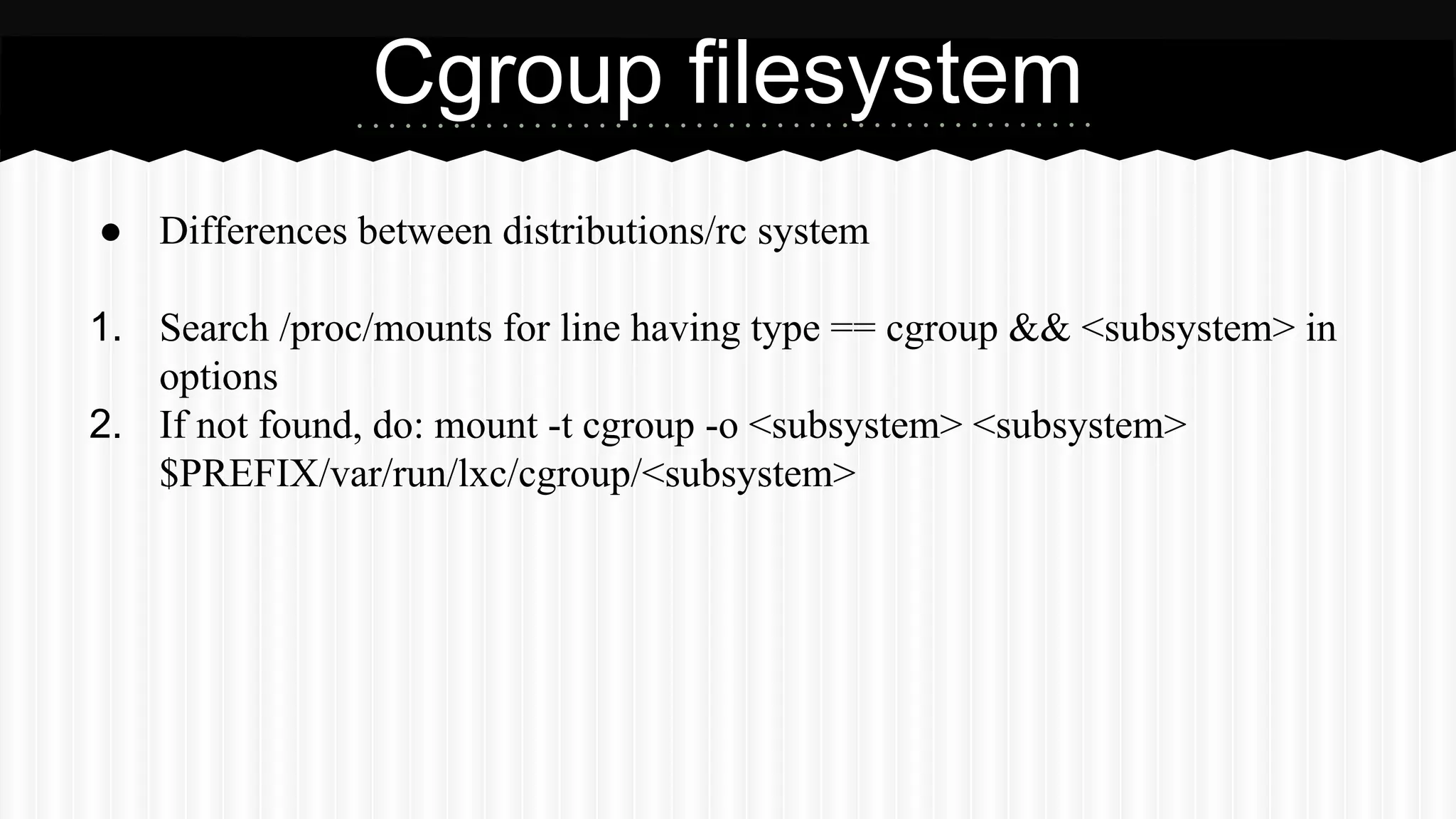
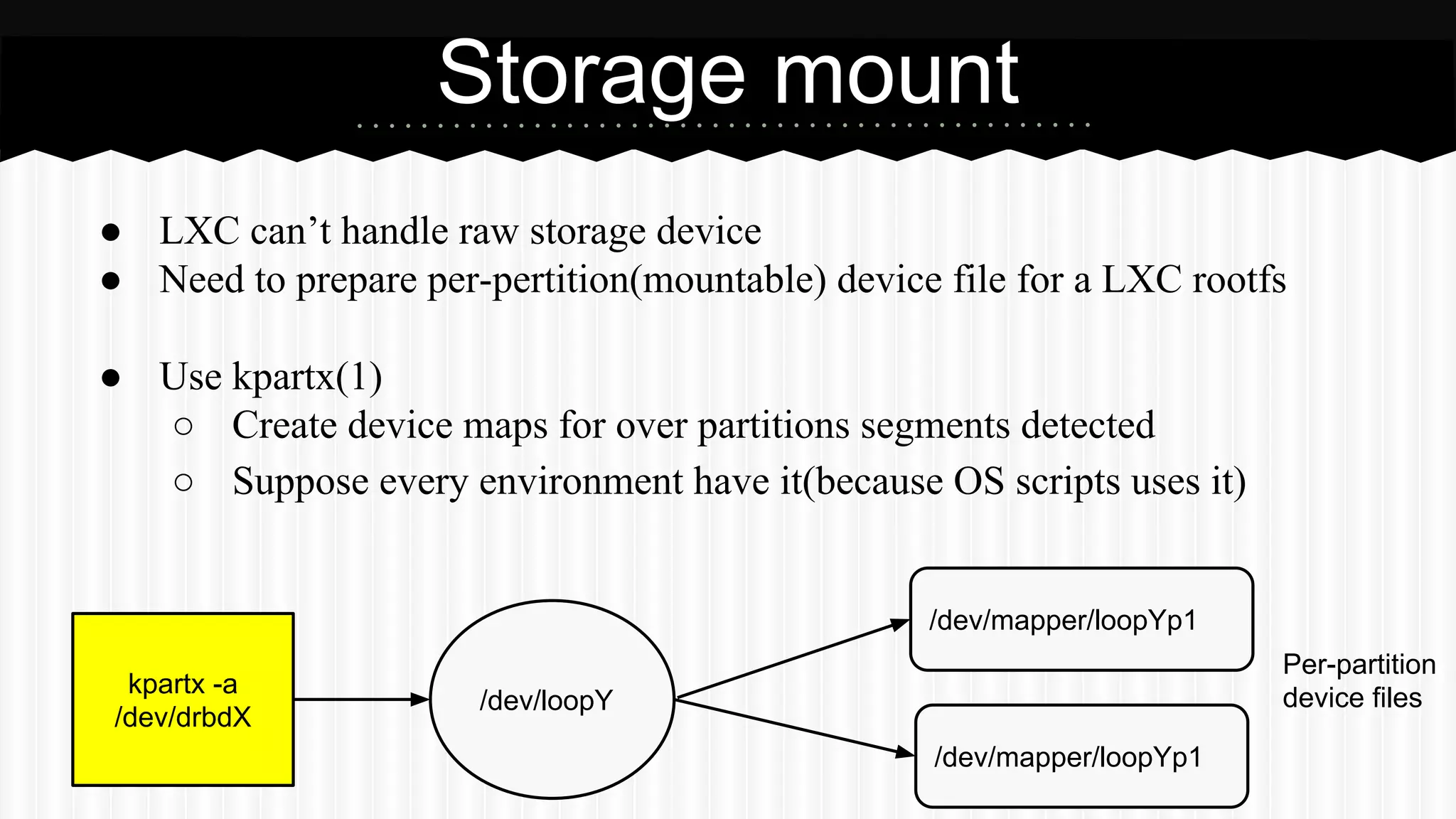
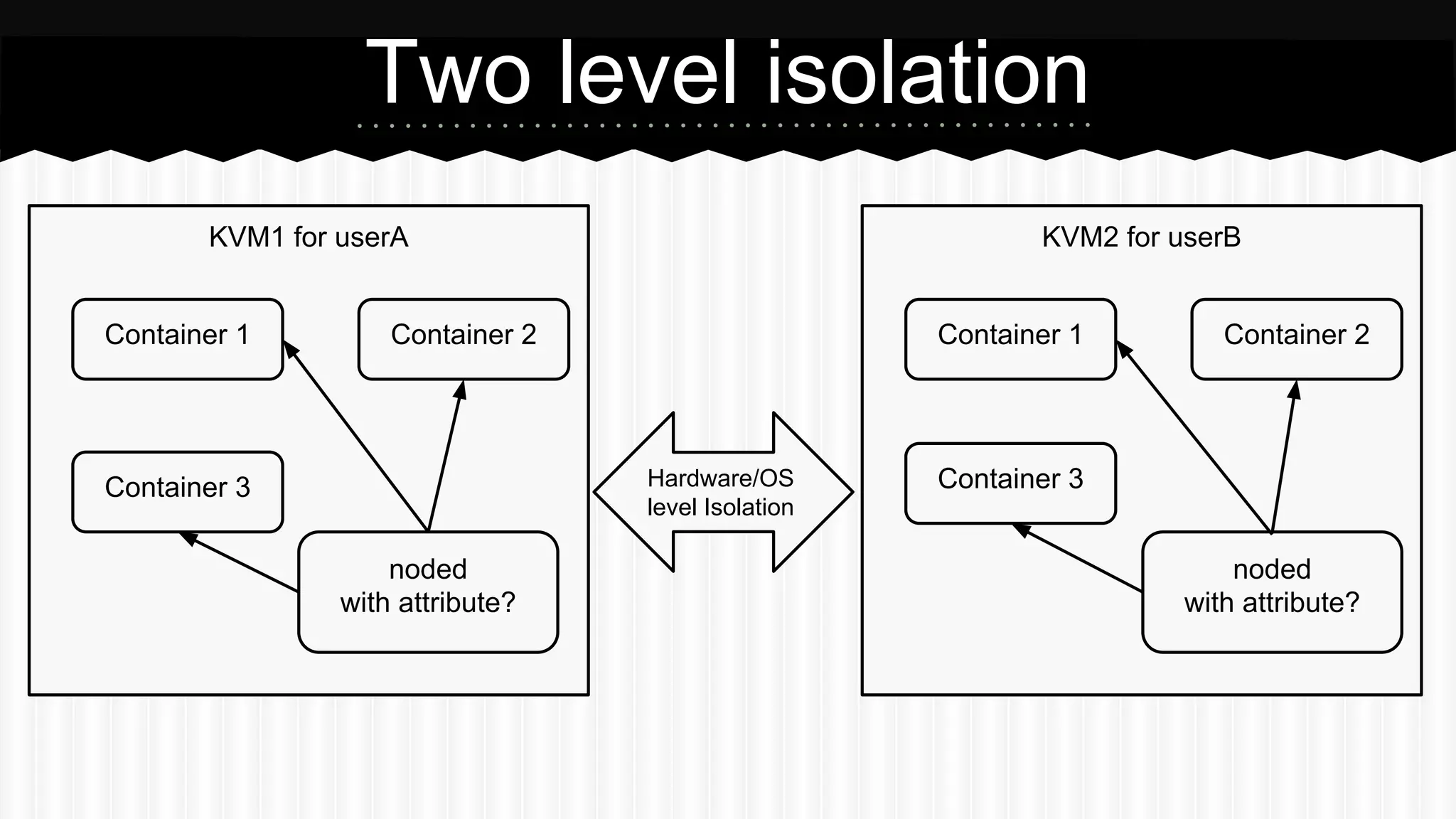
