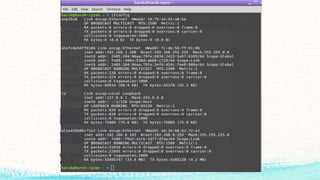
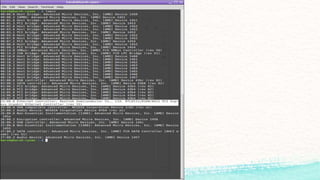
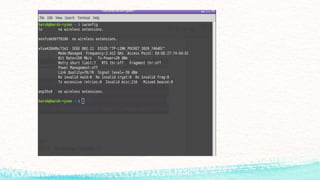
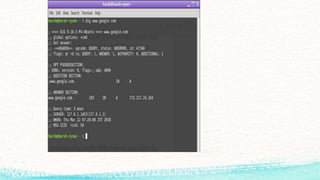
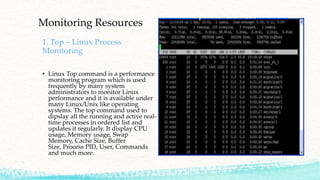
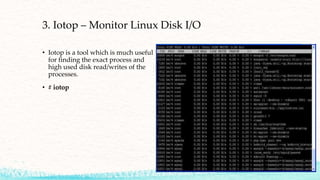
The document details various commands and practices for managing system and network connections in Linux, particularly focusing on monitoring network resources and connections. It covers commands like ifconfig, iwconfig, and wget for managing interfaces and downloading files, as well as performance monitoring tools such as top, vmstat, and iotop. Additionally, it mentions the significance of DNS in name resolution for TCP/IP networks.