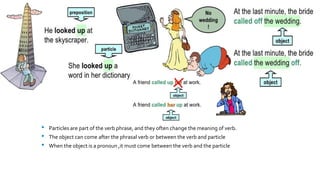
The document discusses phrasal verbs, which are combinations of verbs with prepositions or adverbs, highlighting their usage in spoken English versus formal texts. It explains the distinction between literal and idiomatic meanings, providing examples of each, and notes the importance of understanding them due to their varying interpretations. Additionally, it defines idioms and their figurative meanings, emphasizing that phrasal verbs should be avoided in academic writing.