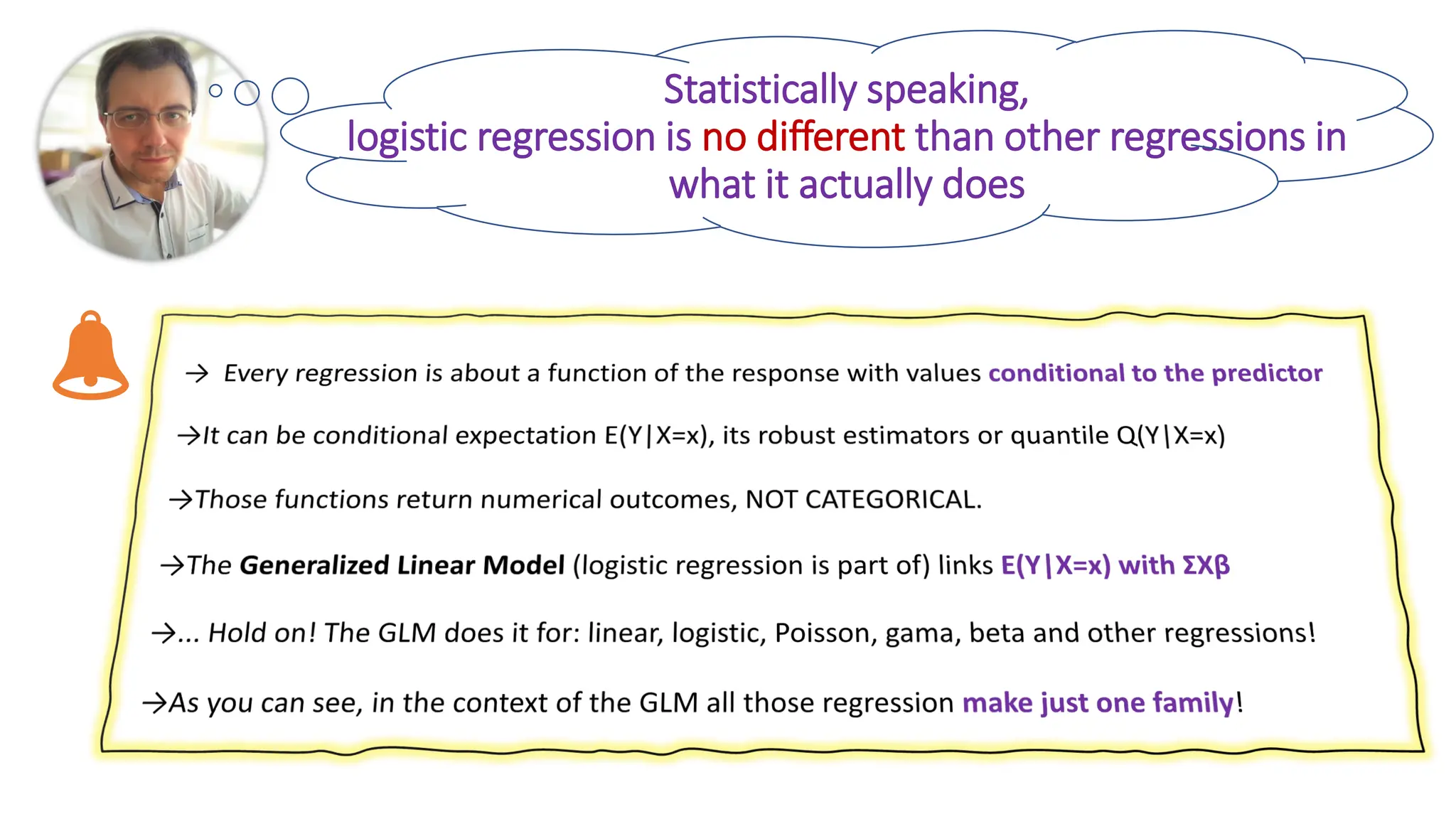
The document discusses the debate surrounding the classification of logistic regression as a regression model versus a classifier, emphasizing its historical and practical use for regression in various fields. It critiques the misrepresentation of logistic regression in machine learning contexts where it is termed a 'logistic classifier,' despite its foundational identity as a regression methodology. The author argues that this mislabeling undermines the established use of logistic regression among statisticians and researchers in experimental settings.













![➡️ Assessment (= direction, magnitude, inference) of the impact of model predictors on the response expressed as: log-odds, odds-
ratios or probability (via predicted means or LS-means or marginal effects), which covers:
➡️ Assessment of the marginal effects of the model predictors for the GLM (non-identity link)
➡️ Inference on the main effects, exploration of interactions for categorical variables = AN[C]OVA
➡️ Inference on the simple effects of interest (via contrasts), both planned and ad hoc.
➡️ Testing for trends in proportions (linear/quadratic/cubic, etc)
➡️ Extending the classic statistical tests of proportions, odd-ratios and stochastic superiority (Wald's and Rao z test, chi2, Cochran-
Armitage, Breslow-Day, Cochran-Mantel-Haenszel, McNemar, Cochran Q, Friedman, Mann-Whitney (Wilcoxon)) for: multiple
variables and their interactions, numerical covariates;
➡️ Bonus: model-based approach allows one to employ advanced parametric adjustment for multiple comparisons via multivariate t
distribution, adjust numerical covariates, employ time-varying covariates, account for repeated and clustered observations and more!
➡️ Direct probability estimator used to implement the IPW - inverse probability weighting and propensity score matching algorithms
➡️ Assessment of the MCAR pattern of missing observations
More precisely speaking…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/logisticregressionisaregression-231221031614-2dfa6491/75/Logistic-regression-vs-logistic-classifier-History-of-the-confusion-and-the-role-of-Logistic-Regression-in-experimental-research-15-2048.jpg)





![There are so many members of the Logistic Regression family!
✅ Binary Logistic Regression = binomial regression with logit link, case of the Generalized Linear Model, modelling the % of successes.
✅ Multinomial Logistic Regression (MLR) = if we deal with a response consisting of multiple non-ordered classes (e.g. colours).
✅ Nested MLR - when the classes in MLR are related
✅ Ordinal LR (aka Proportional Odds Model) = if we deal with multiple ordered classes, like responses in questionnaires, called Likert
items, e.g. {bad, average, good}. The OLR is a generalization of the Mann-Whitney (-Wilcoxon) test, if you need a flexible non-parametric
test, that: a) handles multiple categorical variables, b) adjusts for numerical covariates (like ANCOVA)
✅ Generalized OLR = Partial Proportional Odds M. when the proportionality of odds doesn't hold.
✅ Alternating Logistic Regression = if we deal with correlated observations, e.g. when we analyse repeated or clustered data. We
have 3 alternatives: mixed-effect LR, LR fit via GEE (generalized estimating equations), or alternatively, the ALR. ALR models the
dependency between pairs of observations by using log odds ratios instead of correlations (like GEE). It handles ordinal responses.
✅ Fractional LR = if we deal with a bounded range. Typically used with [0-100] percentages rather than just [TRUE] and [FALSE]. More
flexible than beta reg., but not as powerful as the simplex reg. or 0-1-inflated beta r.
✅ Logistic Quantile Regression - application as above.
✅ Conditional LR = if we deal with stratification and matching groups of data, e.g. in observational studies without randomization, to
match subjects by some characteristics and create homogenous "baseline".](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/logisticregressionisaregression-231221031614-2dfa6491/75/Logistic-regression-vs-logistic-classifier-History-of-the-confusion-and-the-role-of-Logistic-Regression-in-experimental-research-21-2048.jpg)








