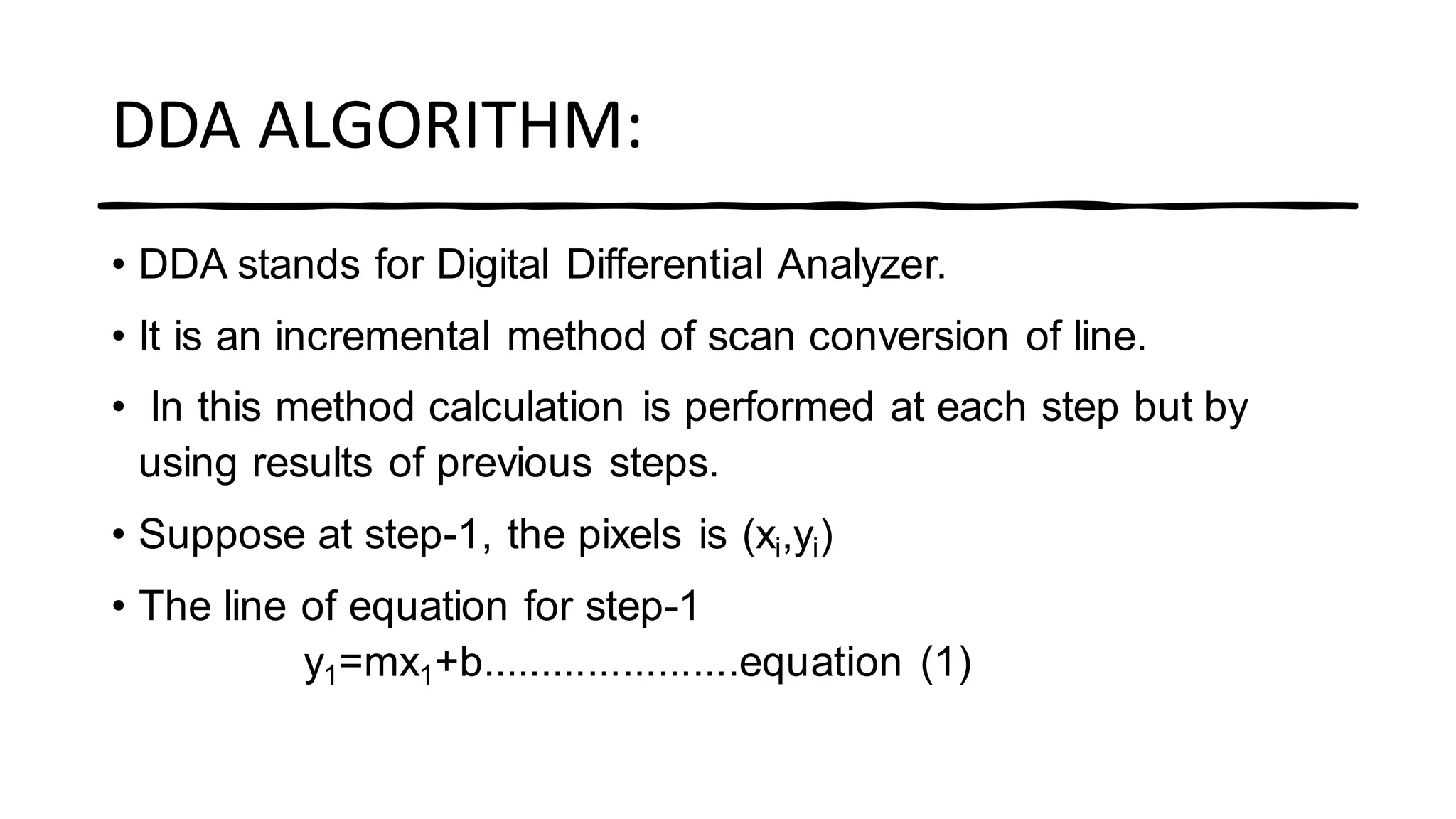
This document describes the Digital Differential Analyzer (DDA) algorithm for drawing lines on a digital display. It works by calculating the change in x and y coordinates between points in small incremental steps, rather than using the full line equation. The algorithm takes points (x1,y1) and (x2,y2) as input, calculates the change in x and y, and then increments x and y by those amounts in a loop until it reaches the endpoint. It handles horizontal, vertical and diagonal lines efficiently with only additions and can detect when it has drawn the same point twice to avoid duplication.