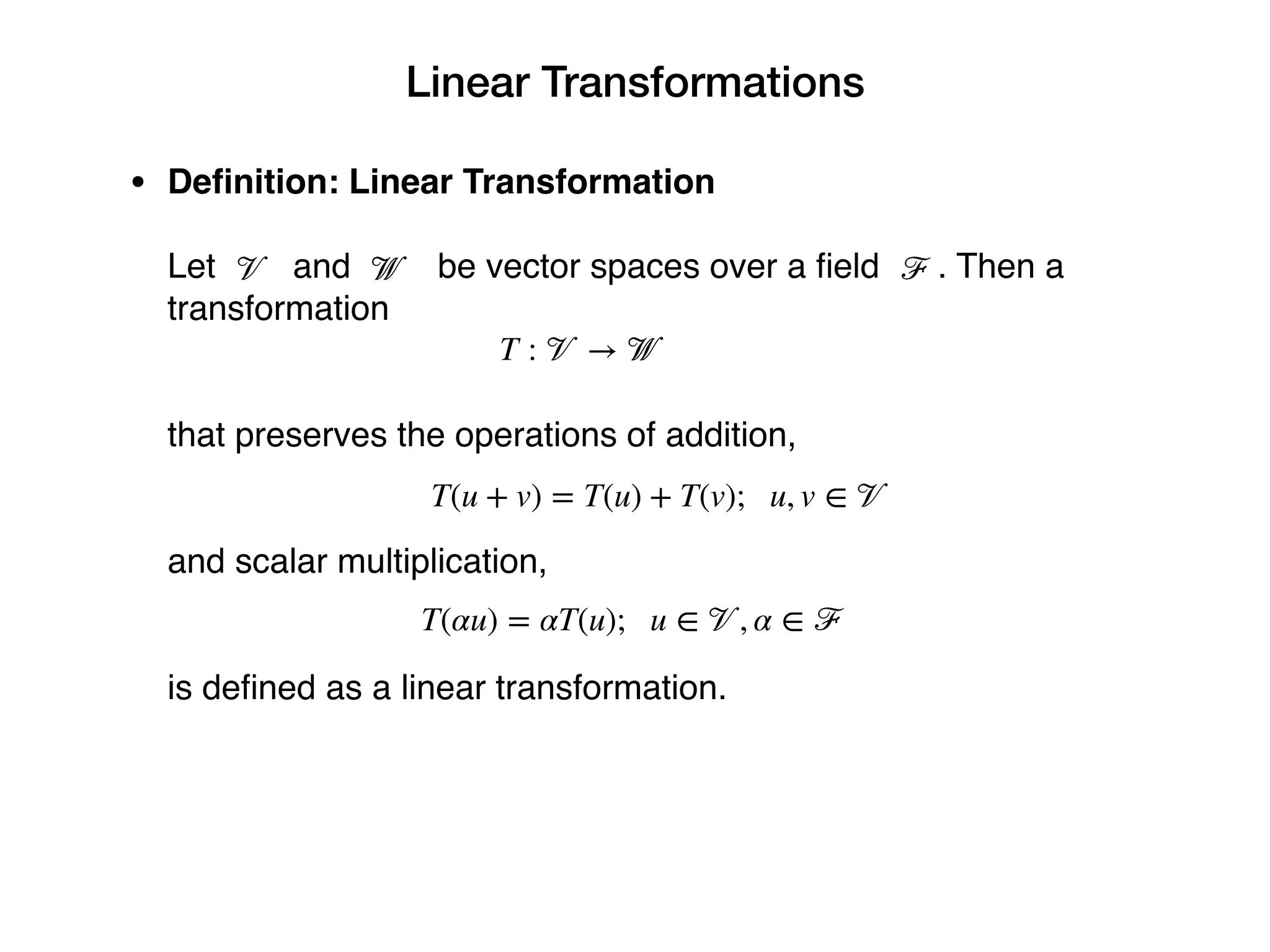
1. A linear transformation is a function between vector spaces that preserves vector addition and scalar multiplication.
2. To be a linear transformation, T(u+v) must equal T(u)+T(v) and T(αu) must equal αT(u) for any vectors u,v and scalar α.
