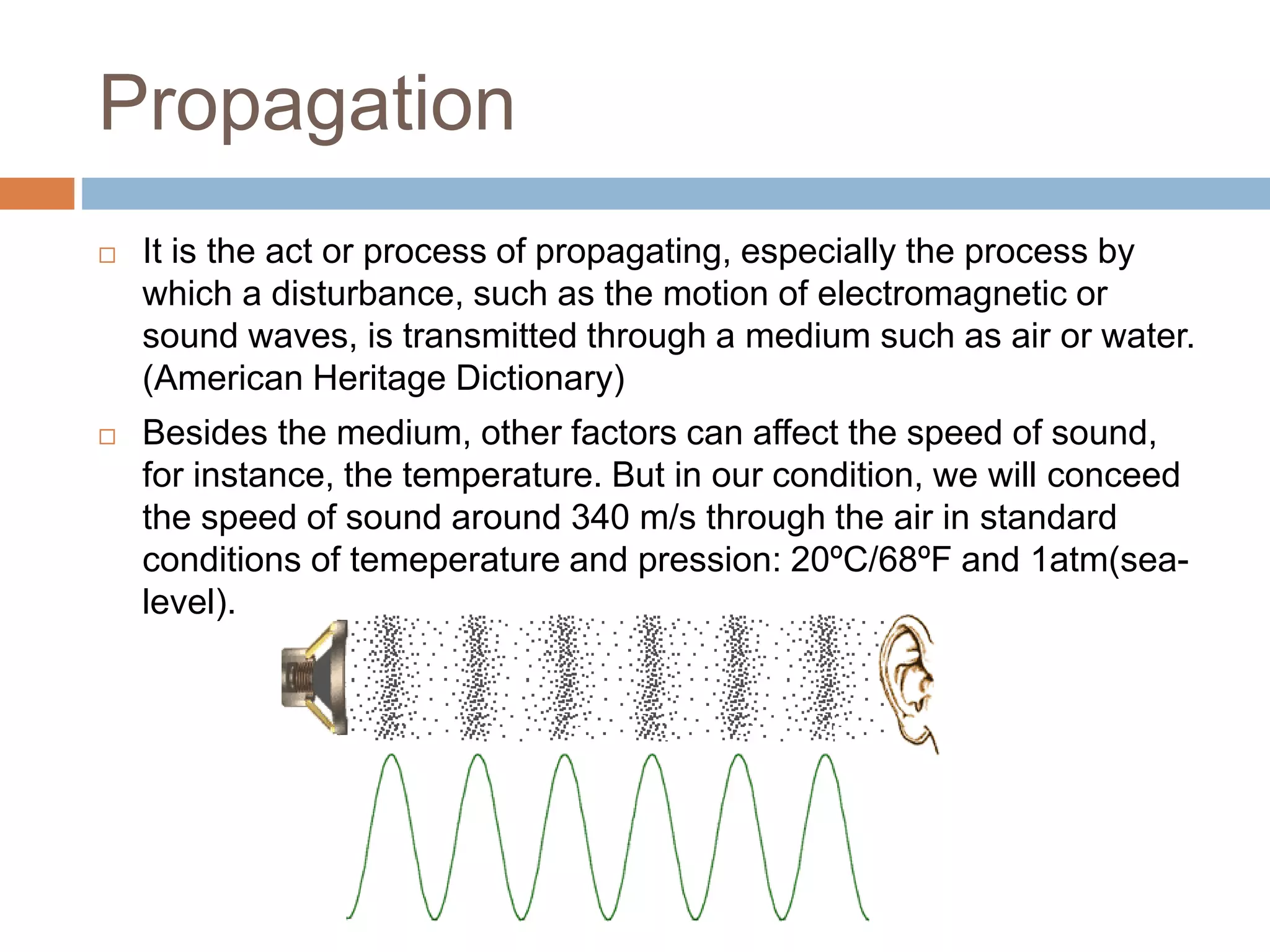
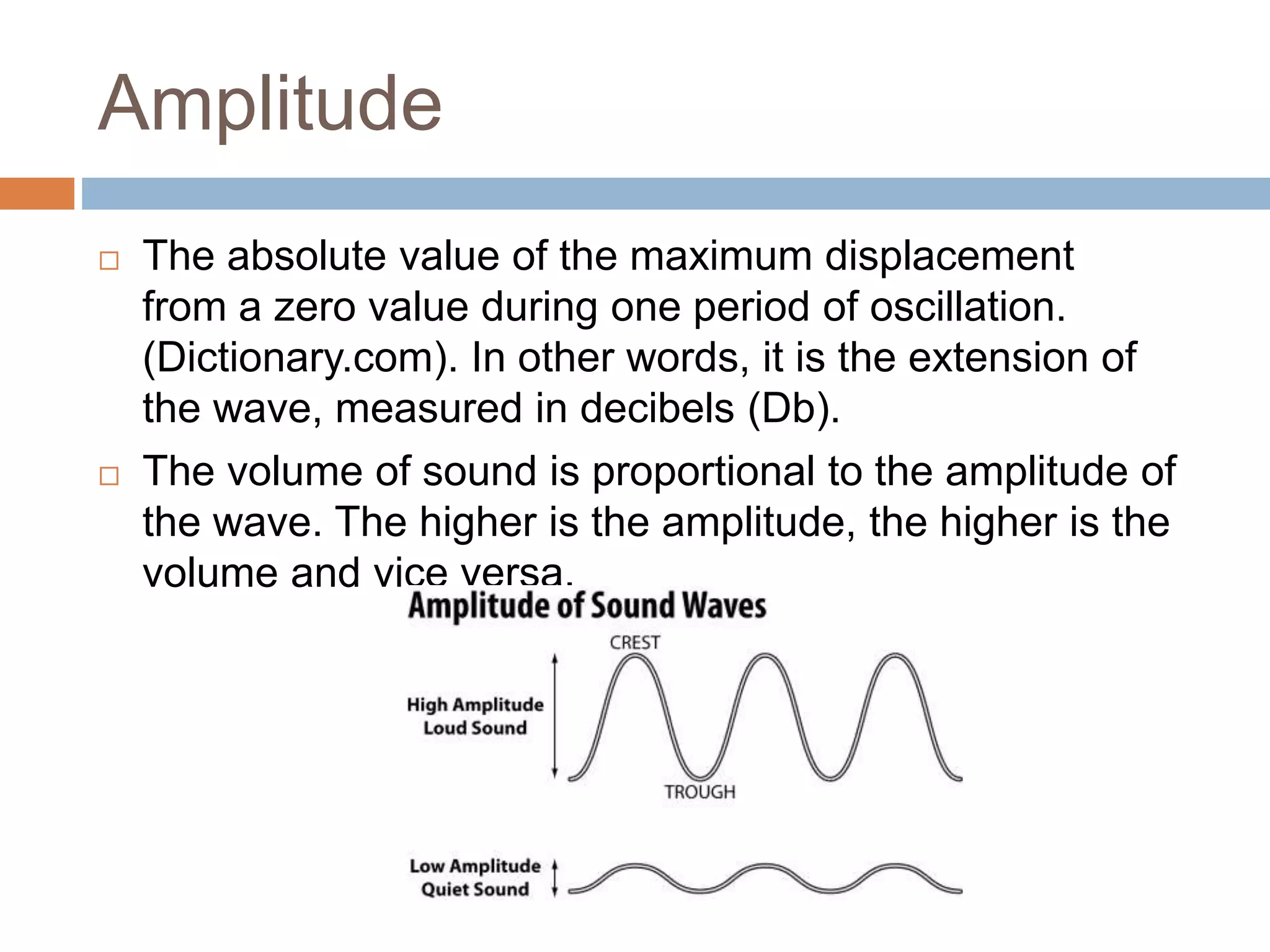
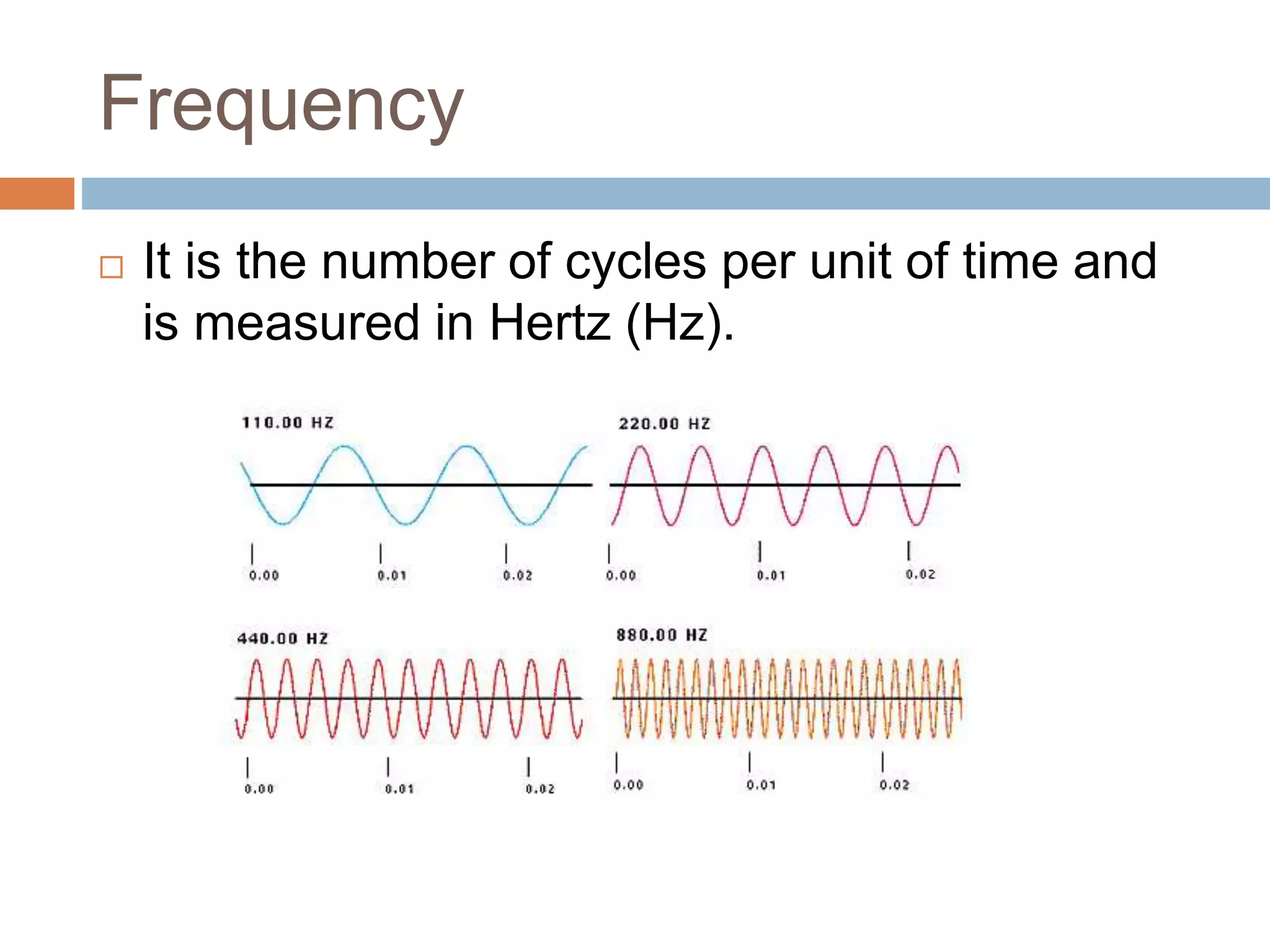
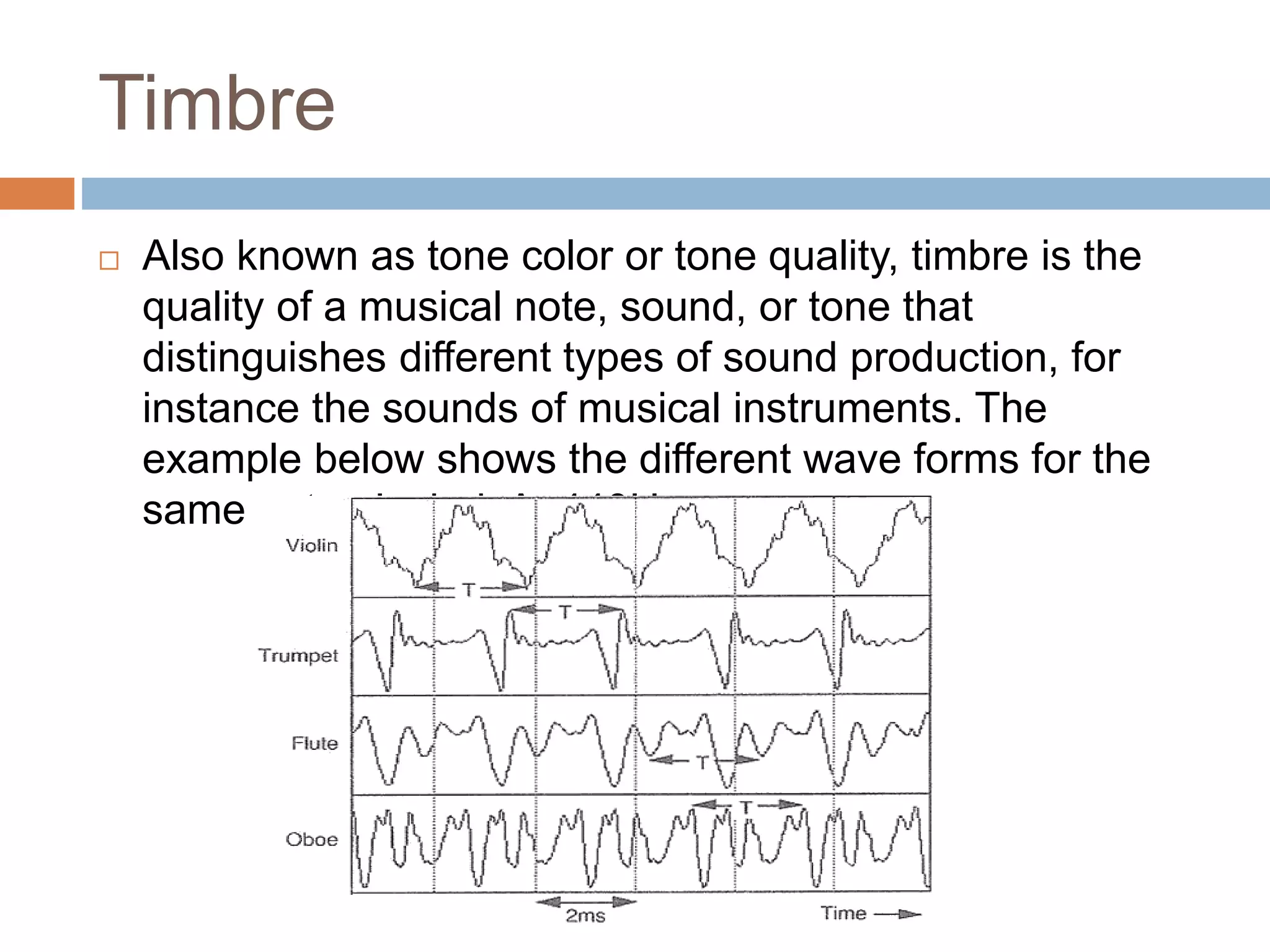
Luth Oliveira introduces the basic audio properties of propagation, amplitude, frequency, and timbre. Propagation refers to how sound travels through a medium like air or water. Amplitude represents the maximum displacement of a sound wave and is measured in decibels, with higher amplitudes relating to louder volumes. Frequency is the number of cycles per unit of time and is measured in Hertz. Timbre distinguishes different musical instrument sounds and refers to the unique tone color of each.