This document discusses the equations of motion for rigid fluids subjected to different types of acceleration.
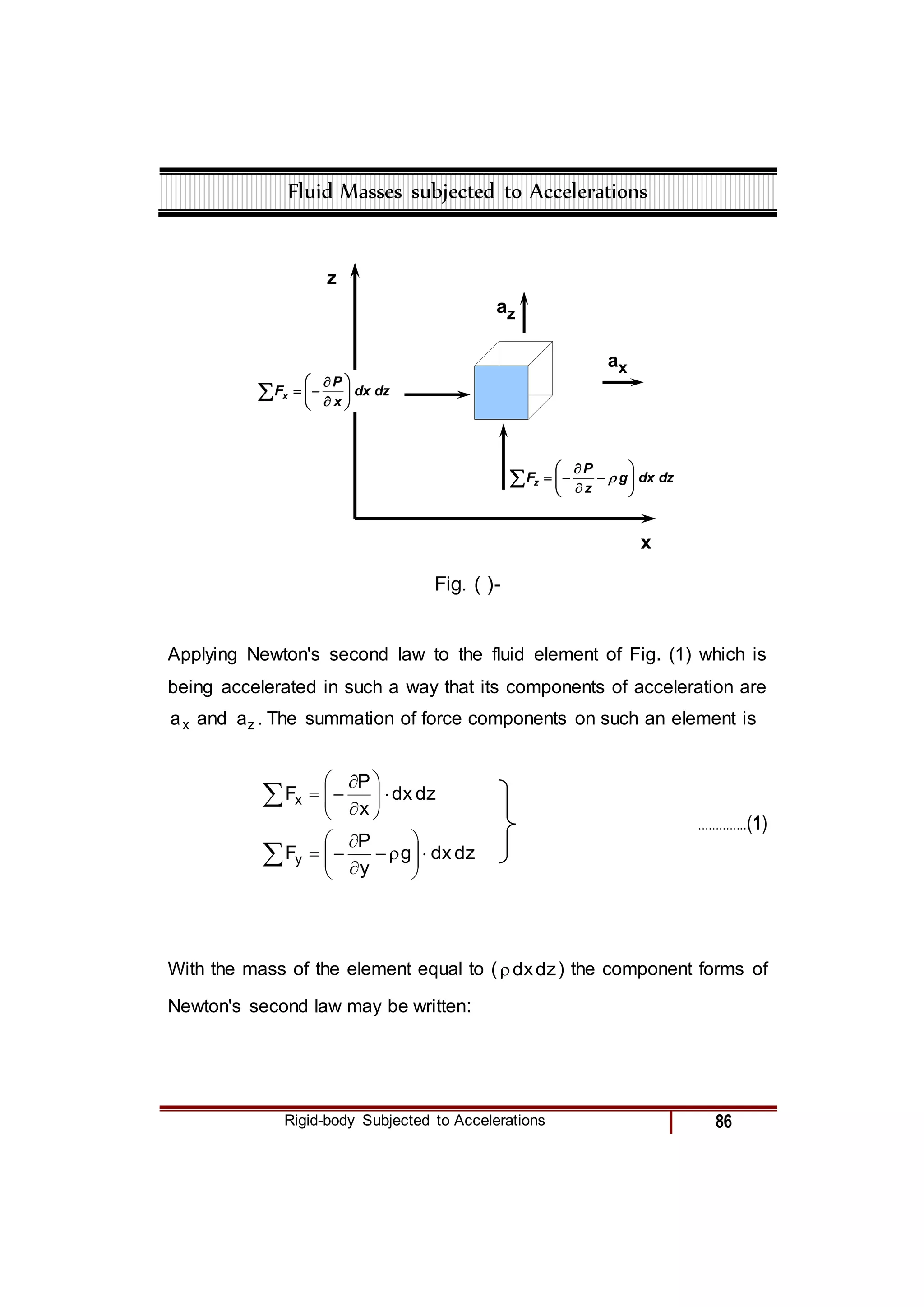
1) The general equation of motion for a rigid fluid is derived from applying Newton's second law to a small fluid element. This relates the fluid acceleration to the pressure gradient and gravitational force.
