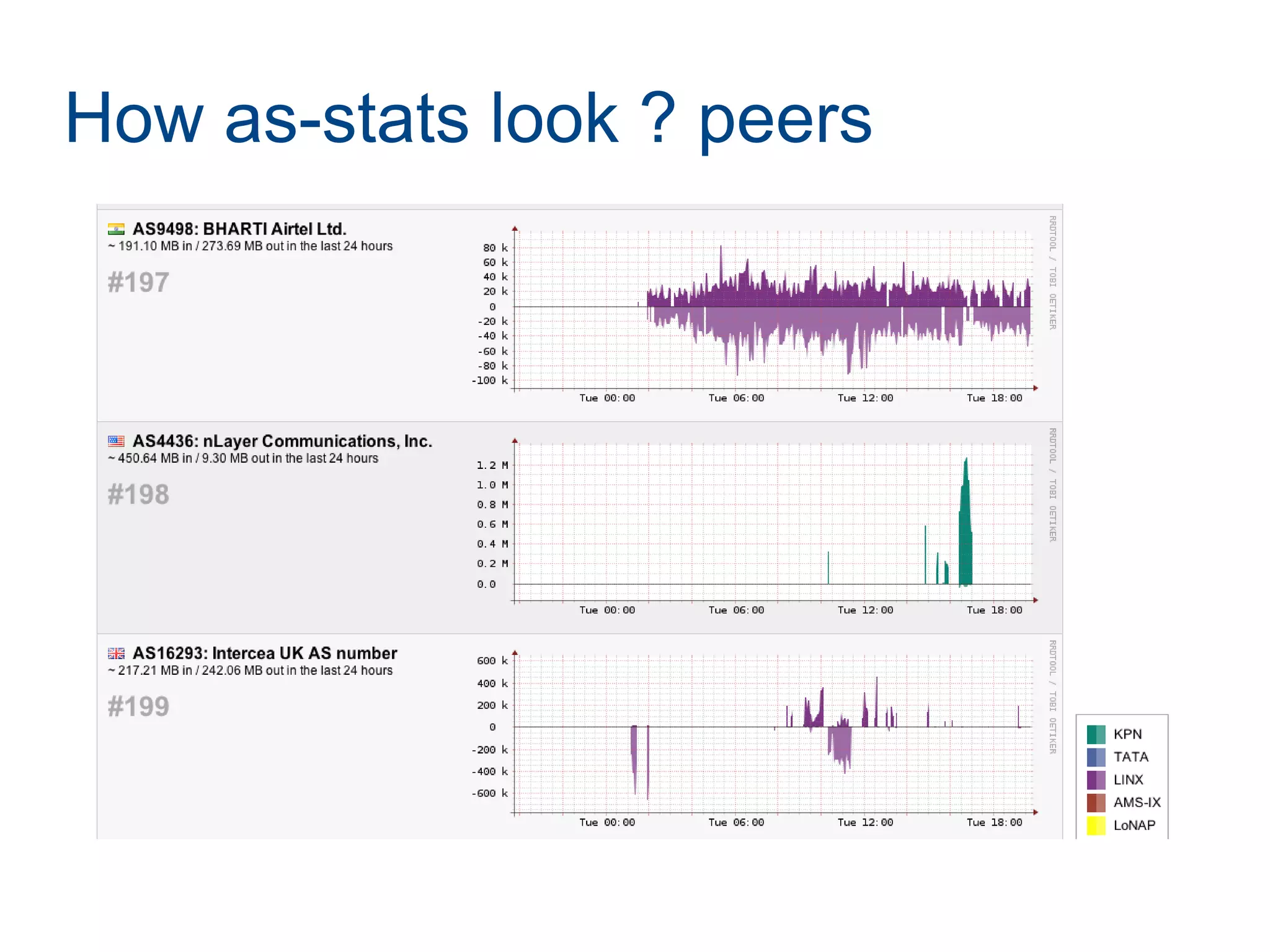
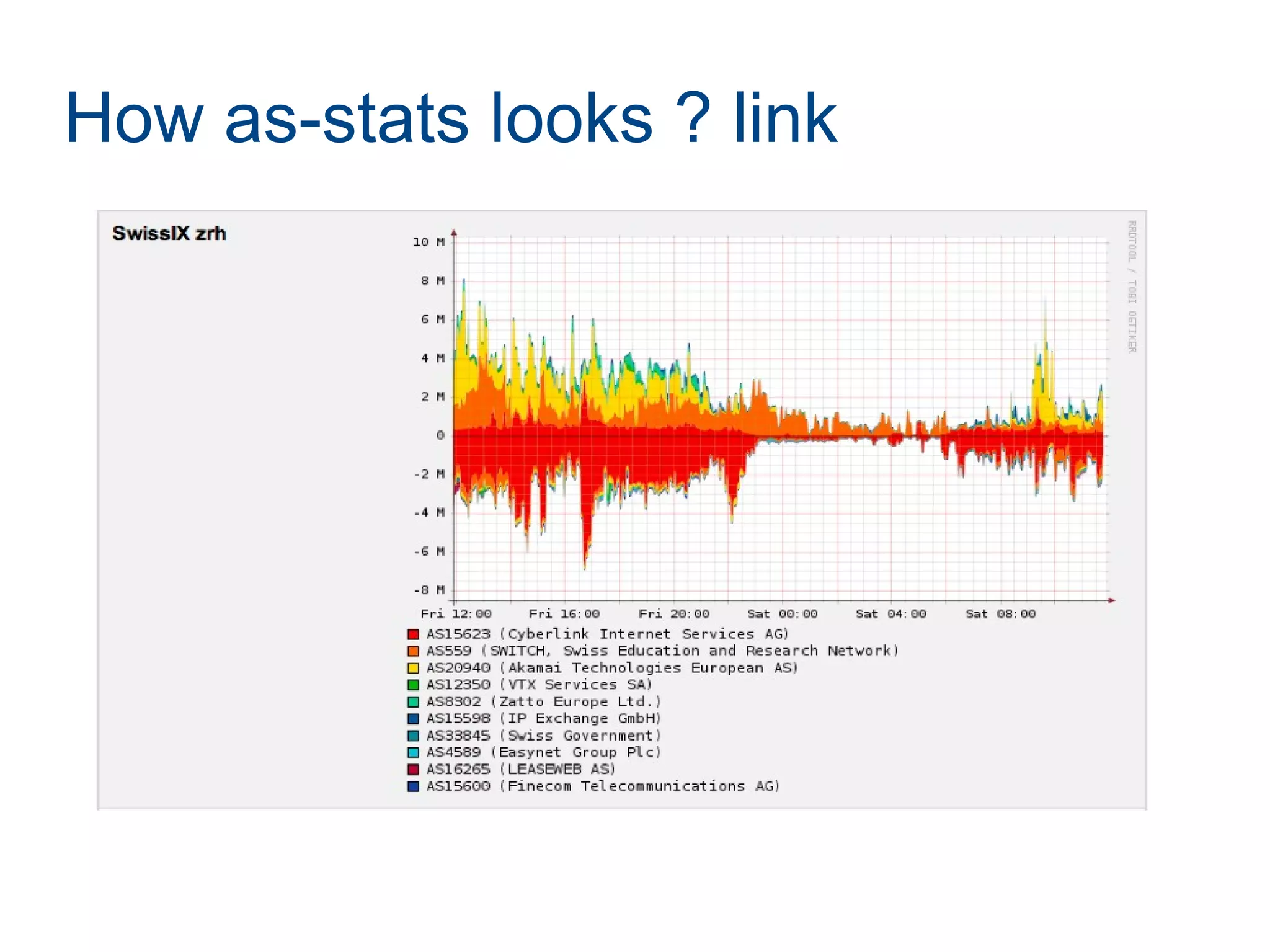
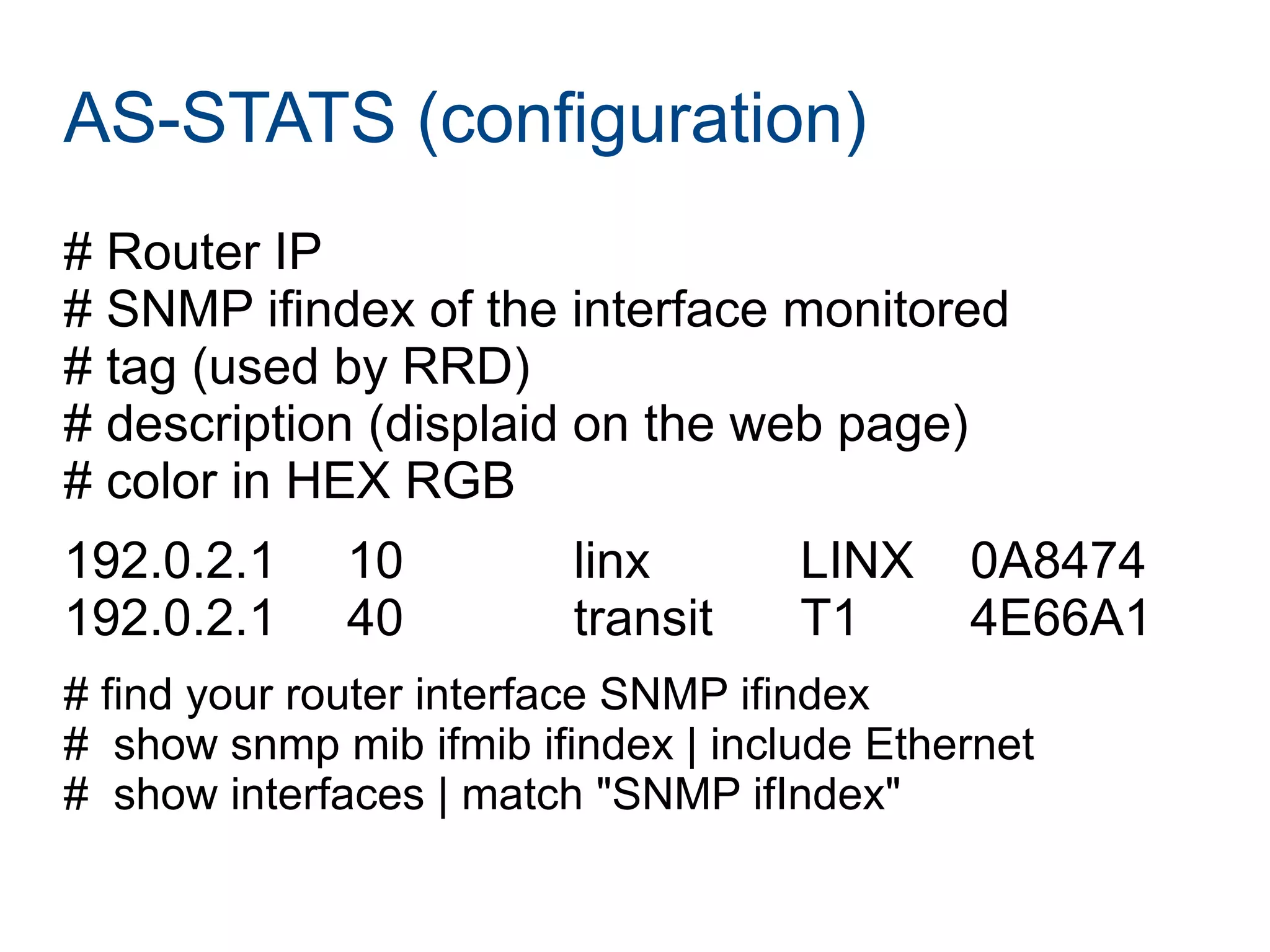
