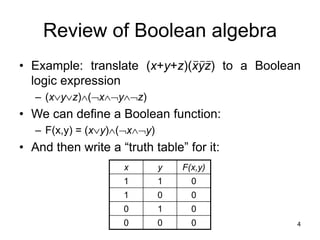
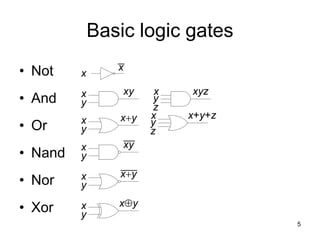
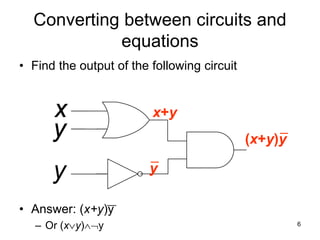
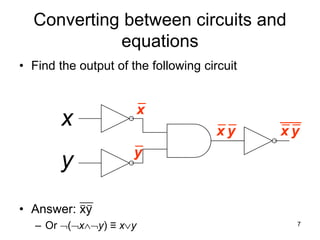
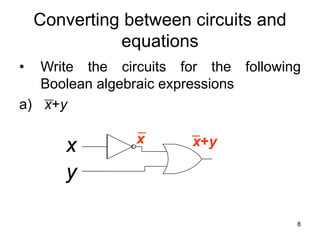
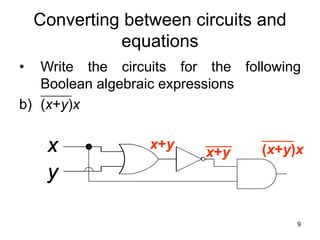
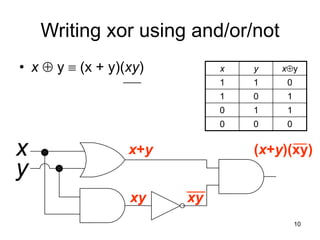
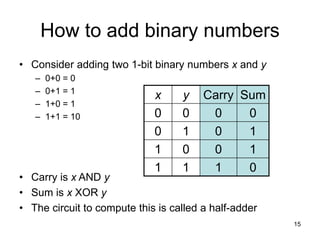
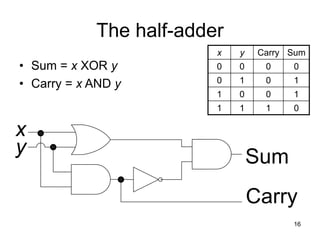
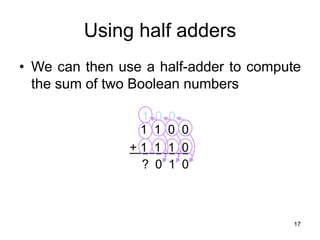
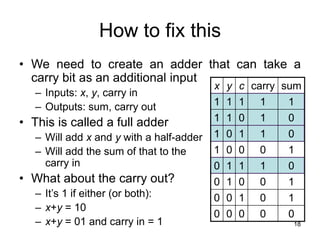
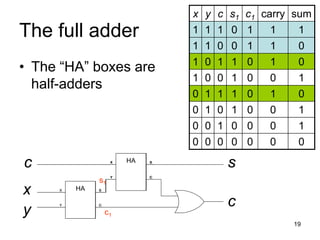
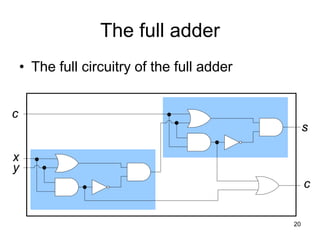
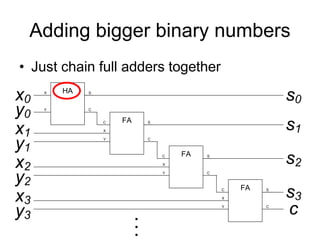
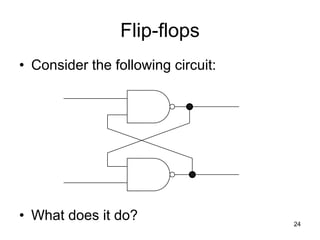
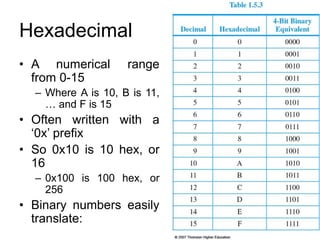
The document provides an overview of Boolean algebra and logic gates. It discusses the basic logic gates like NOT, AND, OR, NAND, NOR, and XOR. It explains how to convert between Boolean logic expressions and logic circuits. It also covers adding binary numbers using half adders and full adders, and how memory is implemented using flip-flops.