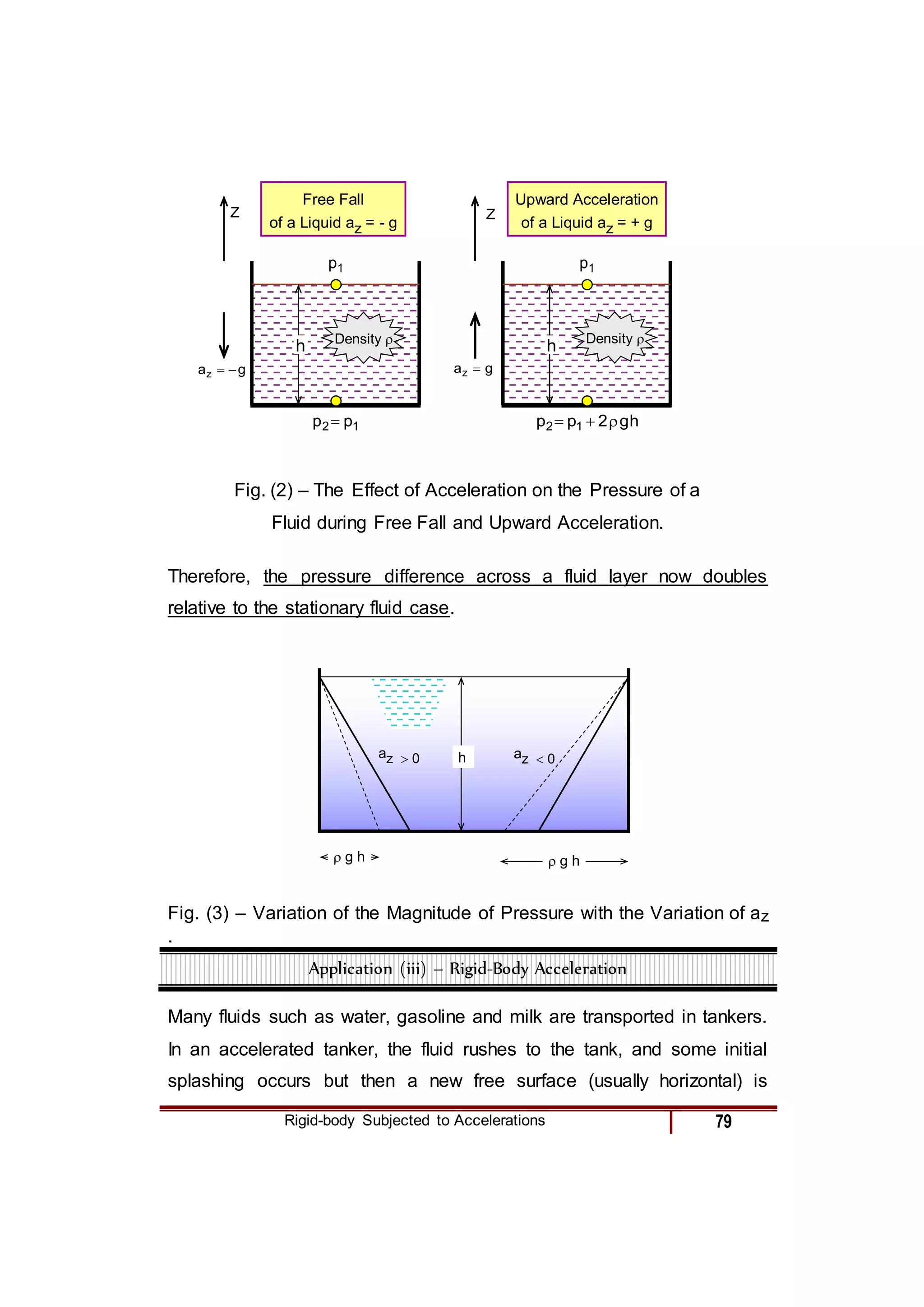
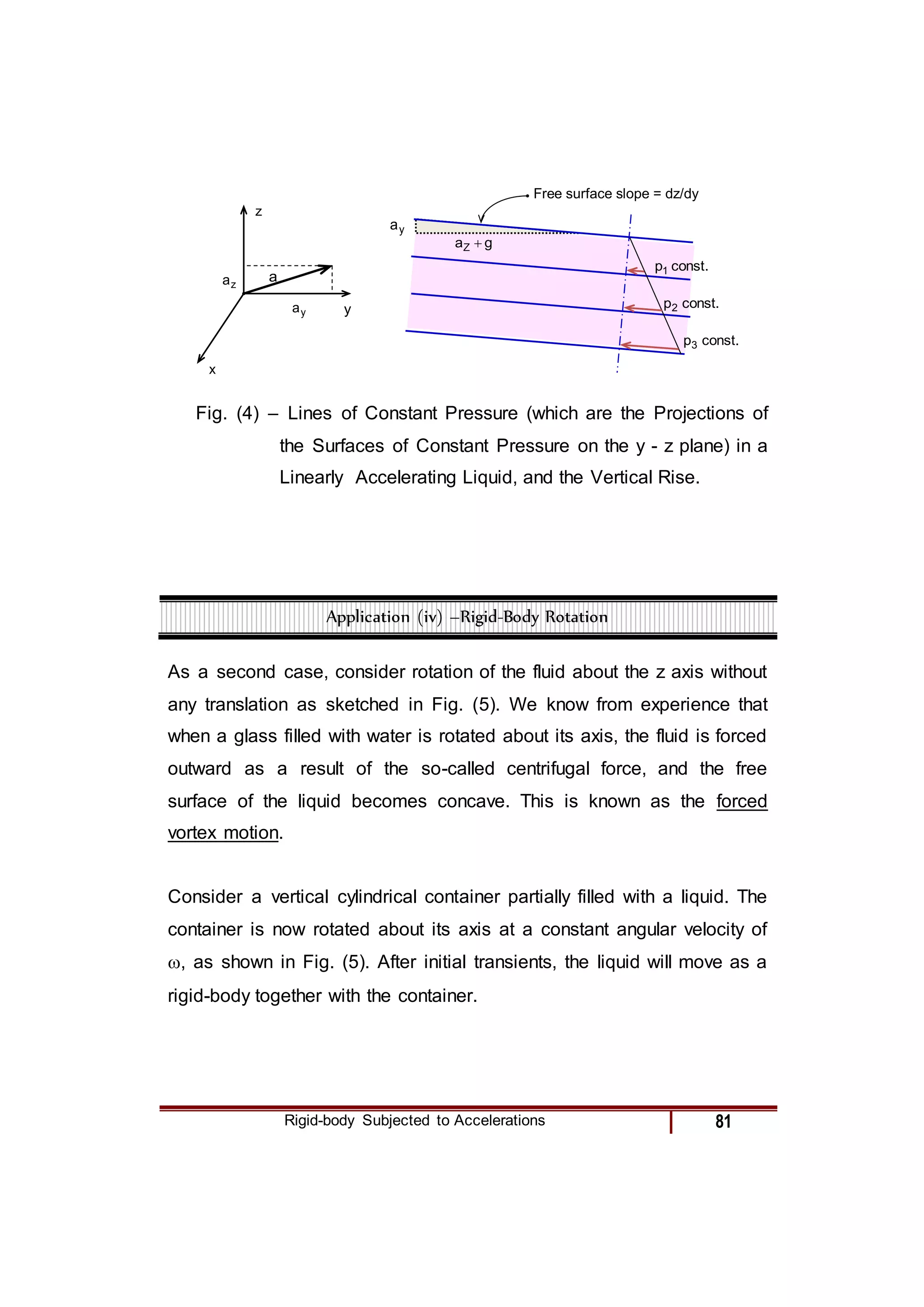
