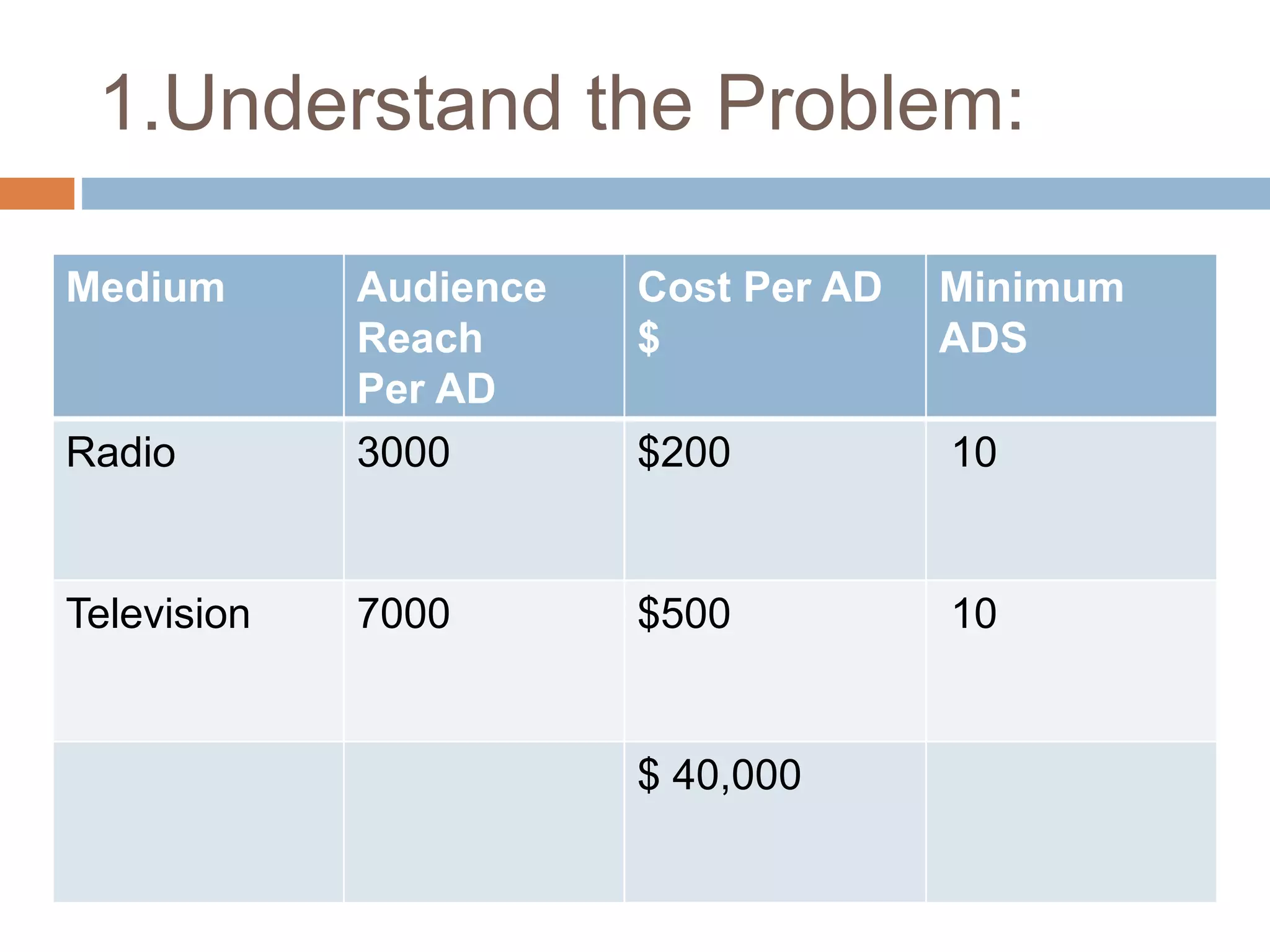
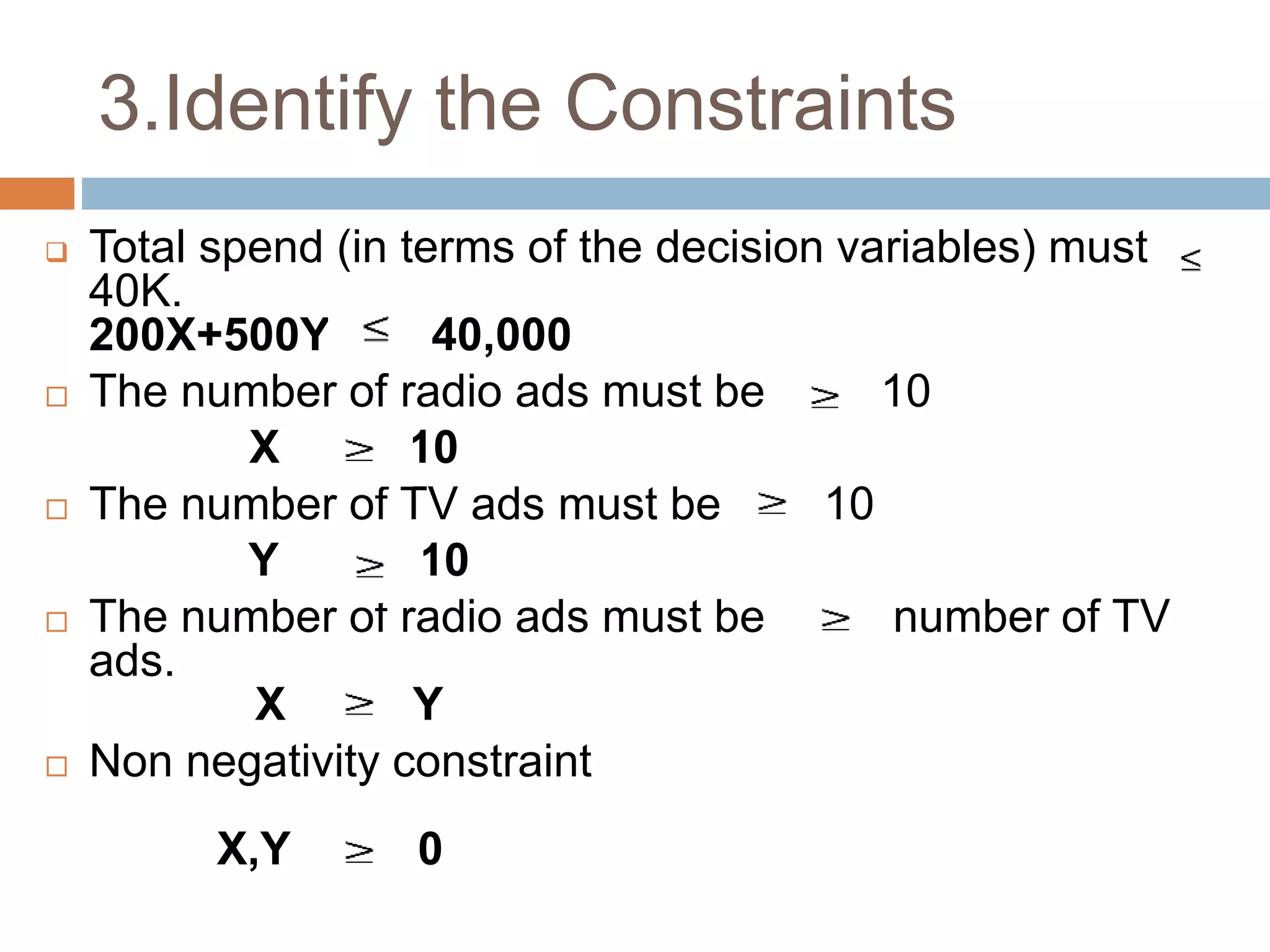
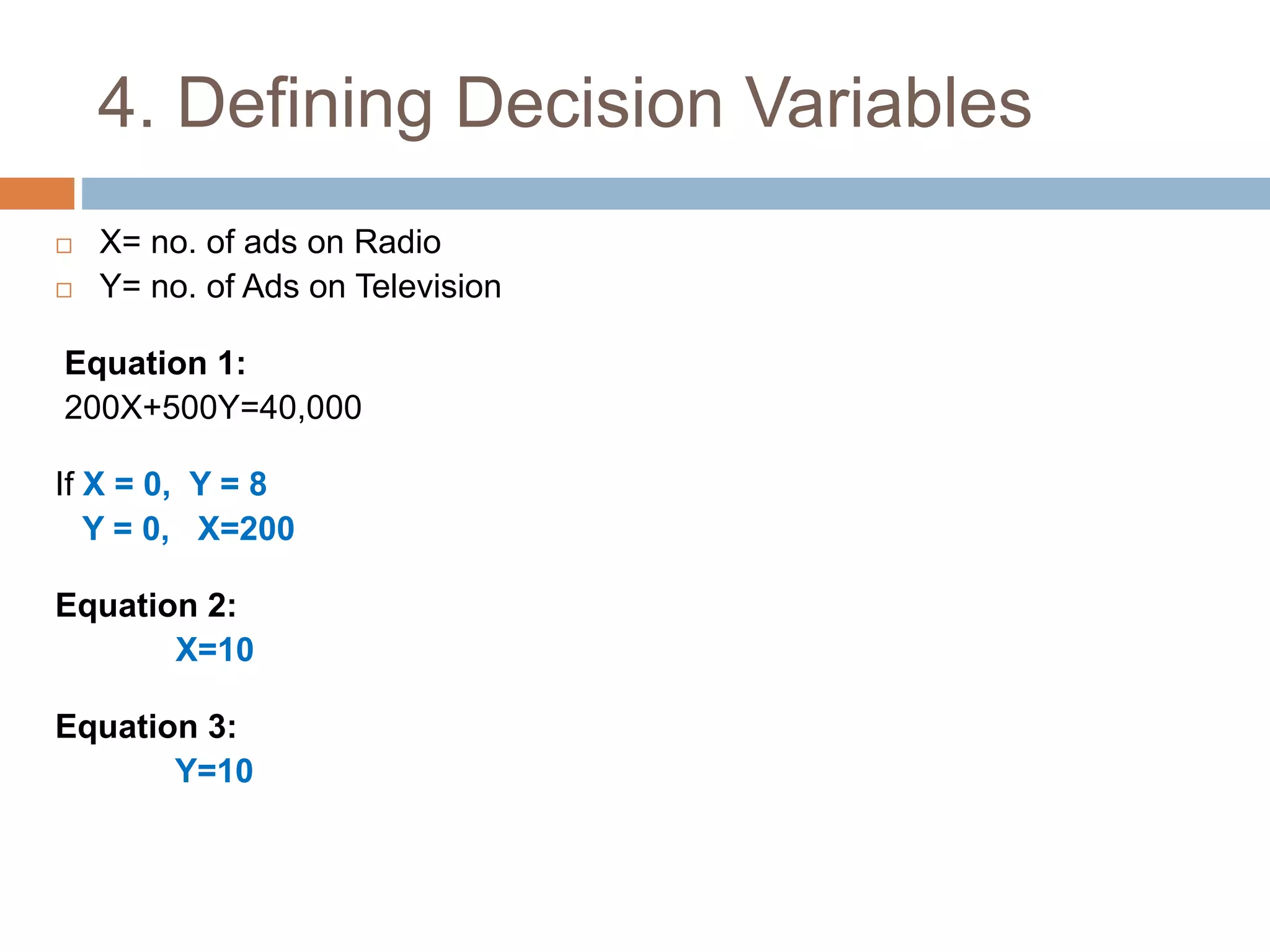
