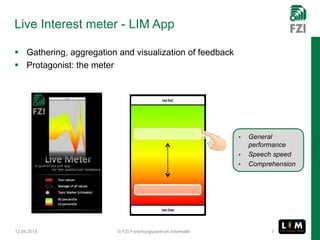
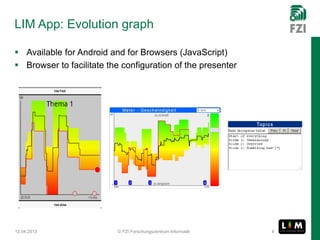
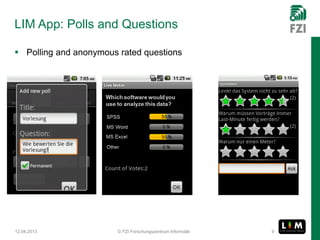
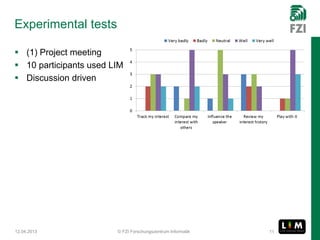
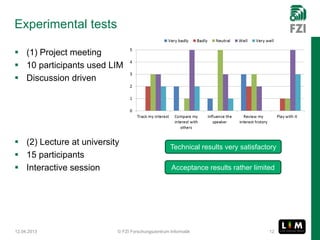
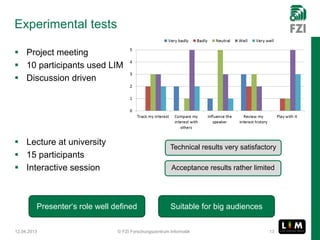
The document summarizes research on the Live Interest Meter (LIM) app, which collects feedback from audiences during presentations to support reflective learning. The LIM app gathers, aggregates, and visualizes audience feedback on an "interest meter." Experimental tests of the app at project meetings and university lectures showed it was technically satisfactory but acceptance was limited. A user study provided guidance to refine the use case and guide further development, showing openness to using quantified feedback for reflection but concerns about distraction. Ongoing work aims to improve usability, add reflection support after presentations, and evolve the approach to be more collaborative.
















![Theoretical background
[1] Applying Quantified Self Approaches to Support Reflective Learning. Verónica Rivera-Pelayo, Valentin Zacharias, Lars Müller,
Simone Braun. Learning Analytics and Knowledge 2012 (LAK 2012), Vancouver, Canada
[2] A Framework for Applying Quantified Self Approaches to Support Reflective Learning. Verónica Rivera-Pelayo, Valentin
Zacharias, Lars Müller, Simone Braun. IADIS International Conference on Mobile Learning (Mlearning 2012), Berlin, Germany
12.04.2013 © FZI Forschungszentrum Informatik 24](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lak2013riveraupload-130411002136-phpapp02/85/Live-Interest-Meter-Learning-from-Quantified-Feedback-in-Mass-Lectures-24-320.jpg)

![ARS and Clickers
[1] M. Akbari, G. Böhm, and U. Schroeder. Enabling communication and feedback in mass
lectures. In ICALT, pages 254{258, 2010.
[2] M. Bonn, S. Dieter, and H. Schmeck. Kooperationstools der Notebook Universität Karlsruhe
(TH). In Mobiles Lernen und Forschen, pages 63-71. Klaus David, Lutz Wegener (Hrsg.),
November 2003.
[3] J. E. Caldwell. Clickers in the large classroom: Current research and Best-Practice tips. CBE
Life SciEduc, 6(1):9-20, Mar. 2007.
[4] D. Duncan and E. Mazur. Clickers in the Classroom: How to Enhance Science Teaching Using
Classroom Response Systems. Pearson Education, 2005.
[5] J. Hadersberger, A. Pohl, and F. Bry. Discerning actuality in backstage - comprehensible
contextual aging. In EC-TEL, volume 7563 of Lecture Notes in Computer Science, pages 126-
139. Springer, 2012.
[6] D. Kundisch, P. Herrmann, M. Whittaker, M. Beutner, G. Fels, J. Magenheim, W. Reinhardt, M.
Sievers, and A. Zoyke. Designing a Web-Based Application to Support Peer Instruction for Very
Large Groups. In ICIS '12, Research in Progress, Orlando, USA, December 2012.
[7] G. Rubner. mbclick - an electronic voting system that returns individual feedback. In WMUTE,
pages 221-222. IEEE, 2012.
[8] A. Wessels, S. Fries, H. Horz, N. Scheele, and W. Effelsberg. Interactive lectures: Effective
teaching and learning in lectures using wireless networks. Comput. Hum. Behav., 23(5):2524-
2537, Sept. 2007.
4/12/2013 © FZI Forschungszentrum Informatik 26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lak2013riveraupload-130411002136-phpapp02/85/Live-Interest-Meter-Learning-from-Quantified-Feedback-in-Mass-Lectures-26-320.jpg)
![Reflective learning in TEL
[1] R. Ferguson, S. B. Shum, and R. D. Crick. EnquiryBlogger: using widgets to support
awareness and reflection in a PLE Setting. In ARPLE11, PLE Conference 2011, Southampton,
UK, 11-13 July, 2011.
[2] S. Govaerts, K. Verbert, E. Duval, and A. Pardo. The student activity meter for awareness and
self-reflection. In CHI '12 Extended Abstracts on Human Factors in Computing Systems, pages
869-884, New York, NY, USA, 2012. ACM.
[3] J. L. Santos, S. Govaerts, K. Verbert, and E. Duval. Goal-oriented visualizations of activity
tracking: a case study with engineering students. In 2nd International Conference on Learning
Analytics and Knowledge, LAK '12, pages 143-152, New York, NY, USA, 2012. ACM.
4/12/2013 © FZI Forschungszentrum Informatik 27](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lak2013riveraupload-130411002136-phpapp02/85/Live-Interest-Meter-Learning-from-Quantified-Feedback-in-Mass-Lectures-27-320.jpg)