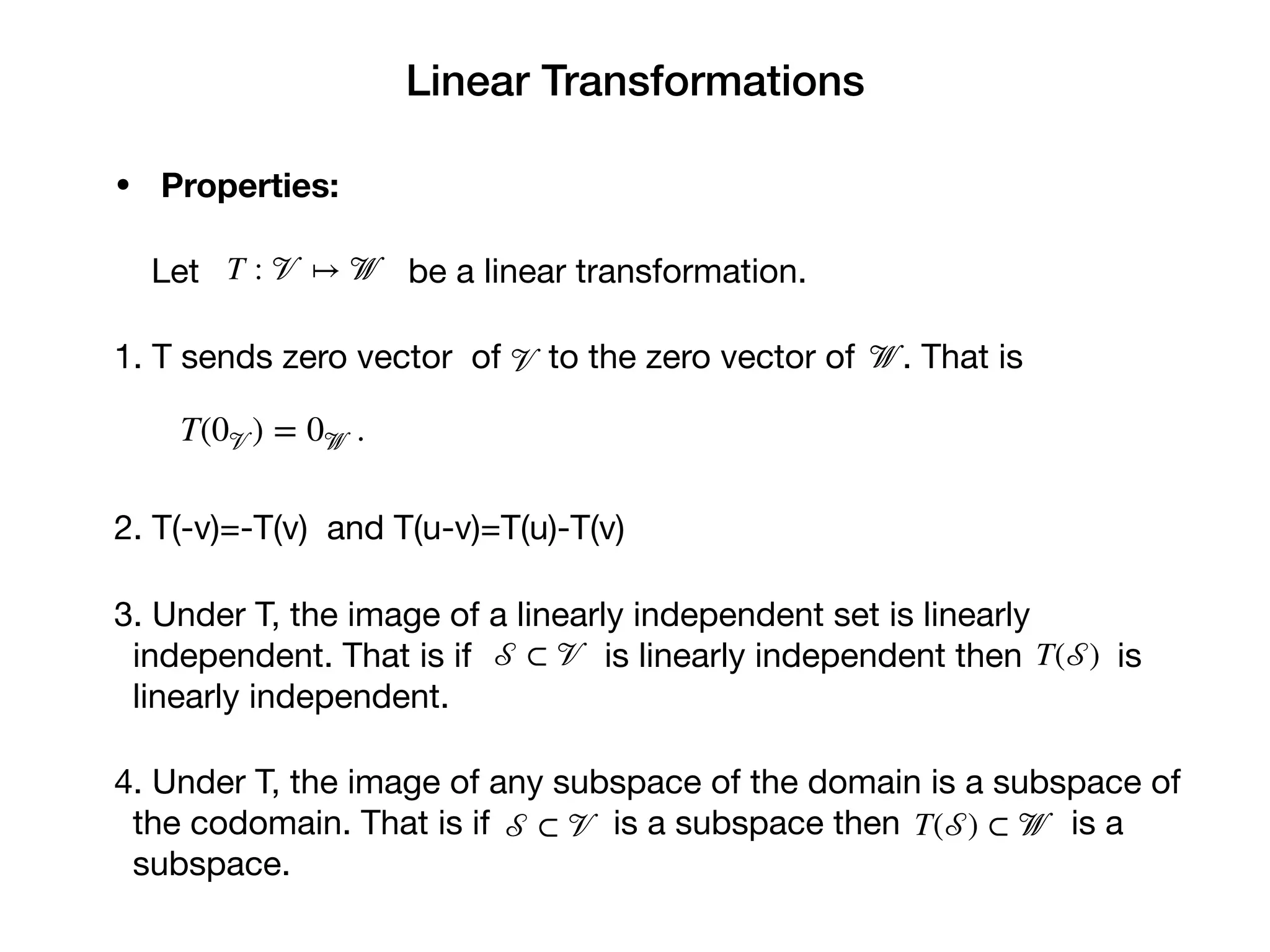
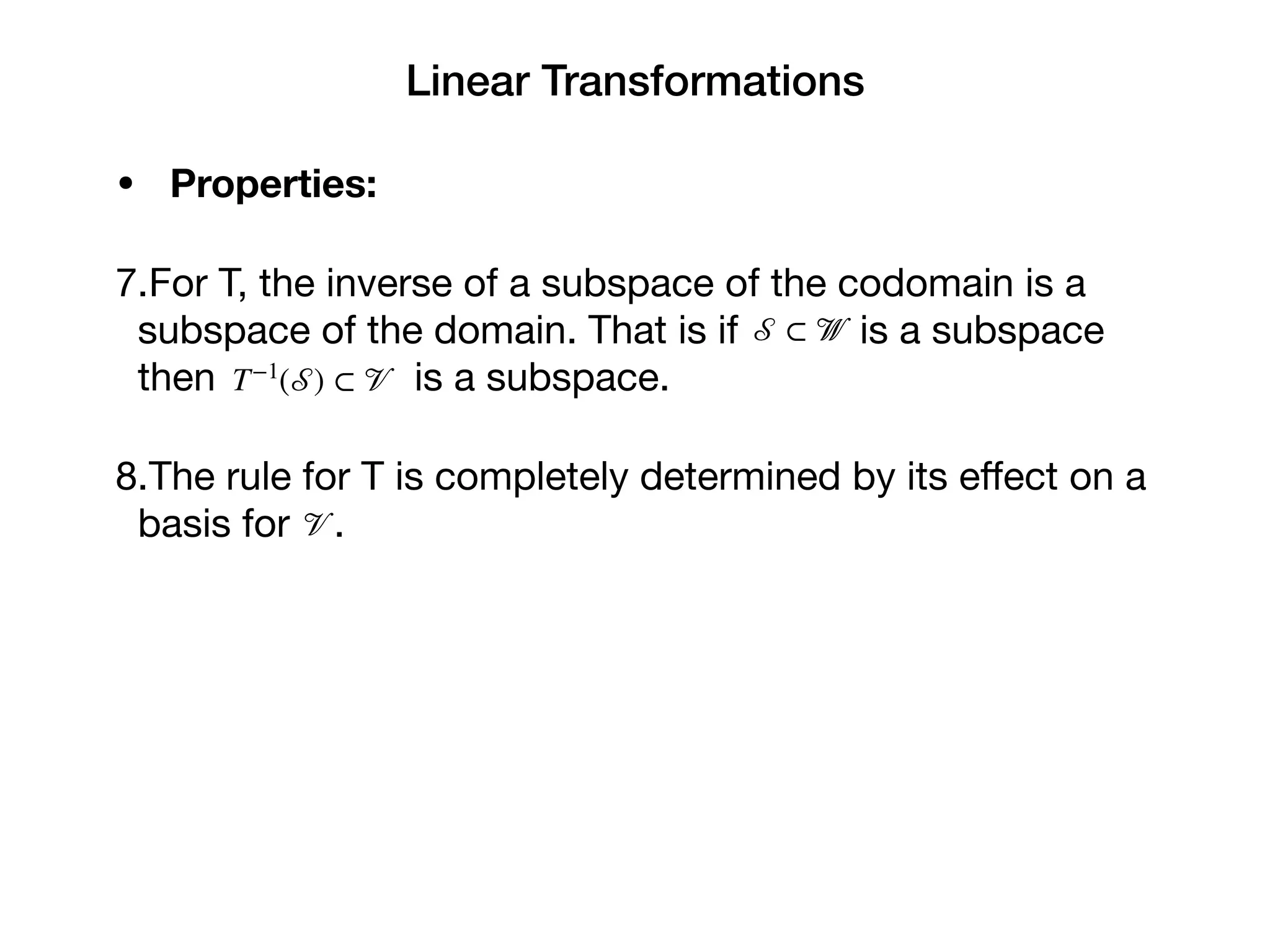
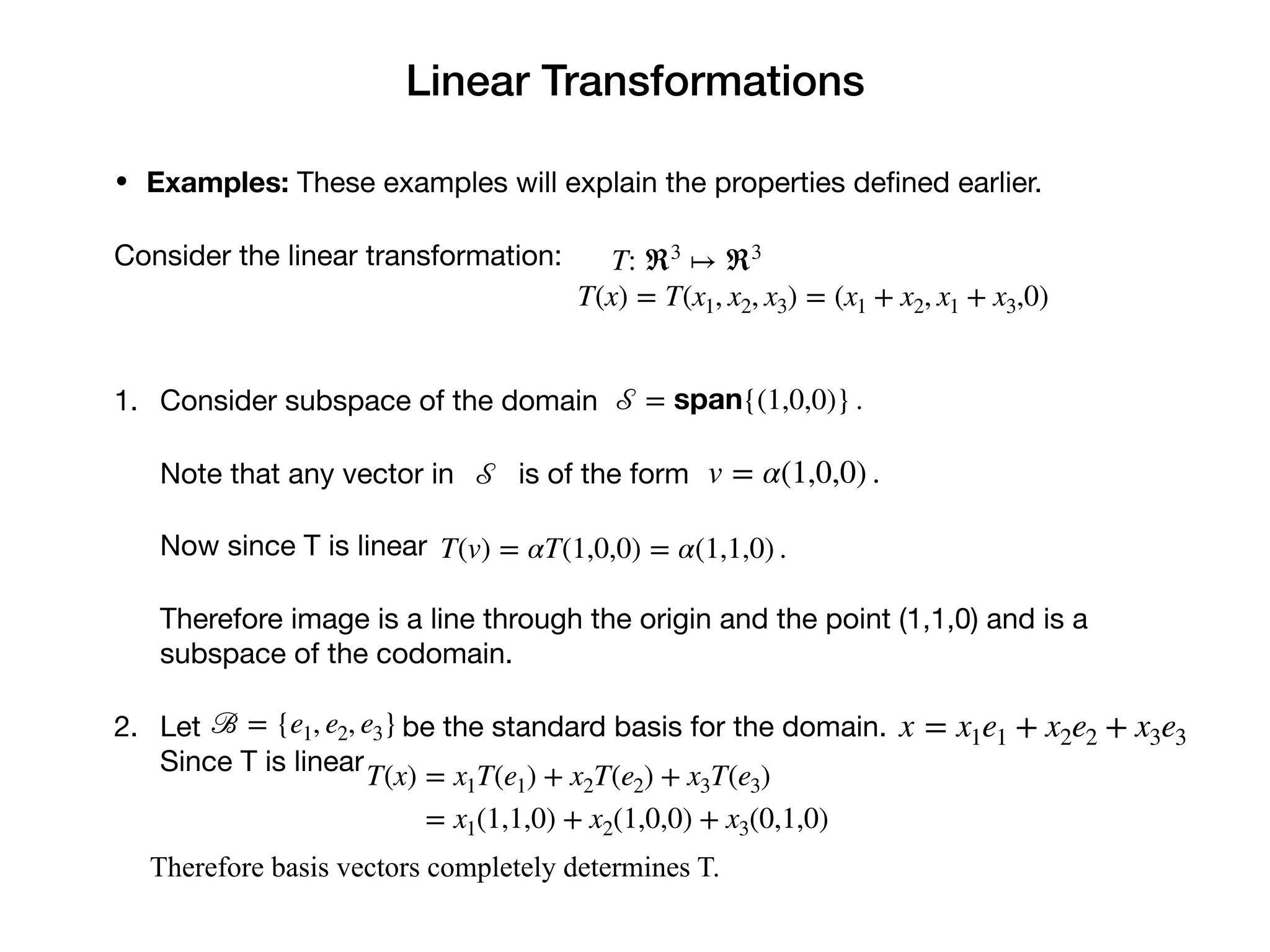
