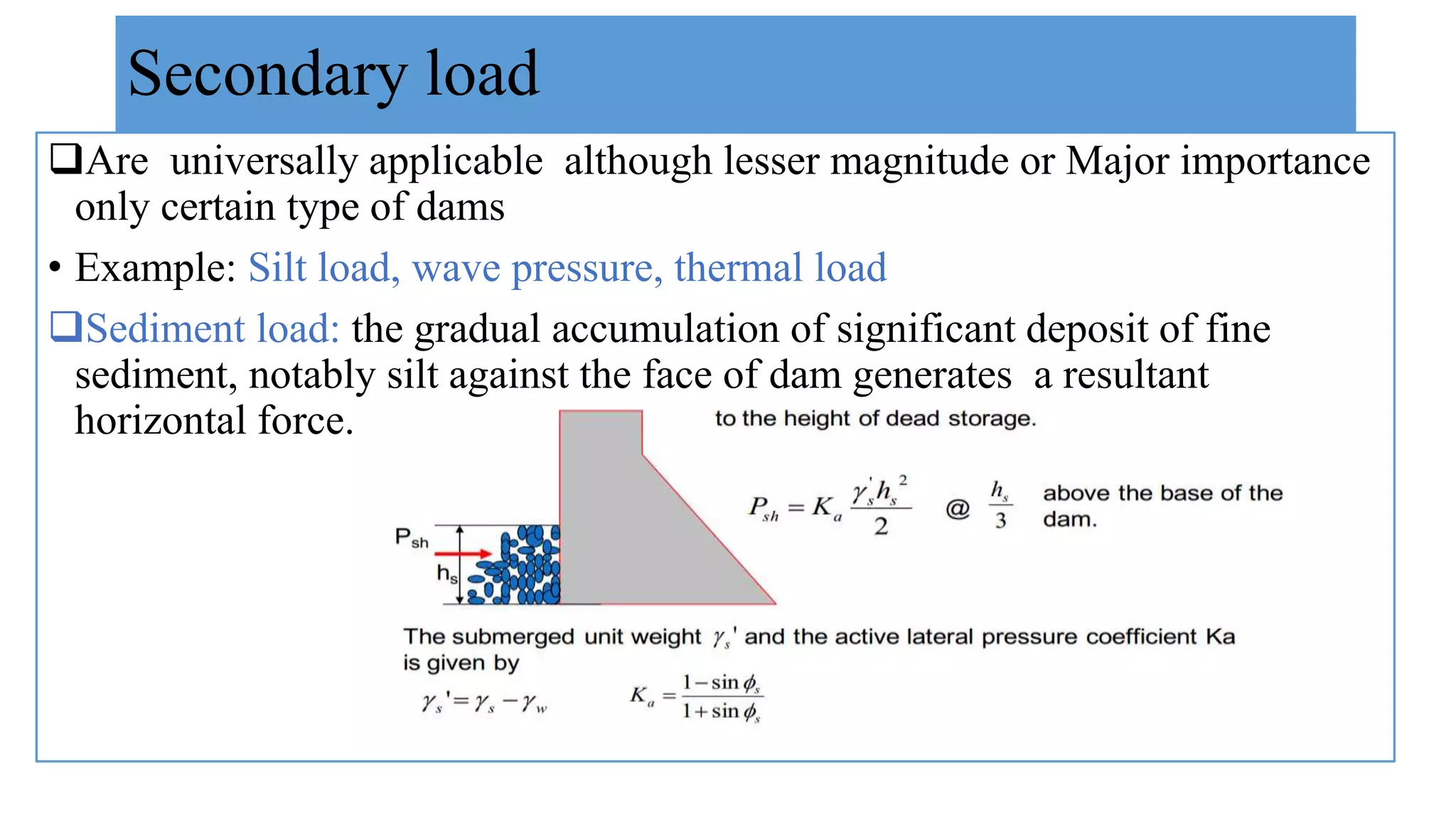
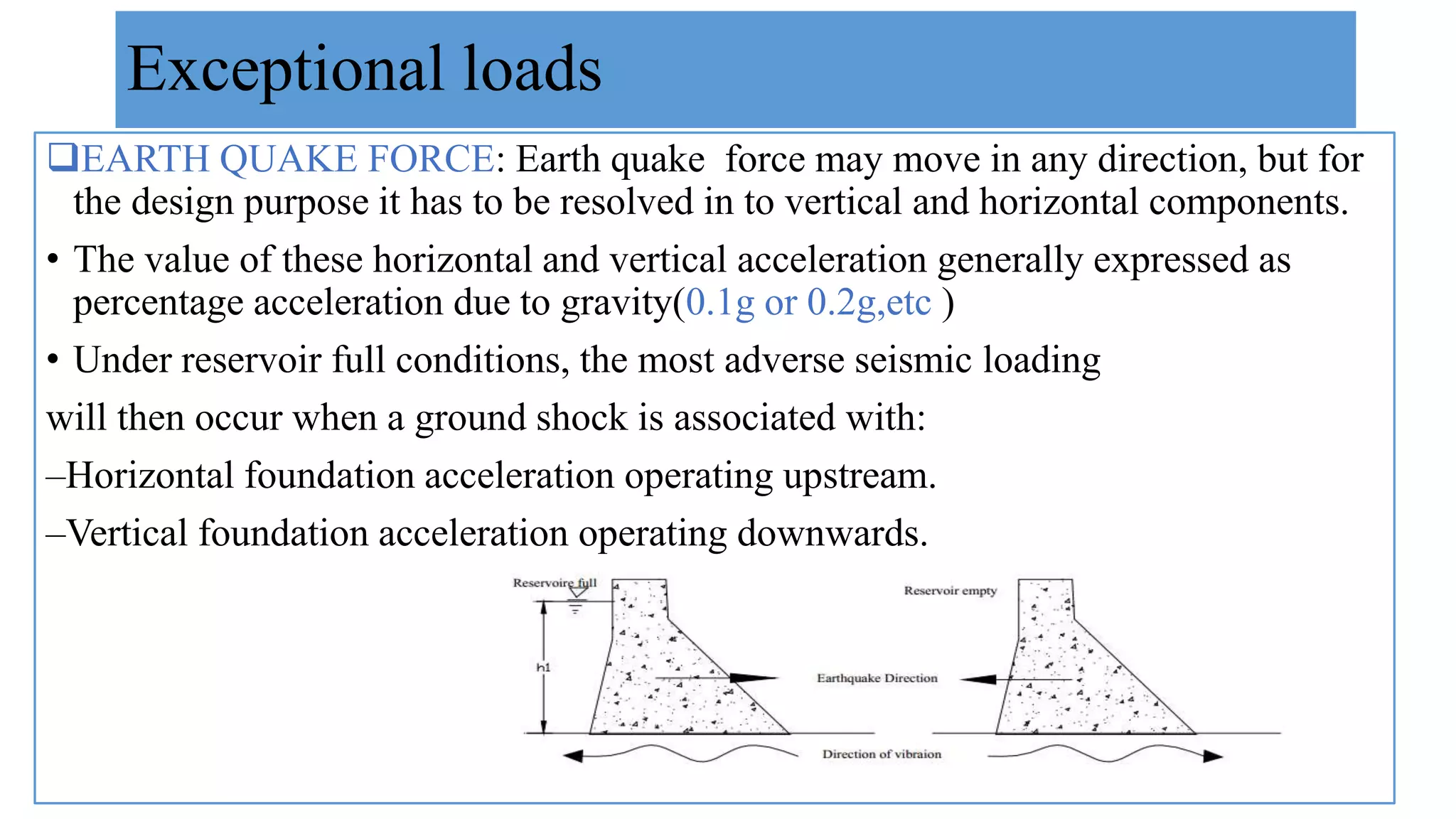
This document discusses the various loads that act on a gravity dam. It identifies primary loads such as water load, self-weight, and uplift pressure as the major loads that are important for all dam types. Secondary loads like silt load, wave pressure, thermal load are also discussed. Exceptional loads include earthquake force, which exerts both vertical and horizontal components that must be designed for. The document provides details on calculating and accounting for these various dam loads in the planning and design of gravity dams.