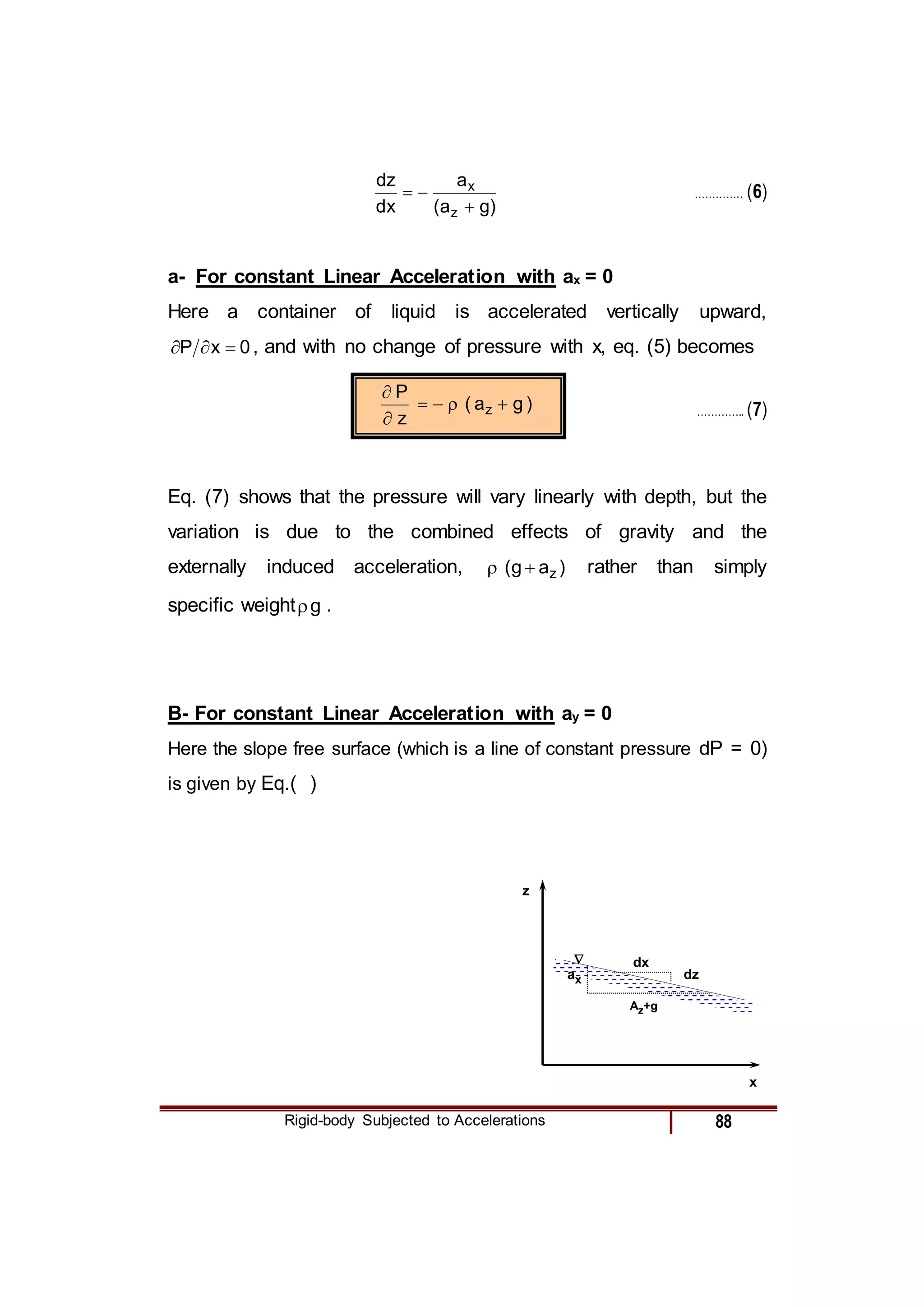
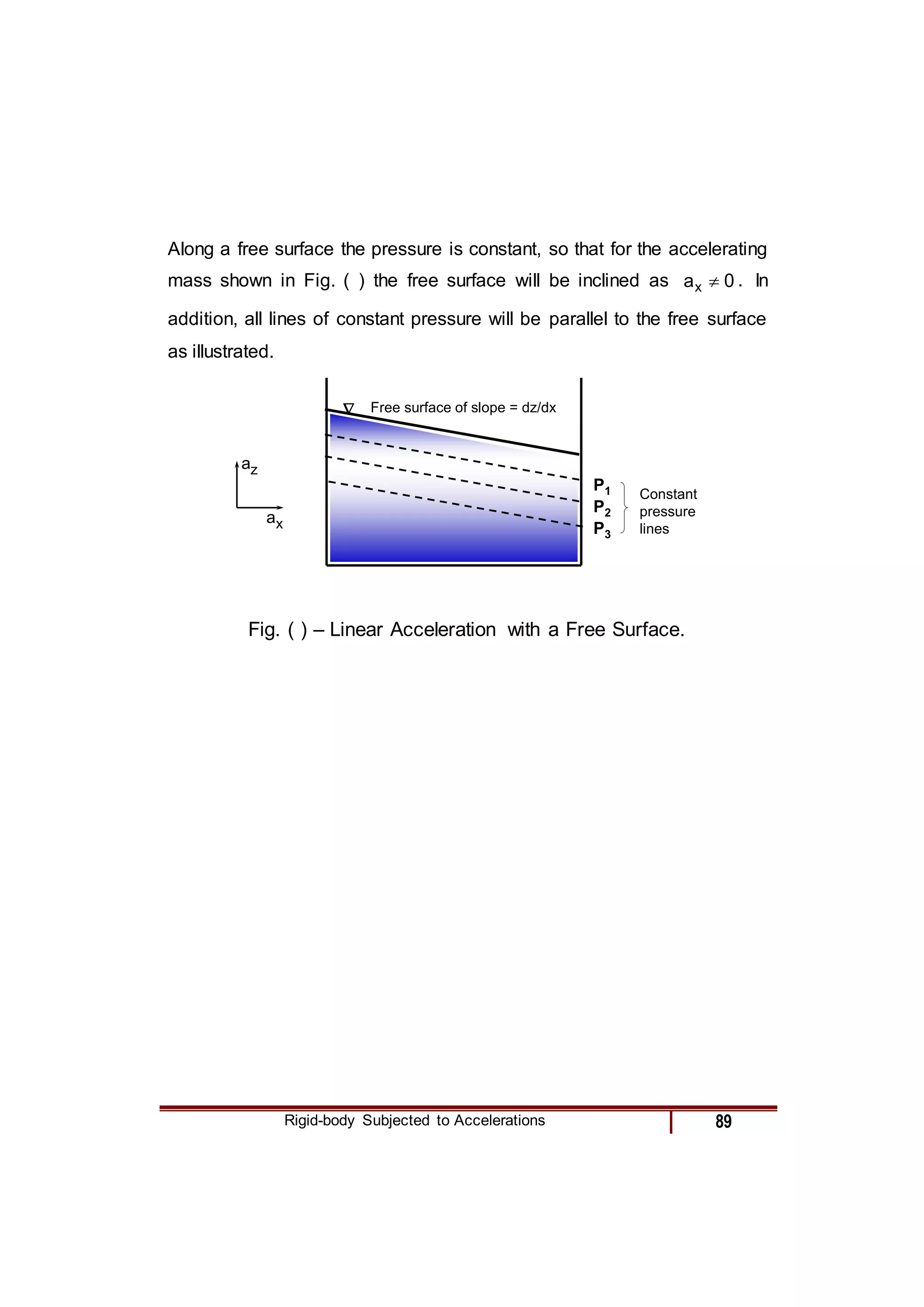
2) For specific cases of a fluid at rest, in free fall, and linearly accelerating, the pressure gradient terms in the equation are simplified.
