This document discusses key concepts in ethics including:
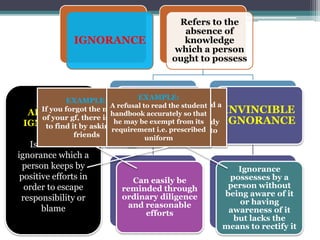
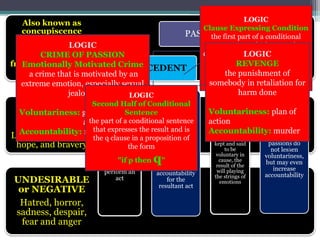
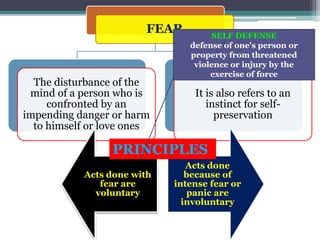
1. Modifiers of human acts refer to factors like ignorance, passions, fear, and habits that can increase or decrease the accountability of a person's actions.
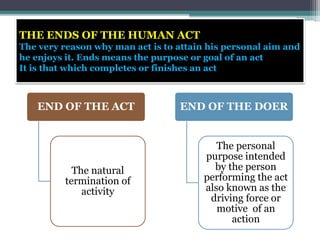
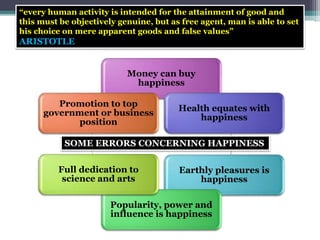
2. The ends or purposes of human acts are important in ethics - acts are aimed at achieving some goal or purpose. Common errors involve believing things like money or popularity constitute happiness.
3. Determinants of morality include aspects of the act itself, the motive or purpose, and surrounding circumstances that contribute to an act's nature and accountability. Intrinsic acts are wrong by their very nature while extrinsic acts are not inherently evil but still prohibited.