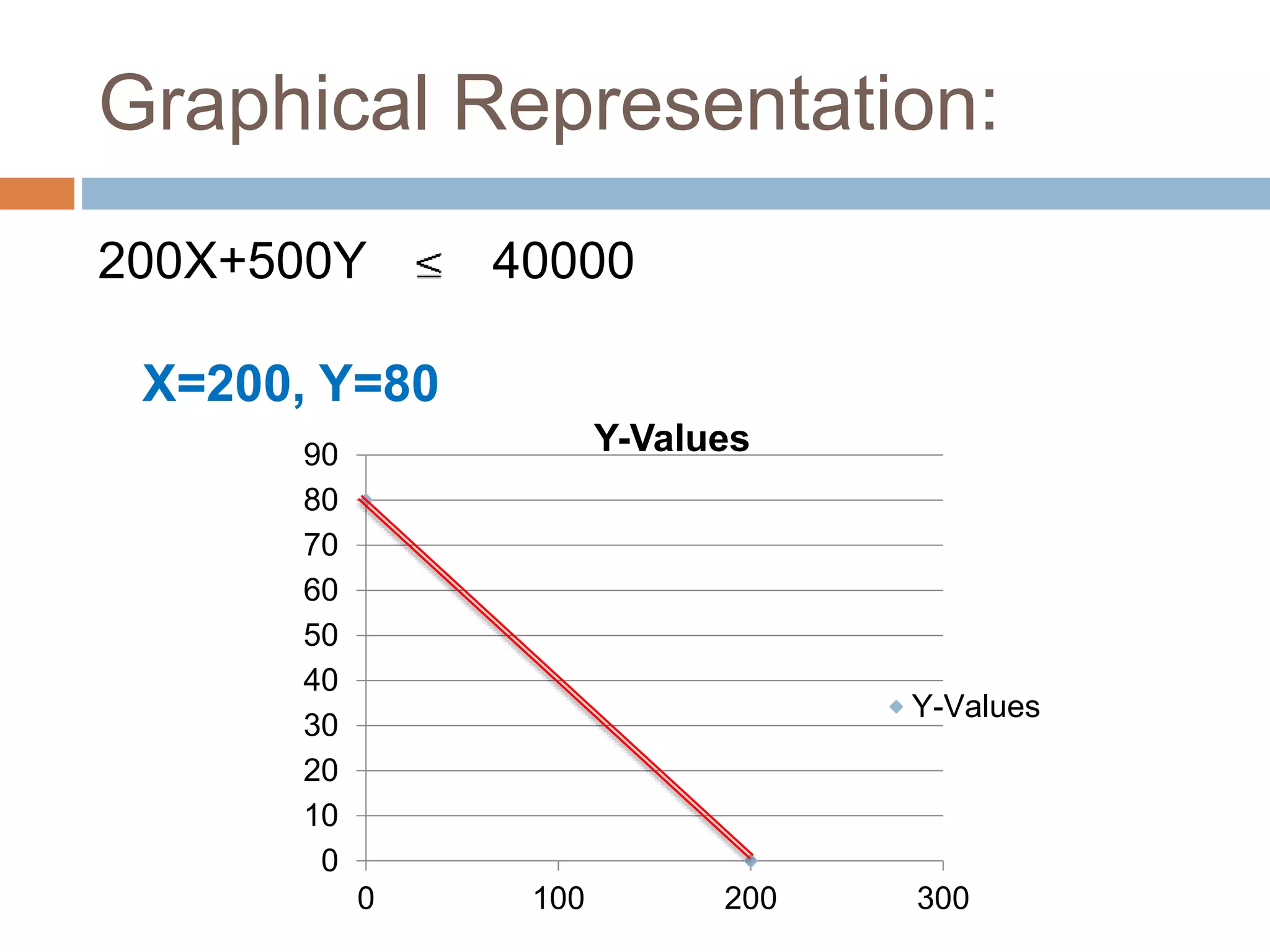
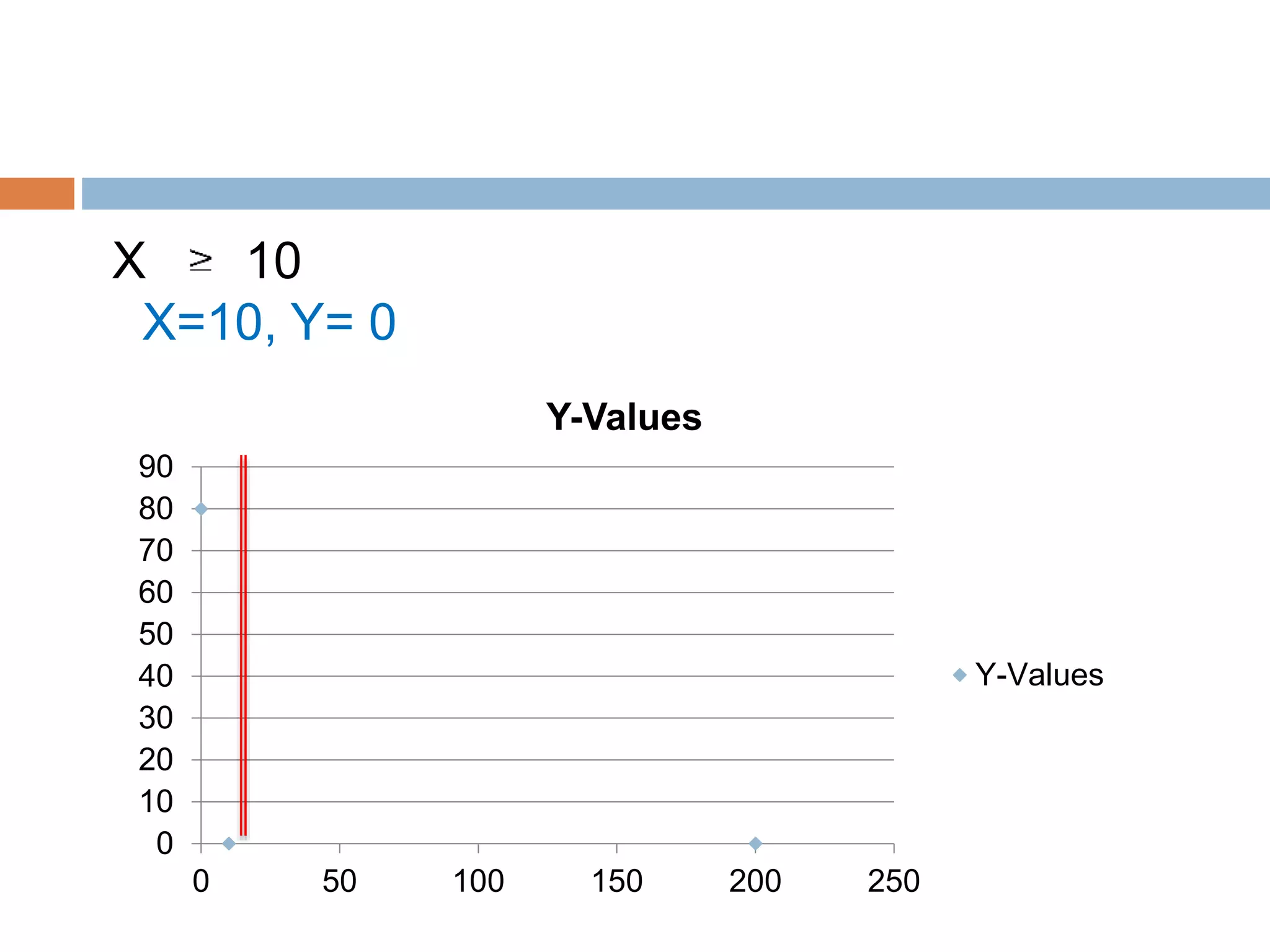