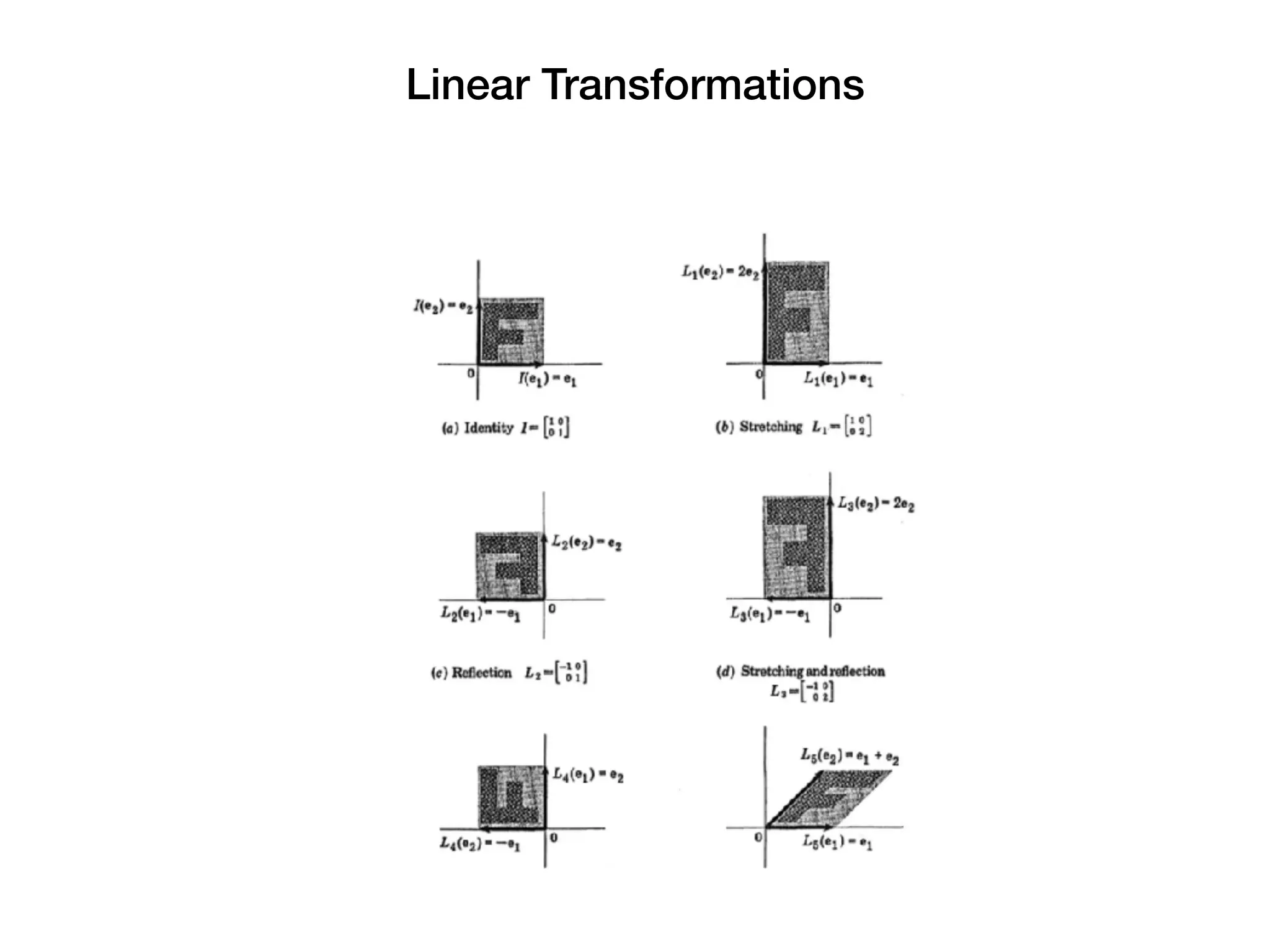
3. Properties of linear transformations include: the zero vector maps to the zero vector; the image of a linearly independent set is linearly independent; and the image of any subspace is a subspace. The transformation is determined by its effect on a basis.



