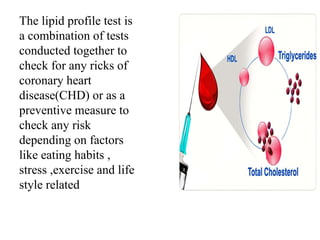
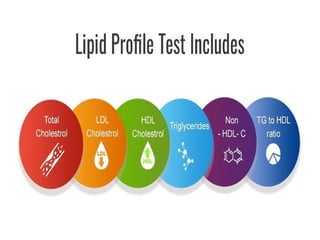
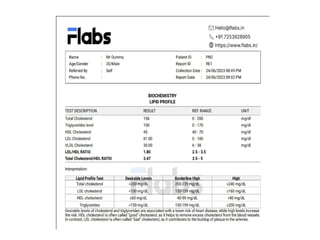
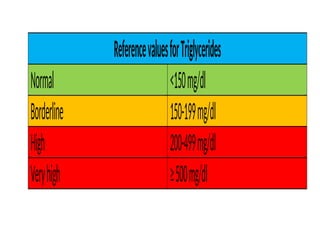
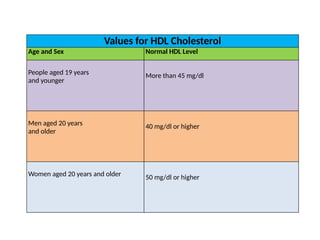
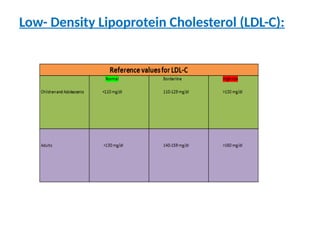
The lipid profile test assesses risk factors for coronary heart disease (CHD) by measuring triglycerides, cholesterol, HDL, and LDL levels. Elevated triglycerides and cholesterol are linked to various health conditions, while decreased levels can indicate different health issues. Additionally, HDL is beneficial for heart health, and its levels, alongside LDL, provide insight into an individual's cardiovascular risk.