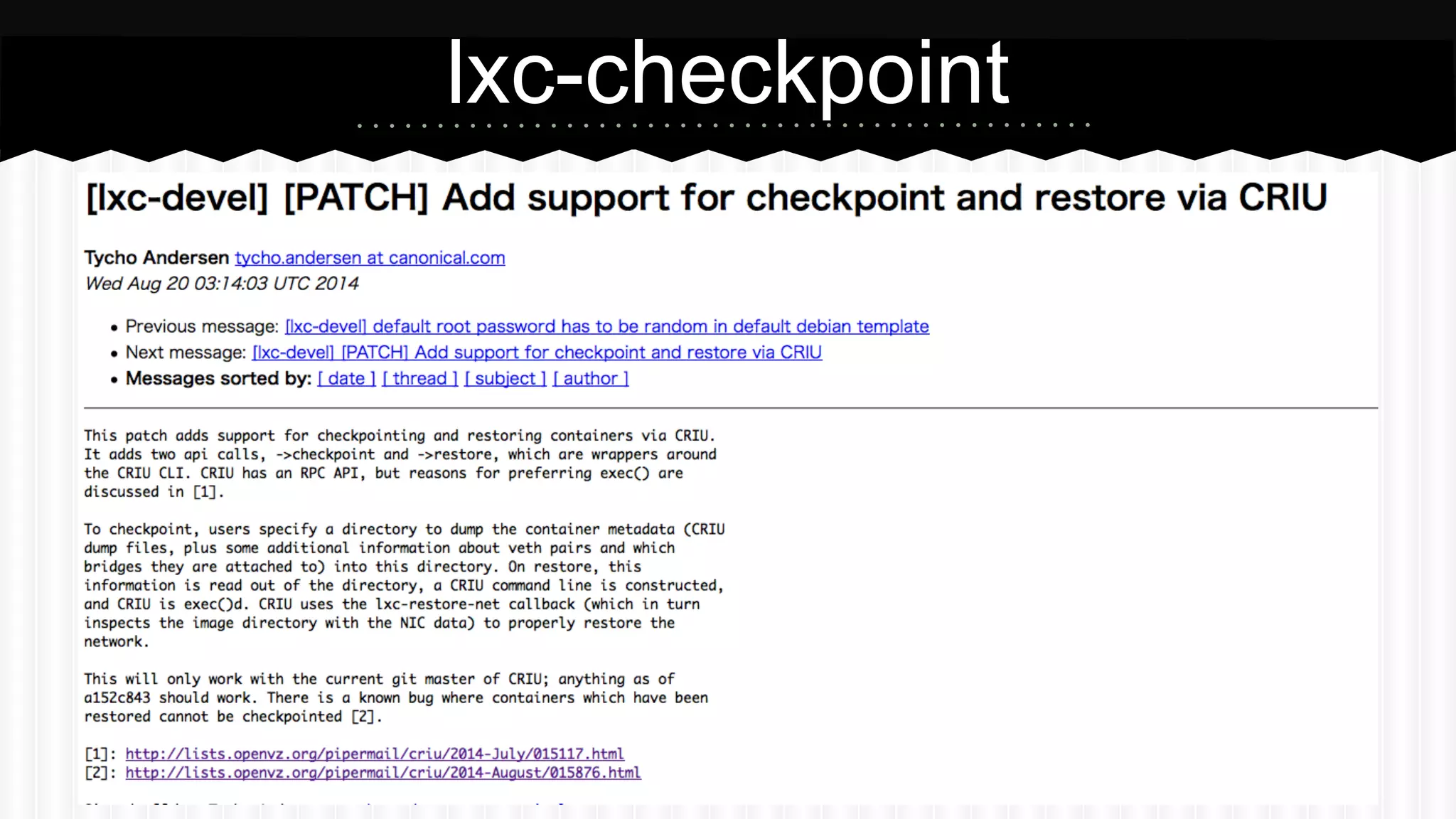
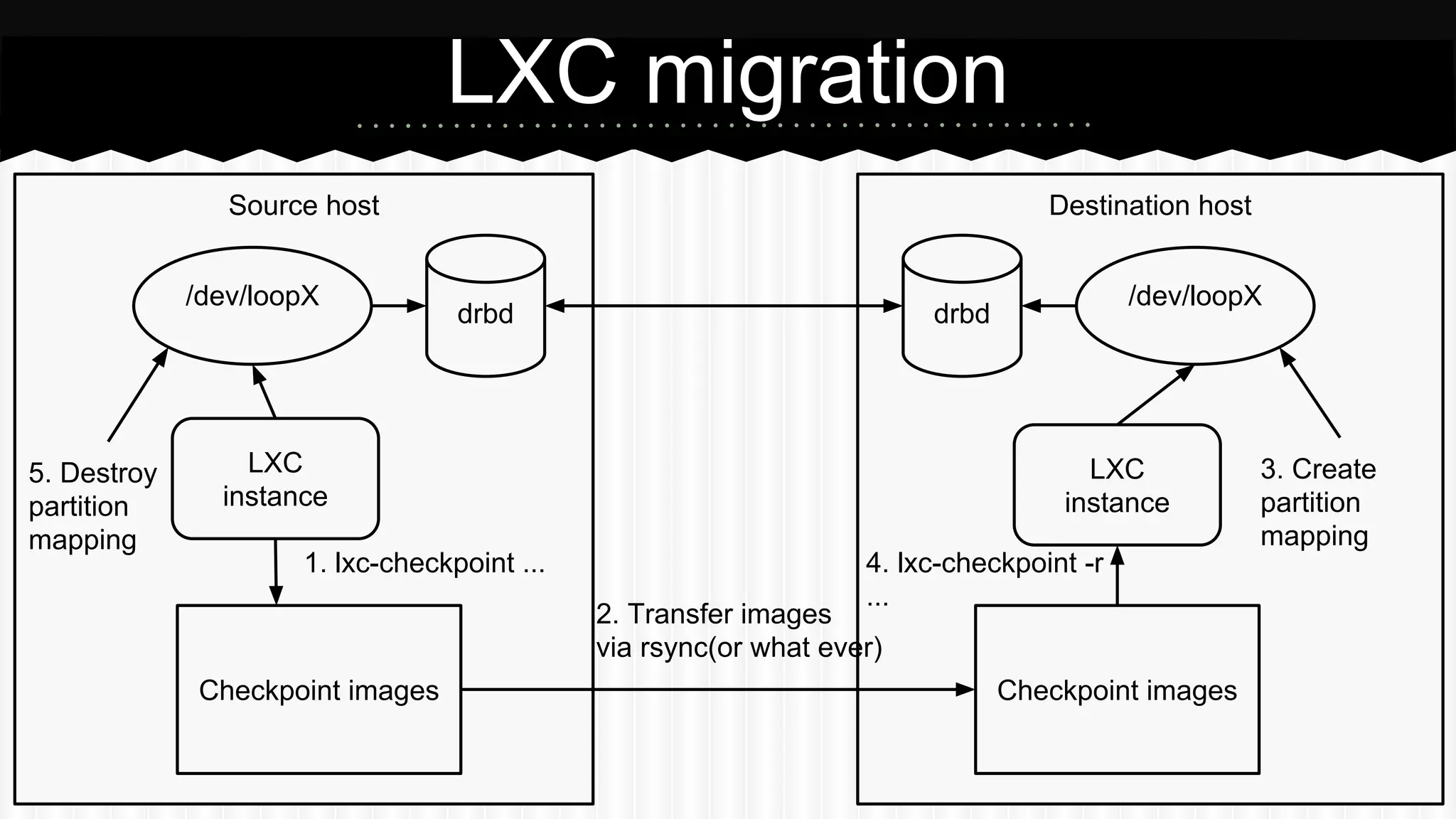