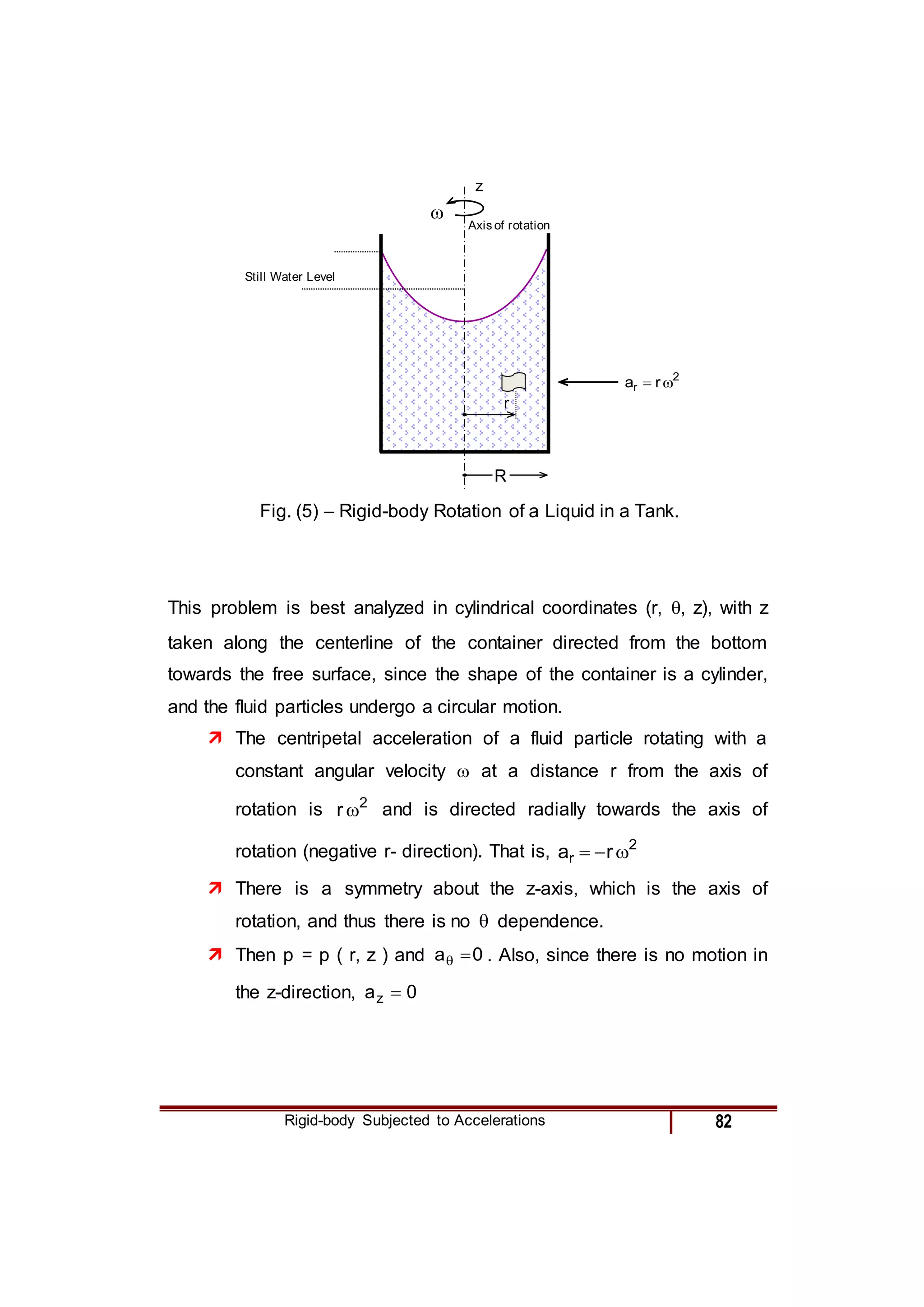
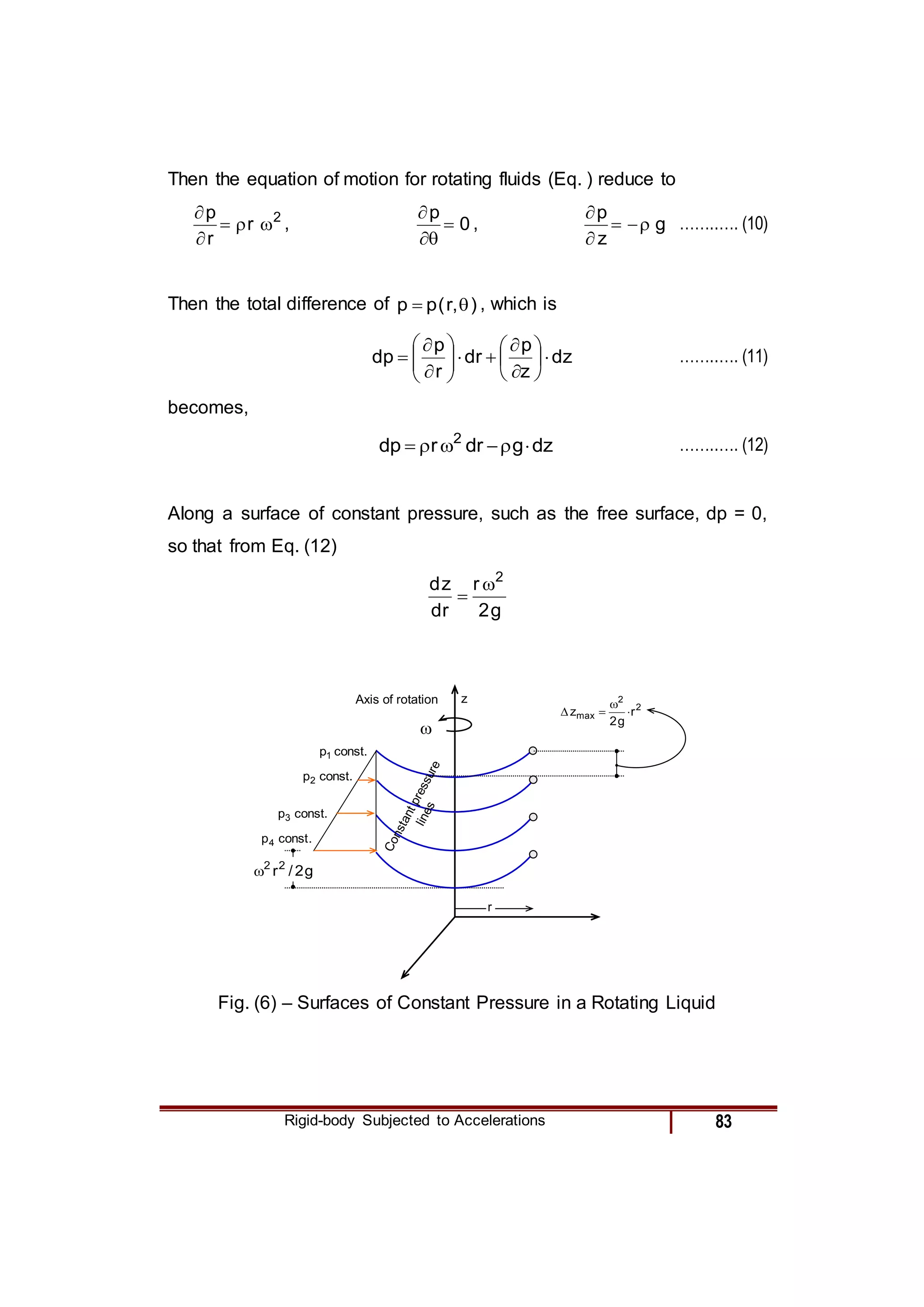
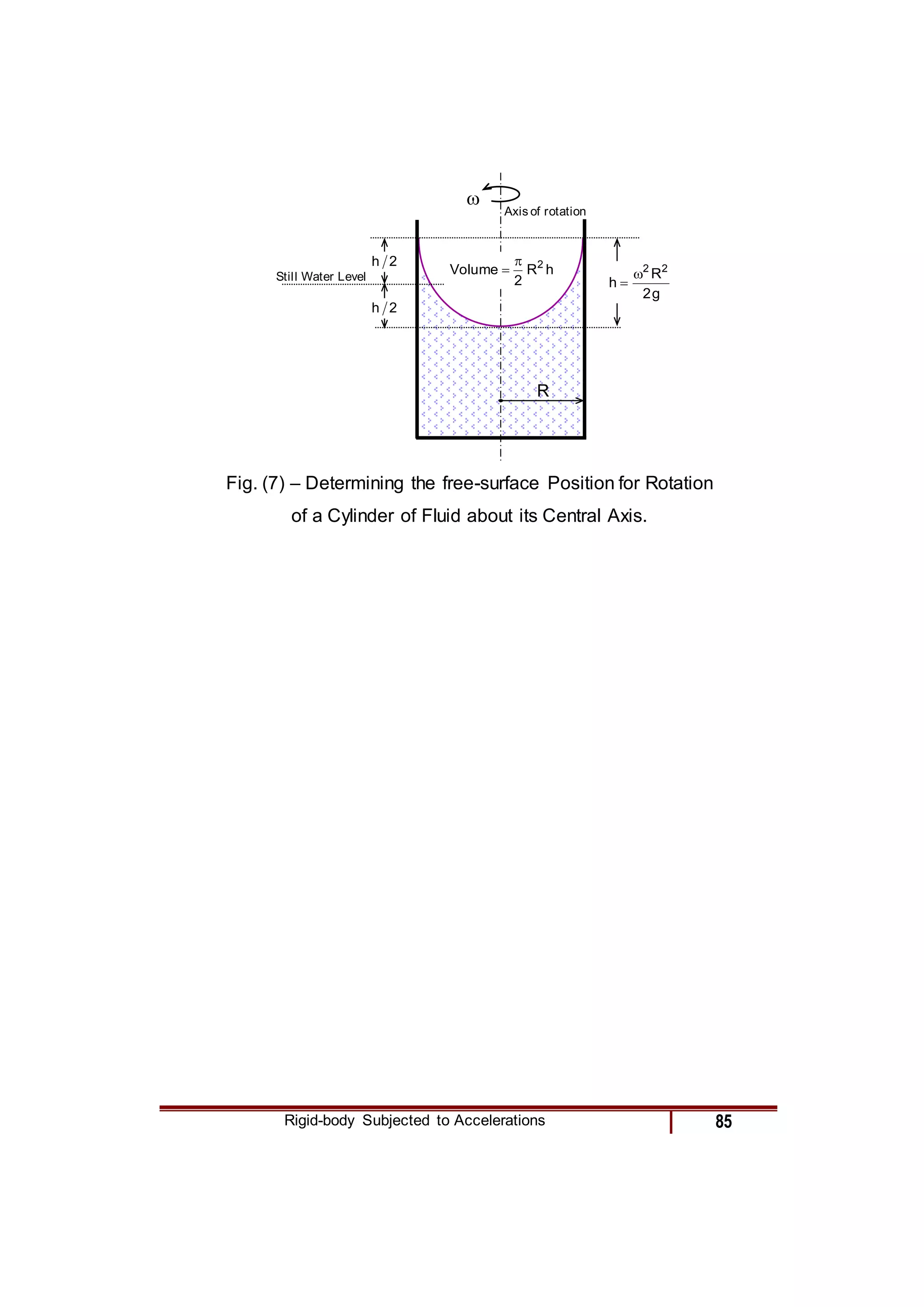
3) For a rotating fluid contained in a cylindrical tank, the equation is derived in cylindrical coordinates and relates the radial pressure gradient to the centripetal acceleration from rotation.