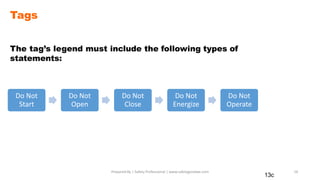
This document outlines lockout/tagout procedures for hazardous energy sources. It discusses identifying energy sources for machines, developing an energy control plan, and preventing injury from unexpected startup of equipment. The procedures cover servicing, maintenance, and normal operations. An energy control program includes authorized employees, affected employees, energy control procedures, training, and audits. Detailed steps are provided for preparing equipment for shutdown, isolating energy sources, applying lockout/tagout devices, releasing stored energy, verifying lockouts, and restoring energy. Requirements are outlined for lockout devices, tags, group lockouts, and removing locks.