![Linear Transformations
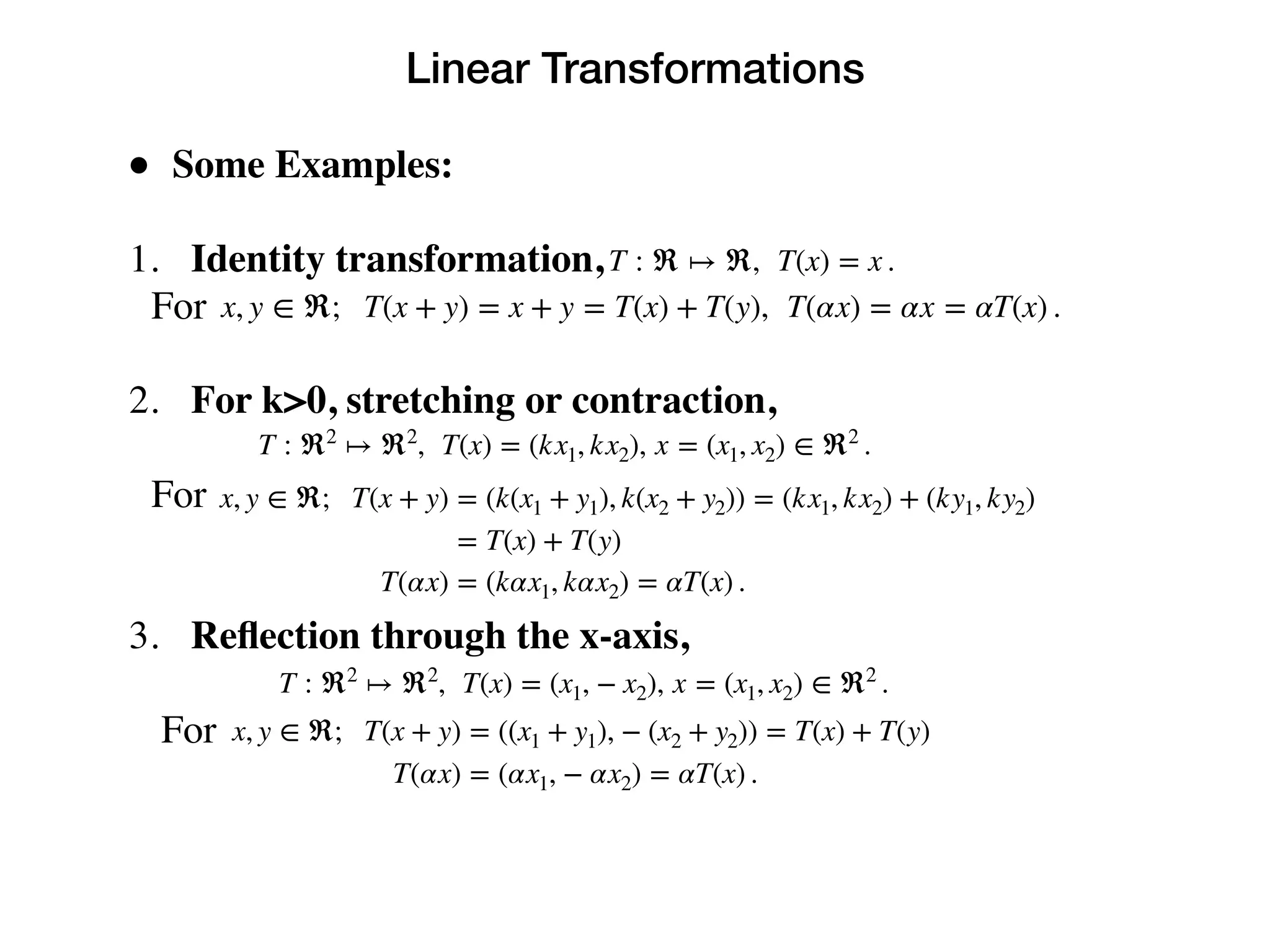
The following are not linear transformations.