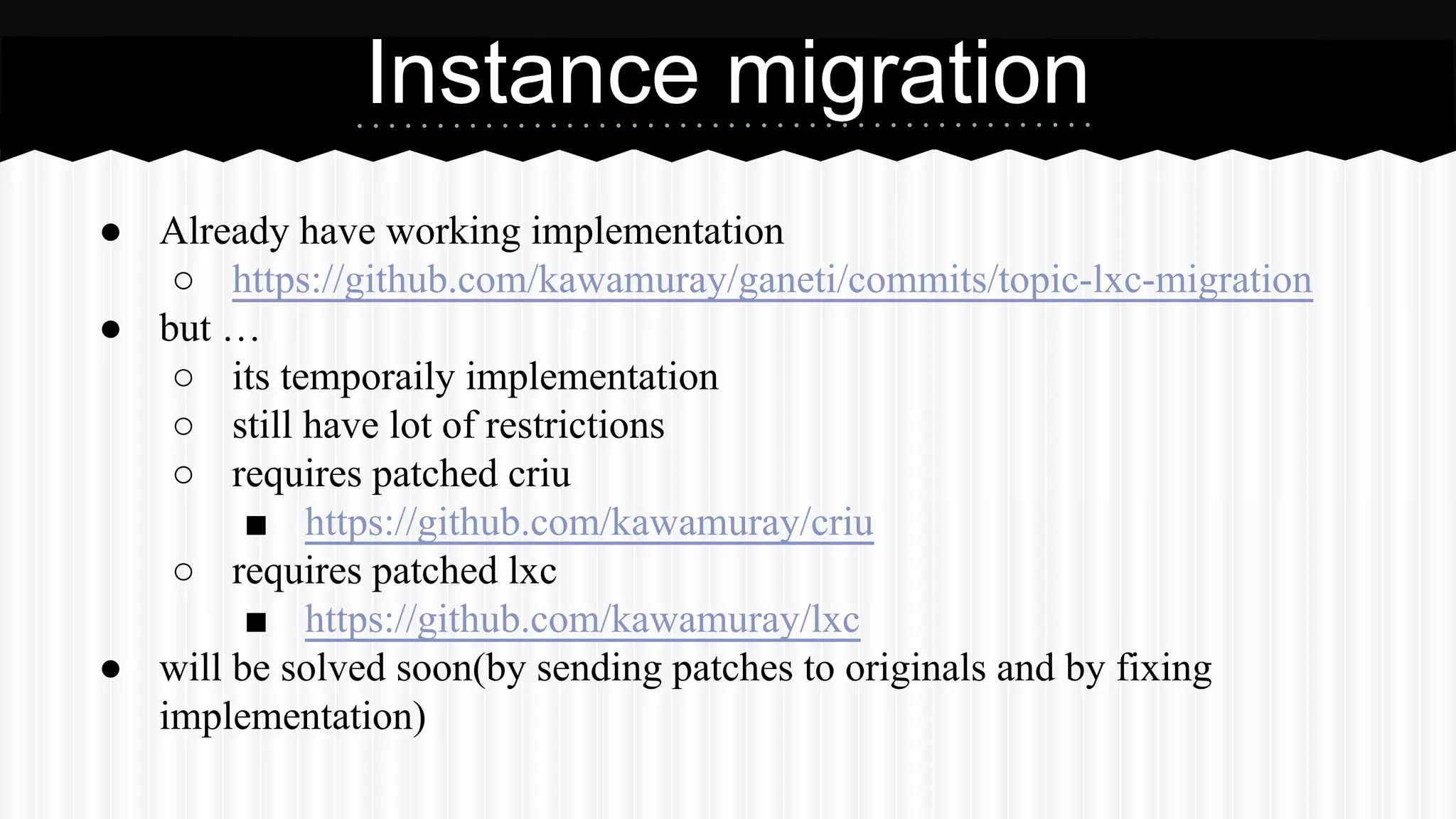
This document discusses improvements made to LXC container support in Ganeti through a Google Summer of Code project. Key areas worked on included fixing existing LXC integration, adding unit tests, setting up quality assurance, and adding features like migration. The project was mentored by Hrvoje Ribicic. Future work may include two-level isolation of containers within VMs and live migration of LXC instances.