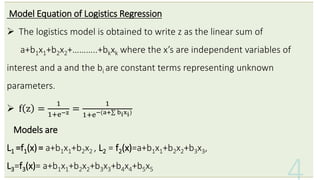
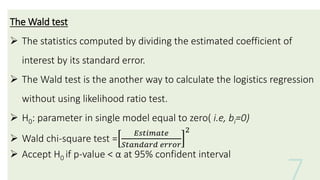
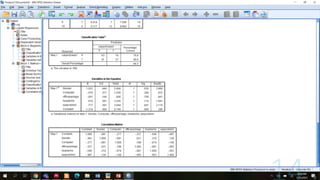
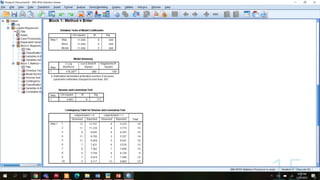
This document provides an overview of logistic regression analysis. It discusses key concepts like the logistic regression model equation, maximum likelihood estimation for model fitting, likelihood ratio and Wald tests for model evaluation, odds ratios, and the Hosmer-Lemeshow test for goodness of fit. Examples of binary, multinomial, and ordinal logistic regression are provided. Steps for conducting logistic regression in SPSS are outlined. References for further reading on logistic regression techniques are included.