1. Translation,
For
2. Quadratic function,
3. Trigonometric functions,
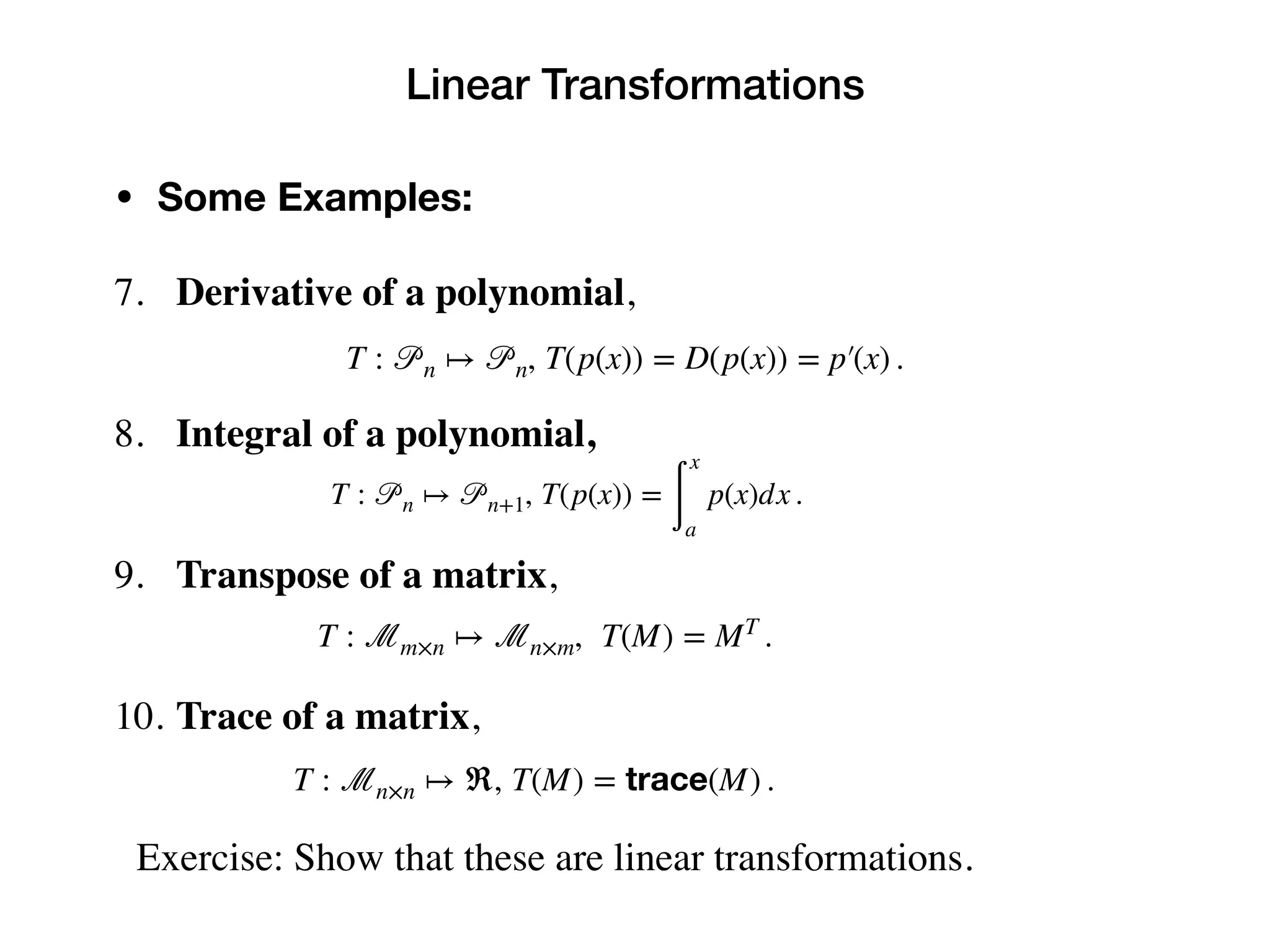
4. Determinant,
Exercise: Show that 2-4 are not linear transformations.
T : ℜ ↦ ℜ, T(x) = x + a, a ≠ 0.
x, y ∈ ℜ, T(x + y) = x + y + a ≠ (x + a) + (y + a) = T(x) + T(y) .
T : ℜ ↦ ℜ, T(x) = x2
.
T : ℜ ↦ [−1,1], T(x) = sin x .
T : ℳn×n ↦ ℜ, T(M) = det(M) .](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lineartransformationspart1-230425035842-e6362a4d/75/Linear-Transformations_part1-pdf-9-2048.jpg)