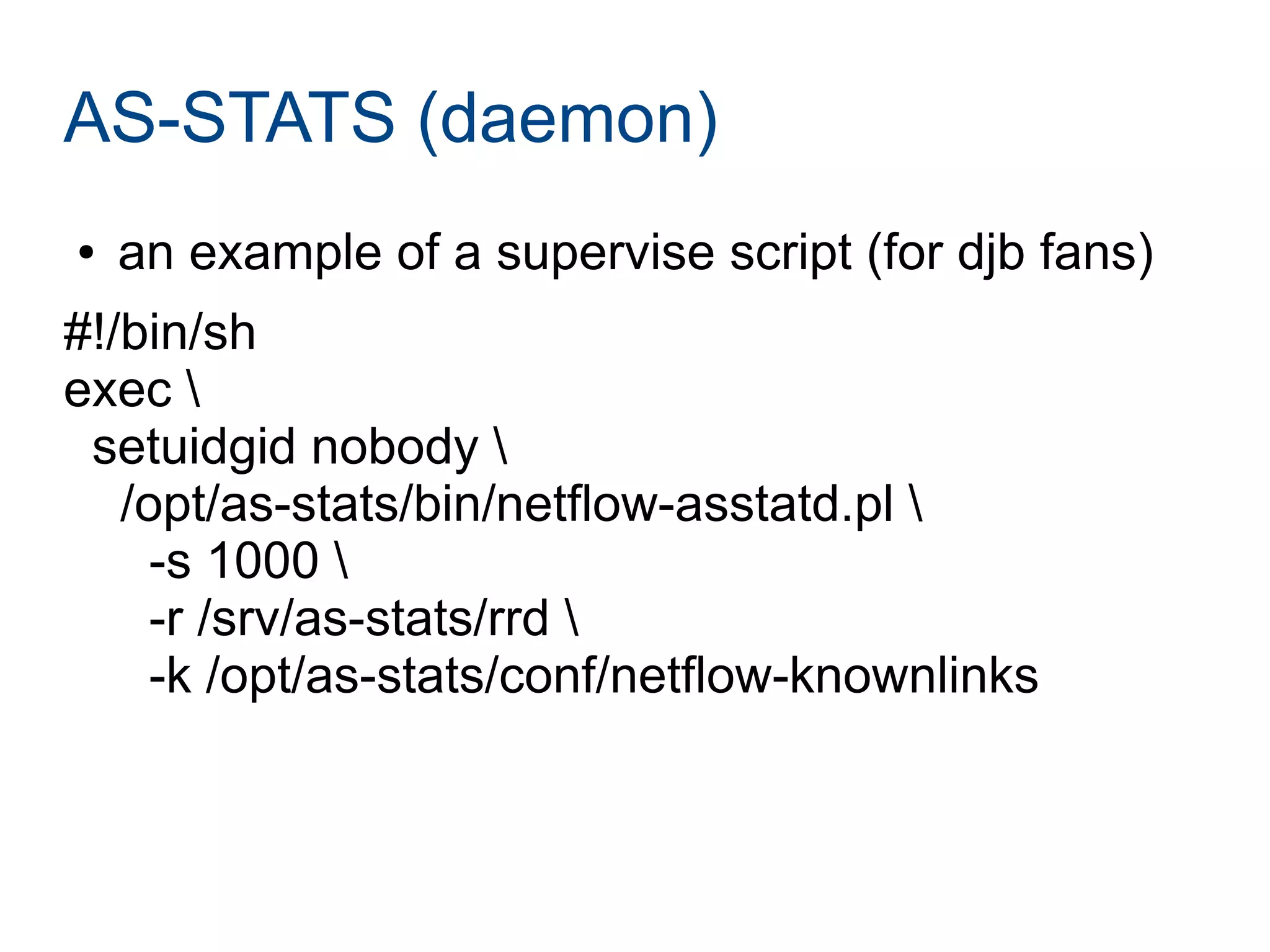
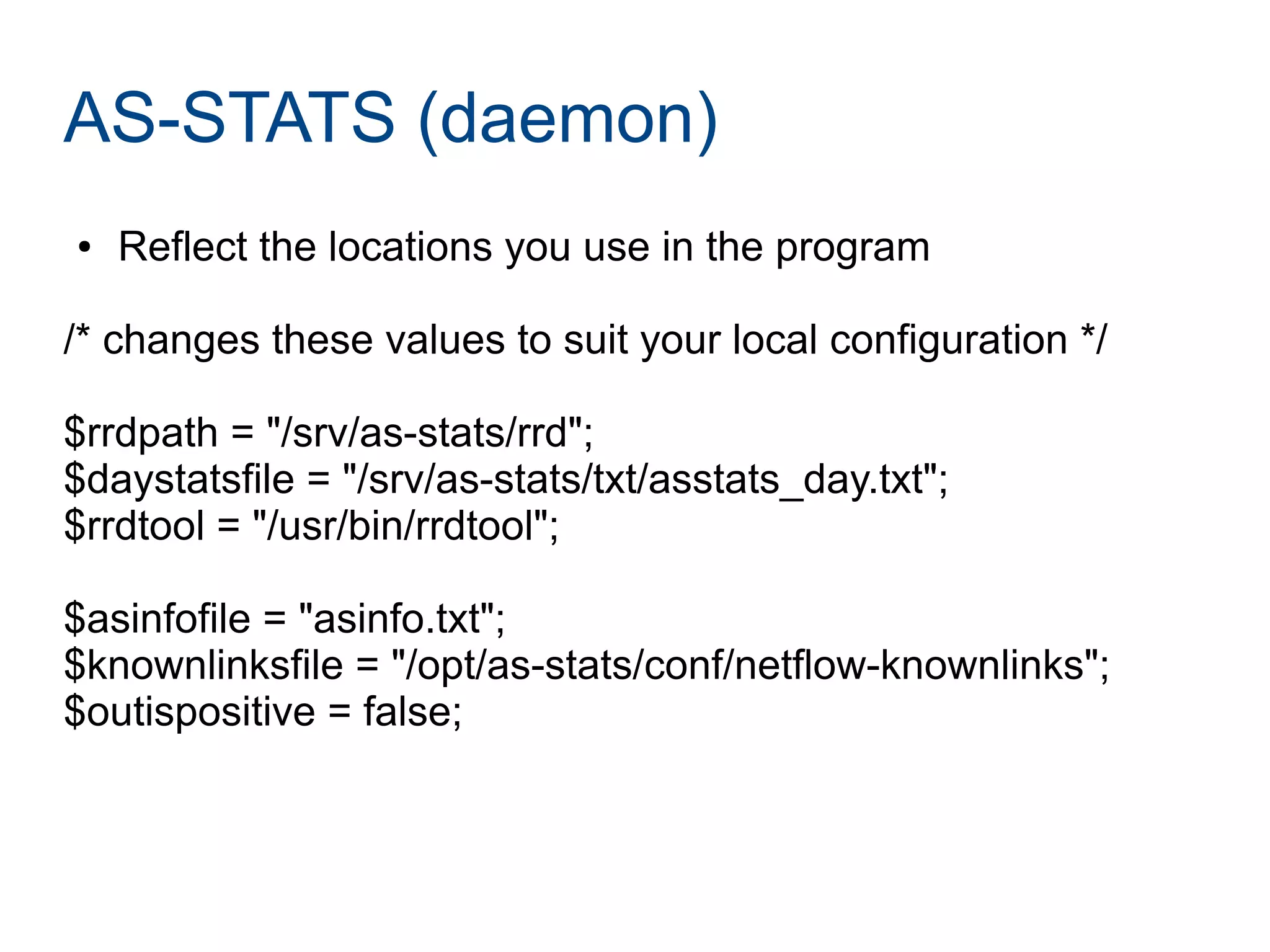
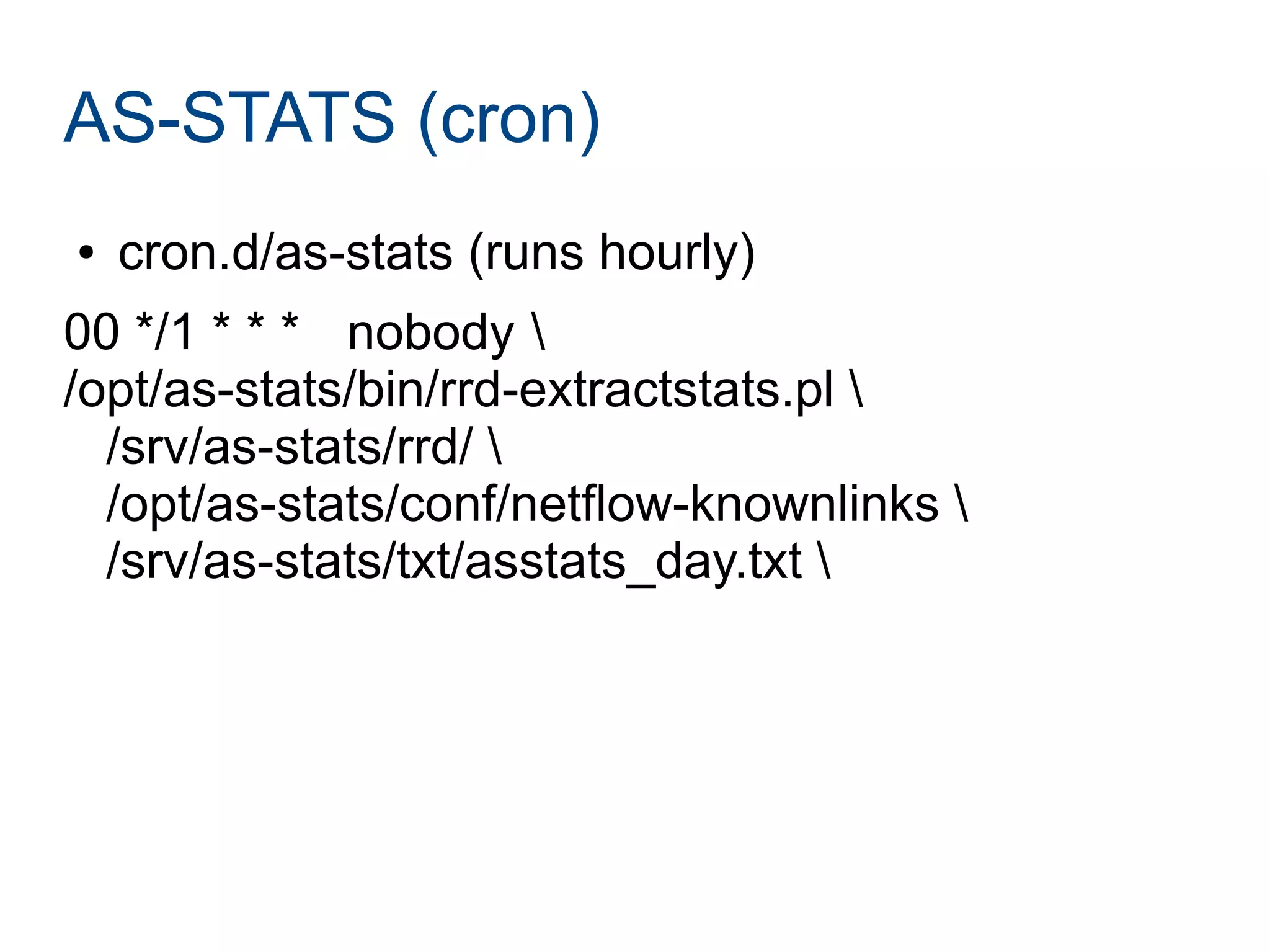
Joining LINX requires paperwork, connecting a router, and connecting to route servers. However, peering with the 356 LINX members is not straightforward and requires contacting each NOC individually. Determining who to peer with depends on analyzing traffic data using tools like traceroute, NetFlow, and the AS-STATS collector. AS-STATS collects and analyzes NetFlow/sFlow data to identify the top sources and destinations of traffic to help members determine which peers matter most.