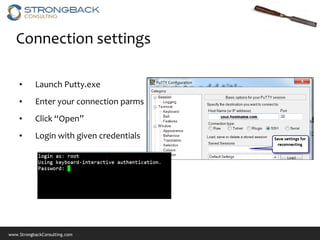
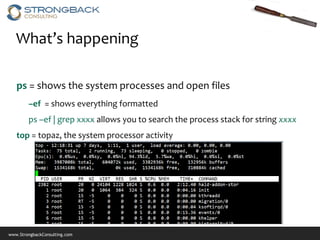
This document provides an overview of basic Linux commands and navigation for new Linux users. It covers how to connect to Linux using terminals or remotely using Putty, navigating files and directories using commands like ls, cd, pwd, and vi, managing files with commands like cp, rm, and chmod, and viewing system processes and information with top, ps, and other commands. The document aims to get users comfortable with fundamental Linux tasks and directs them to additional resources for learning more advanced topics.