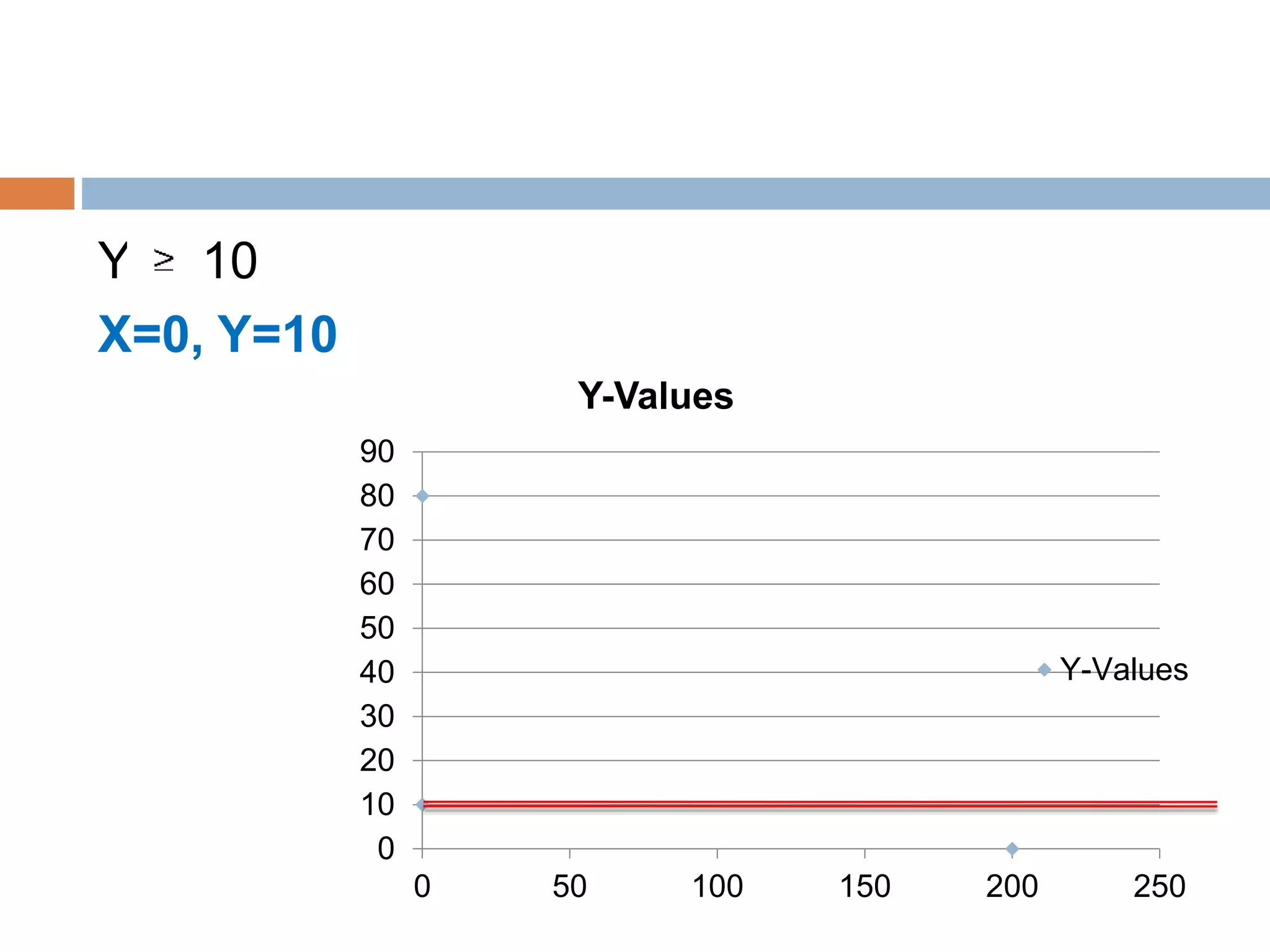
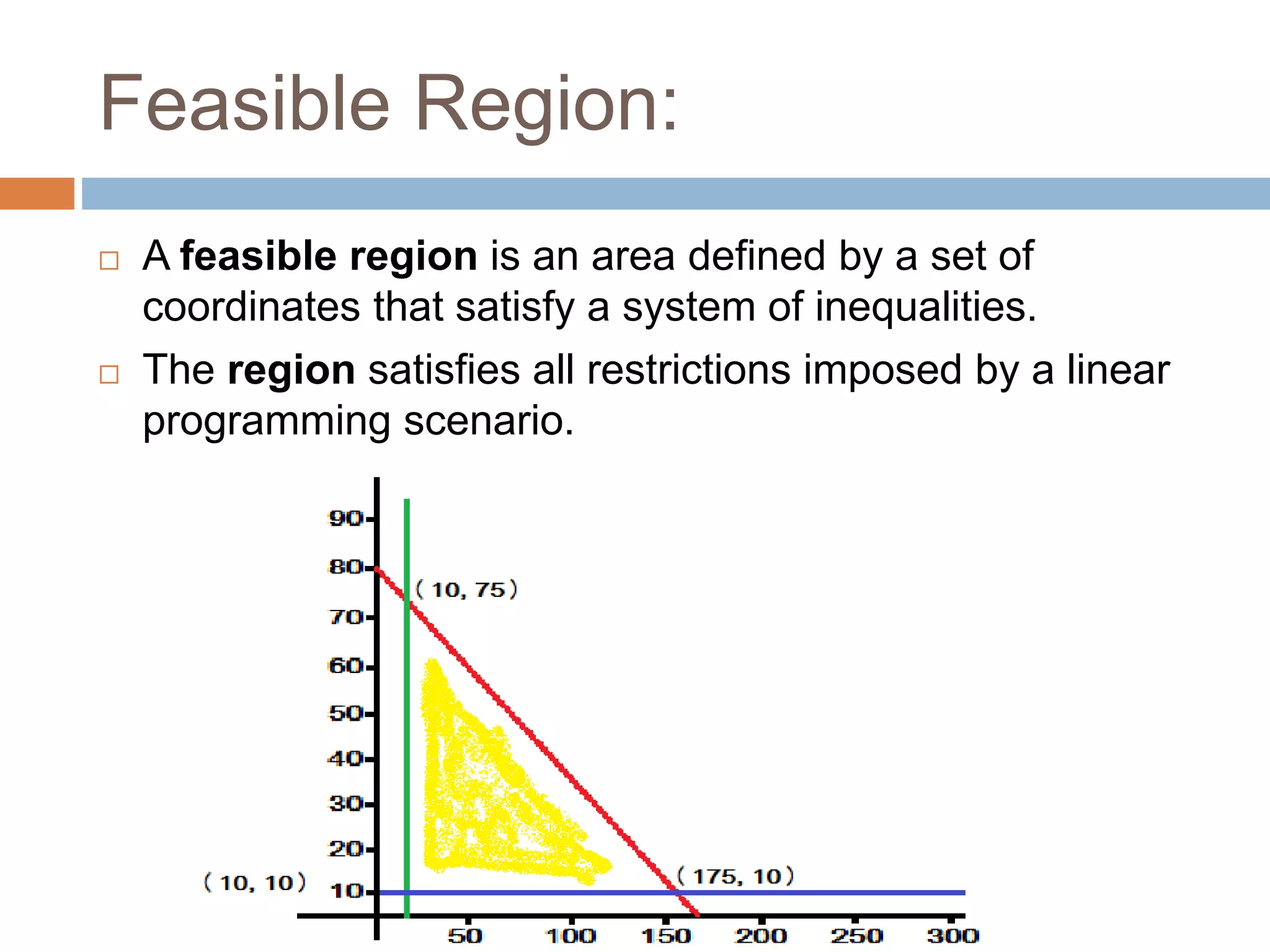
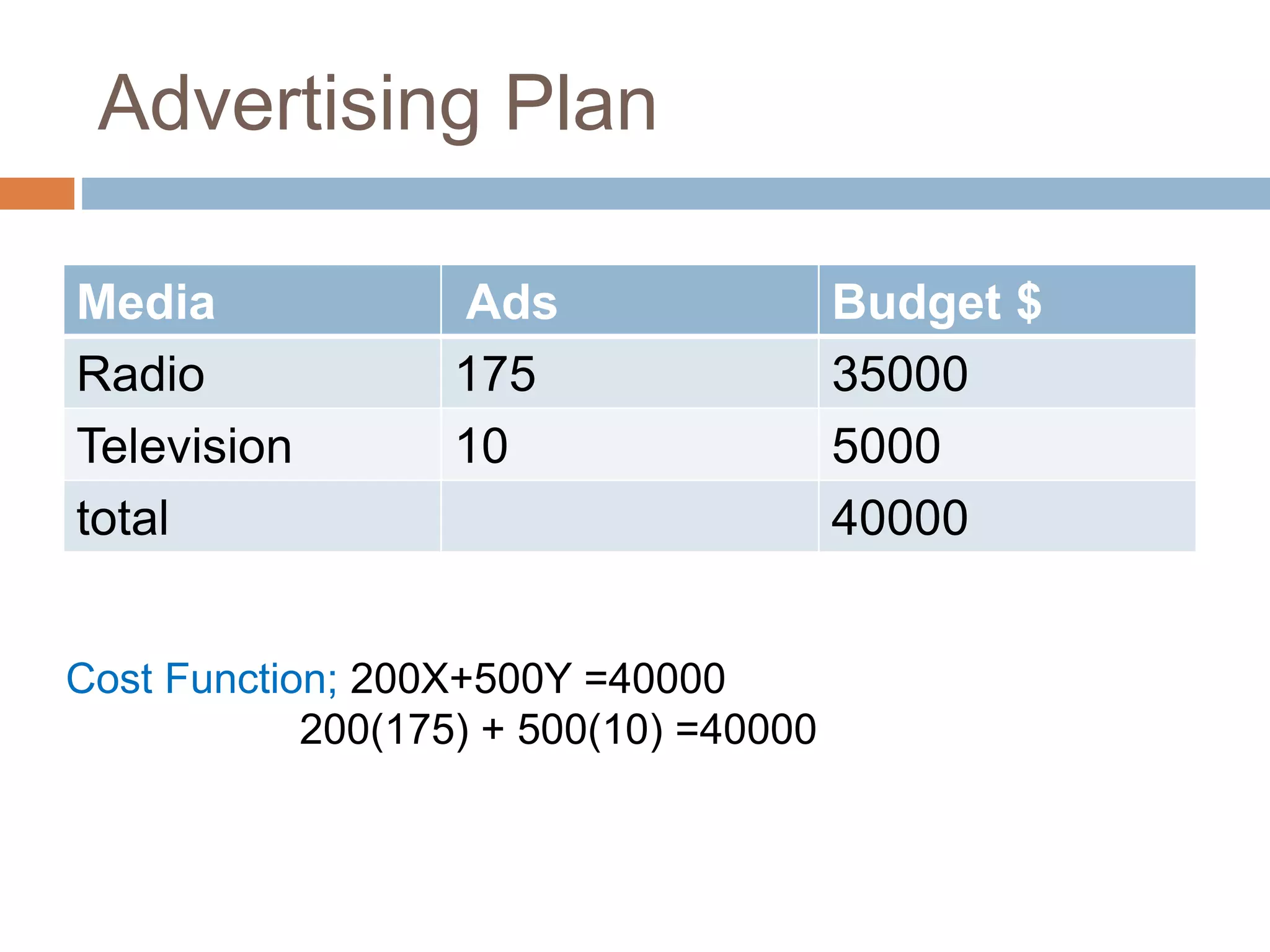
This document discusses linear programming and its application to marketing. It covers topics like the requirements, methods, advantages/disadvantages of linear programming. It also provides steps to formulate a linear programming problem, including understanding the problem, identifying the objective and constraints, defining decision variables, and writing the mathematical model. Finally, it formulates an example problem to maximize advertisement reach within a budget, finds the optimal solution is 175 radio ads and 10 TV ads reaching 595,000 people.