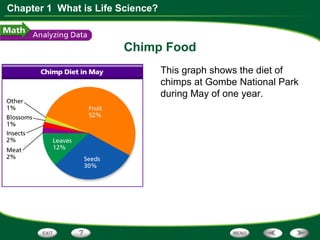
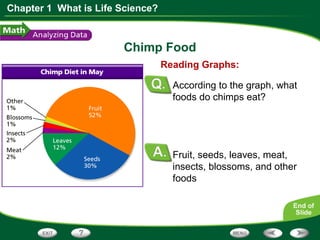
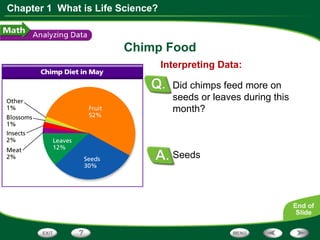
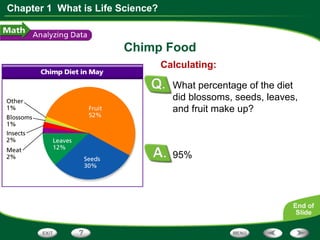
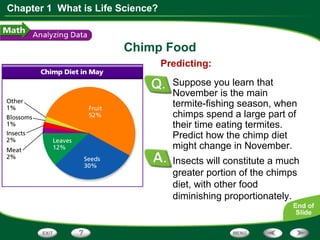
This document discusses the key skills used in life science: observing, inferring, predicting, classifying, and making models. It provides examples of each skill using Jane Goodall's observations of chimpanzees. It also includes a graph about chimp diets and questions to interpret the data, requiring skills like reading graphs, interpreting data, calculating percentages, and predicting based on evidence.