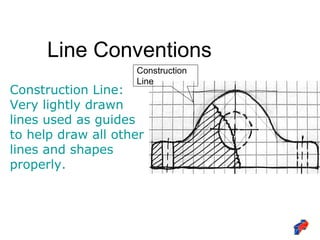
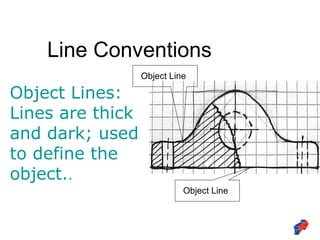
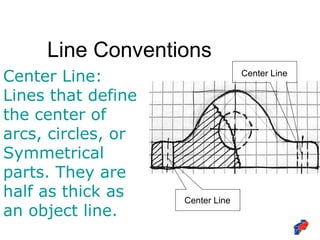
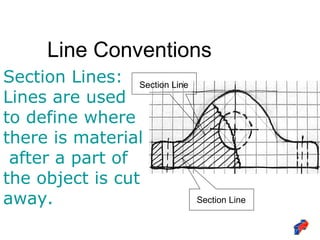
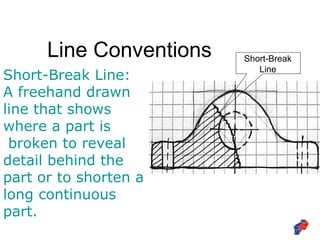
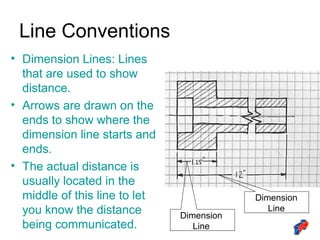
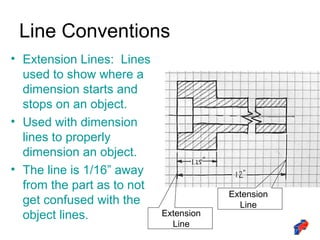
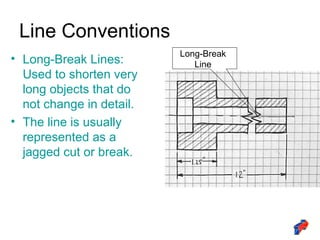
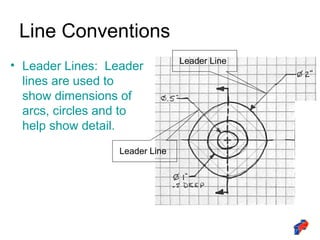
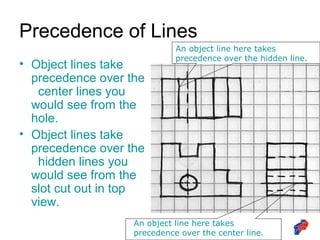
The document discusses line conventions used in technical drawings to convey geometric information. It describes different types of lines like construction lines, object lines, hidden lines, center lines, section lines, and dimension lines. It explains what each line type is used for and provides visual examples. The document also covers line precedence rules that govern which lines are drawn over others in complex sketches and drawings.