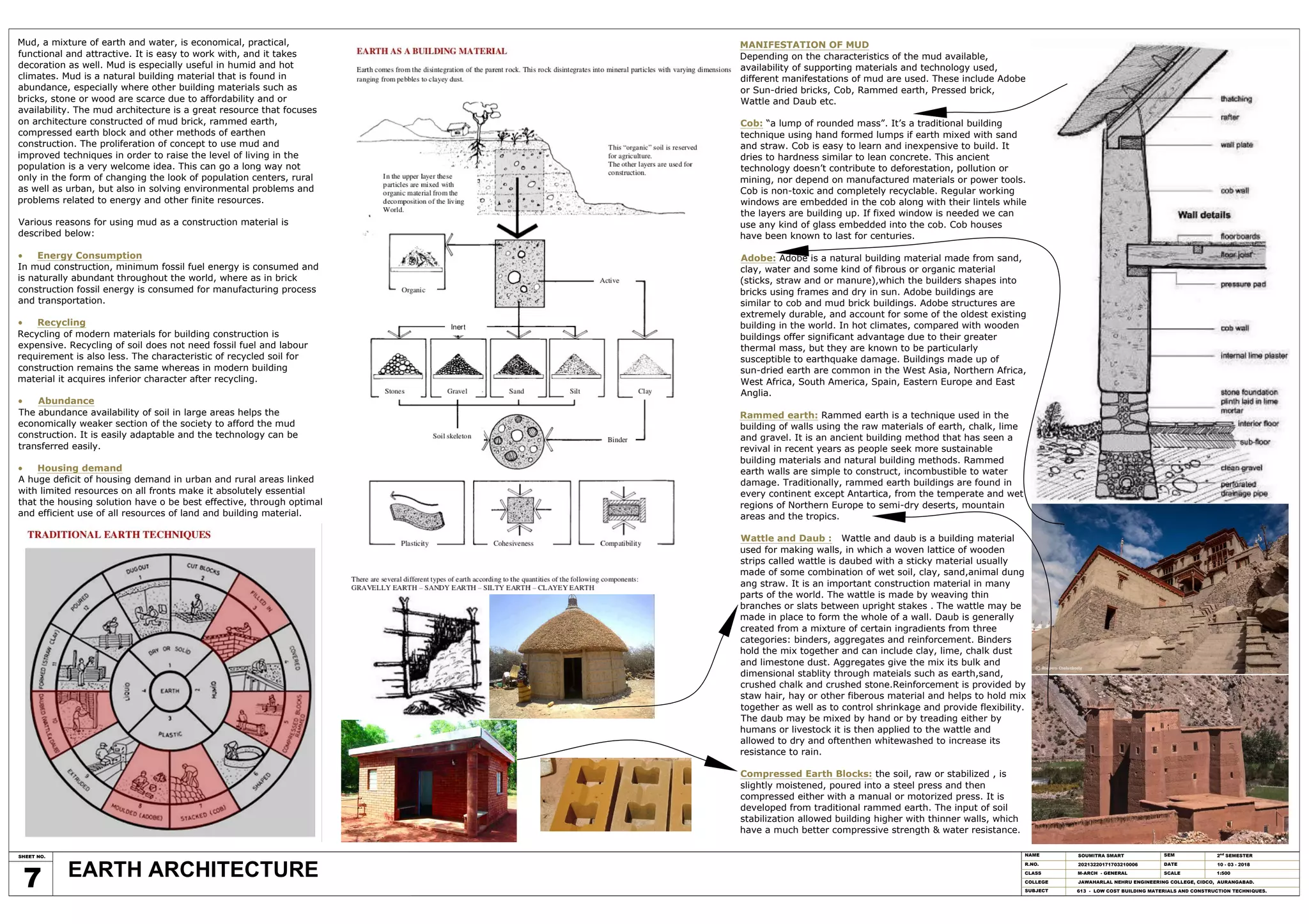
Mud is an economical and sustainable building material that is abundant worldwide. It has low energy needs and is easily recycled. Various mud construction techniques exist, including cob, adobe blocks, rammed earth, and wattle and daub. Cob involves forming mud and straw mixtures by hand into walls, while adobe uses sun-dried brick formed from clay, sand, straw and water. Rammed earth compacts earth, gravel and lime into strong walls using wooden forms. Wattle and daub uses a lattice of wooden strips called wattle covered in daub, a sticky mud-based plaster. Mud architecture provides affordable housing and helps address issues of resources, energy use and the environment.