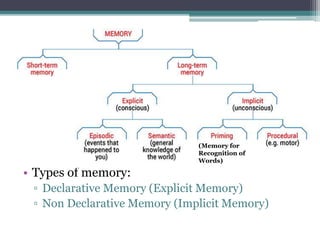
The document summarizes key aspects of memory from a psychological perspective. It discusses the physiology of memory including the role of the hippocampus and synaptic plasticity in memory formation. It also outlines several theories of memory like the information processing theory. The document elaborates on the organization and retrieval of long-term memory as well as factors that can lead to forgetting. It concludes by examining different types of amnesia including psychological amnesia from childhood and dreams as well as biological amnesia from conditions like Alzheimer's disease.